Induction generators have become very popular choices to use in various applications because they are capable of operating at variable speeds & handling fluctuating loads. So these generators have an assuring future within renewable energy systems as well as other applications because of their ongoing investigation & efforts in development. As development efforts and investigation address the challenges which are associated with these generators continuously then their acceptance within various applications is predictable to develop, supplying a more efficient and sustainable energy future. This article provides brief information on an induction generator, their working, and their applications.
What is an Induction Generator?
An induction generator (Asynchronous Generator) is a type of AC electrical generator that uses the electromagnetic induction principle to change the energy from mechanical to electrical. These generators simply operate by turning their rotors faster compared to synchronous speed mechanically. These types of generators are very popular because of their simplicity, cost-effectiveness & robustness which makes them used in various renewable energy-based applications like hydroelectric & wind power generation, in different applications like wind turbines, mini hydro power plants, and also to reduce gas streams from high-pressure to lower pressure.
Induction Generator Construction
The construction of this Generator is similar to an induction motor. But the machine works as a generator or motor mainly depends on the condition of whether the slip is positive (or) negative. These generators are provided always with squirrel cage rotors. The induction generator includes different parts like a rotor, stator, shaft, end plate, bearing, and electrical terminals. The construction of the induction generator is shown below.
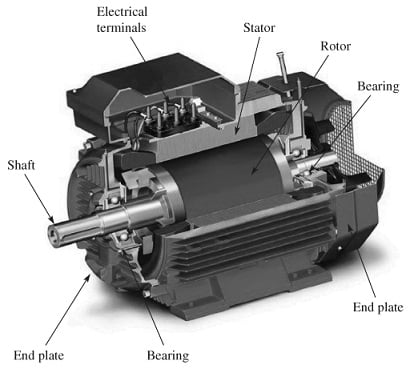
Induction Generator Construction
The rotor in this generator acts as a moving component. The rotation of the rotor is mainly because of the interaction between the magnetic fields & windings which generates torque around the axis of the rotor.
The stator in this generator is a stationary part that provides a magnetic field to drive the rotating armature. The stator simply changes the rotary magnetic field into an electric current.
The shaft in this generator is a handle that is connected to the coil. This shaft is used to move the coil. The shaft helps in making rotation very fast and easier.
The end plates in this generator help provide mechanical support to the components of the generator, help in enclosing the magnetic circuit & guard the inside of the generator against moisture, dust, etc.
The bearings are significant parts in the generator which helps in reducing friction & also allows for very smoother rotation. Bearings support the generator shaft that turns in the generator.
The electrical terminals of the generator are the connection points between the main stator windings & the load.
Working Principle
The induction generator works on Faraday’s electromagnetic induction principle which states that the electromotive force (EMF) is induced within the armature coil if it is moving within a consistent magnetic field. This generator mainly includes two main parts; the stator & the rotor. The stator includes three-phase windings wherever AC is generated whereas the rotor is made up of bars or short-circuited windings that are accountable to induce electromotive force (EMF). Whenever the rotor of this generator is rotated by a mechanical force externally then it will induce a current within the windings of the stator through electromagnetic induction. After that, this current will generate an electrical output.
Induction Generator Circuit Diagram
The induction machine circuit is shown below. Similar to a DC Machine, an induction machine can be used as an induction generator or motor without any inside modifications. So this circuit explains how this machine works as an induction generator. An induction machine works as an induction generator in two cases. When slip becomes negative because of the rotor current & rotor emf achieves a negative value. The torque of the prime mover becomes reverse to electric torque.
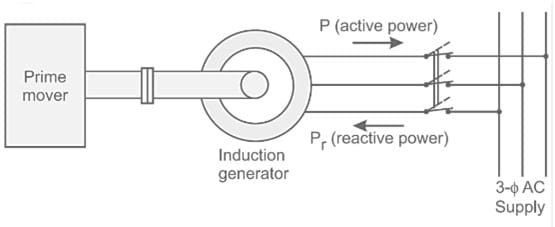
Induction Generator Circuit
The working of this circuit is; that whenever an AC supply is provided to an induction machine’s stator terminals then a rotating magnetic field can be generated within the stator and it pulls the rotor to run behind it.
If the rotor in this machine goes faster to the synchronous speed through a prime mover, then the slip will be zero & thus the net torque can also be zero. So, whenever the rotor of the induction machine is running at synchronous speed then the rotor current will become zero.
If the rotor is designed to turn above the synchronous speed, then the slip will become negative. So, rotor current will be generated within the reverse direction because of the rotor conductor’s cutting stator magnetic field.
The rotor current that is generated will produce a rotary magnetic field within the rotor & it pushes on the stator field. So this causes a stator voltage which pushes current flowing from the stator winding against the voltage applied. Therefore, the machine now works as an induction generator
This is not a self-excited machine. Thus, whenever it works as a generator, then the machine uses reactive power from the AC power line & provides active power reverse into the power line. Here, reactive power is mainly required for generating a rotary magnetic field and the active power which is supplied reverse within the power line is simply proportional to slip at the synchronous speed.
Induction Generator Types
Induction generators are available in different types which are discussed below.
Squirrel Cage Induction Generators
Squirrel Cage Induction Generators or SCIGs are the most frequently used type of generator because of their robustness, durability, reliability, low maintenance requirements & simple design. This generator has a very simple electrical & mechanical design without slip rings & brushes. These are very lightweight & compact even with their high performance.
The rotor of this generator has short-circuited conductive bars which are embedded within a laminated iron core to give a squirrel cage appearance. So this design simply allows for simple startup & a self-excited induction generator to make it perfect for applications like; small-scale-based wind power generation.

