Thomas Davenport invented the first real motor later Micheal Faraday and Joseph supported his work. Micheal Faraday did his work mostly related to the working of electromagnetic fields. This invention became the basic principle behind the working of an electrical motor. Beyond the invention of motor further investigations have been done to study the different types of motors such that different motor operations have been discovered. The operation of these different kinds of motors has been further investigated by determining the characteristics in order to know the performance. In this article, we shall discuss the basics of DC motor, and characteristics of different self-excited motors like DC shunt, series, and Compound motor.
Basics of DC Motor
A DC motor is a device that works on the principle of Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. It generally converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It is commonly used in household appliances and also in large industries for the operating heavy loads. A normal DC type motor is shown in the figure below.

Basic DC motor
Characteristics of DC Motor
The characteristics of any motor are determined to know the performance. By this, we can conclude where it can be applied and the necessary precautions can also be taken to avoid any damages. For instance, a series motor should not be started directly by applying load because heavy currents flow to the windings which in fact damages the winding. So, this type of damages can be avoided by knowing its performance characteristics such that we can take necessary precautionary methods to avoid such instances.
Torque and speed play a vital role in the operation of the motor. Generally, torque is produced by the flux which gets interacted with the armature flux. The interaction of these two fluxes develops a unidirectional torque that enables the motor to rotate. Now, the speed with which the rotor should rotate comes into the picture. The speed of the rotor generally depends on the back emf and flux produced inside the motor. The relation between the torque and speed explains to us how we can draw a characteristic curve between them. Based on the arrangement of the winding, these different types have been classified and accordingly, the characteristics also differ.
The voltage equation of a motor is represented as Eb = V – Ia Ra
The speed of the motor mainly depends upon the value of back emf and flux. The relationship between speed and back emf is given by N ∝ Eb/ɸ
Torque Speed Characteristics of Shunt Motor
Basically, in a shunt motor, the field winding is connected in parallel to the armature winding. Whenever a current is supplied by means of a DC source, flux is produced which in turn interacts with the armature flux to produce a unidirectional torque. As φ flux is constant in the case of a shunt motor. The speed of the motor is directly proportional to the back emf.
The relationship between torque and speed of a shunt motor is given by T α φ Ia. (φ) flux is constant in the case of a shunt motor. So, torque is directly proportional to the armature current. The torque and speed characteristics are similar to that of the characteristics of speed vs armature current. But a slight decrease in the value because the back emf decreases slightly practically.
The characteristic curve drawn between the torque and speed is shown in the figure below.
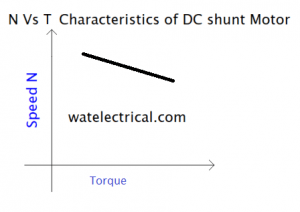
Torque Vs speed characteristics DC shunt motor
Torque Speed Curve of Series Motor
Basically, in a series motor, the field winding is connected in series to the armature winding. Whenever a current is supplied by means of a DC source, flux is produced which in turn interacts with the armature flux to produce a unidirectional torque. The relationship between the torque and armature current is given by T α φ Ia
Please refer to this link to know more about DC Motor MCQs
. The relationship between speed and flux is given by N ∝ Eb/ɸ. The flux is inversely proportional to the speed and directly proportional to the armature current. Now, T α (Ia )2 torque varies directly proportional to the square of the current. The relationship between the torque and speed also remains the same I,e torque and the speed are inversely proportional to each other. The figure that depicts the characteristics of DC shunt motor is shown in the figure below.

Torque Vs speed characteristics DC shunt motor
Torque Speed of Compound Motor
DC compound Motor is classified into two kinds such as long shunt and short shunt depending upon the winding placement. It is also a kind self-excited motor and it uses the advantages of both shunt and series DC motors. It uses the good speed regulation property of shunt motor and high starting torque capability of a series motor. The compound wound circuit diagram is shown in the figure below.
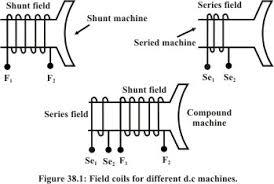
compound wound circuit diagram
Characteristics of Compound Motor
The torque-speed characteristics of DC compound motor are shown in the figure below.
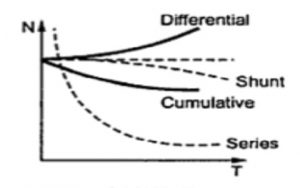
speed torque characteristics DC compound motor
Thus, in this article, we had discussed the basics of DC motor. The DC motor is a type of machine that transitions the form of input electrical energy to output mechanical energy. Apart from the basics, we had also studied the characteristics of different types of motors such as shunt, series, and compound motor. Here is a question for the readers, what are the applications of the DC shunt, series, and compound motor?
Leave a Reply