Squirrel Cage Type
This type of generator is decoupled completely from the grid through the frequency converter & it can be controlled simply over a wide speed range. This generator operation & the wind turbine’s drive train cannot be influenced by the usual grid fluctuations. The turbine is adapted optimally to the current wind conditions and results in a positive annual value.
Wound Rotor Induction Generators
A wound rotor induction motor is a special type of three-phase AC induction motor that is mainly designed to provide high starting torque by simply connecting an exterior resistance to the rotor circuit. This motor has a wound rotor, so it is known as a wound rotor. These generators have a wound rotor with a set of insulated windings which are connected to external terminals via slip rings and brushes. So this arrangement gives maximum control on the performance of the generator & it allows uneven speed operation. But, these generators are more complex & need extra maintenance because of their brushes & slip rings.
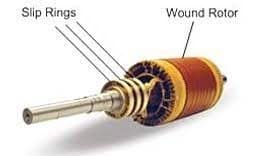
Wound Rotor Type
Doubly-Fed Induction Generator
This is a type of electrical generator that plays a key role within wind energy systems. These generators are mostly used in various wind turbine systems because of their benefits and unique characteristics. These generators are related to AC electrical generators with extra features that let them run at somewhat below or above their normal synchronous speed.

Doubly-Fed Induction Generator
This generator includes two main parts the stator & rotor. So, the stator is the same as a typical induction generator with a three-phase winding and the rotor is a wound rotor that is connected through a converter & slip rings to the grid. This simple design simply allows for changeable speed operation & power flow in two ways.
These generators are used in wind turbines and other renewable energy systems like; small hydro & tidal energy generation plants. These are capable of operating across a broad range of speeds lacking a significant loss within efficiency is highly preferred in these applications.
Self-Excited Induction Generator
An induction generator operates as a self-excited induction generator if capacitors are simply connected to the terminals of the stator to supply the required reactive power to generate electrical energy within remote areas. These capacitors will provide the excitation current necessary for the generator to work as a generator. So these capacitors supply required reactive power to the induction generator and also to the load to build voltage. These generators are used mainly for the generation of power with renewable energy sources such as windmill generators within isolated areas.

Self Excited Type
Grid Excited Induction Generator
As the name suggests, whenever an induction generator is simply connected to the grid, then the supplies reactive power to control the generator is known as grid excited induction generator. These types of generators develop their excitation using the Utility grid. So the power generated is simply fed to the supply system whenever the generator is run at synchronous speed.

Grid Type
Induction Generator Vs Synchronous Generator
The differences between induction generators and synchronous generators are discussed below.
Induction Generator | Synchronous Generator |
| An induction generator is a type of generator that utilizes electromagnetic induction in between the rotors to induce the current supply within the rotor to attain the conversion of electromechanical energy. | A synchronous generator is an alternator with a similar rotor speed to the stator’s rotary magnetic field. |
| It is also known as an asynchronous generator. | It is also known as an AC generator. |
| Synchronous generators are capable of generating at a fixed power factor (PF) into the grid through a power factor controller. | This draws KVARs at a lagging power factor from the utility grid of the public to give excitation. |
| This generator uses reactive power for field excitation from the power system. | This generator needs a separate DC excitation system. |
| Its construction is less complicated because it does not need a slip ring & brushes arrangement.
| Its construction is complicated because it needs brushes to supply DC voltage mainly to the rotor for excitation |
| The o/p voltage frequency in this generator is regulated through the power system. If this generator is supplying a separate load, then the o/p frequency will be somewhat lower than is measured using the f = N * P/120 formula | The generated voltage waveform in this generator is synchronized directly with the rotor speed. The output frequency can be calculated by using the f = N * P/120 Hz formula. where ‘N’ is the rotor speed within rpm & ‘P’ is several poles. |
| These are available in different types like; squirrel-cage, Grid-connected, self-excited & doubly-fed induction generators. | These are available in two types; cylindrical rotor & non-cylindrical rotor. |
| It is cheaper. | Synchronous generators are costly as compared to induction type with the same voltage rating & output. |
| These generators are less efficient. | These generators are more efficient. |
| These generators are used frequently in some micro hydro installations & wind turbines because of their capability to generate helpful power at unstable rotor speeds. | These generators are used commonly in wind turbines with variable speed applications because of their low rotating synchronous speeds that generate the voltage on grid frequency. |
Advantages & Disadvantages
The advantages of an induction generator include the following.
- This generator needs less maintenance.
- This generator is quite cheap.
- It runs separately without hunting.
- It possesses a tiny size for each kW output power which means higher energy density.
- Similar to a synchronous generator, it requires no synchronization to the required supply line.
- It needs less maintenance due to its strong construction.
- The prime mover of speed variation is less prominent.
- It requires low auxiliary equipment.
- This generator has a self-protection feature.
- This generator has several benefits as compared to other kinds of generators like; simplicity, robustness & low cost.
- They can operate above a wide range of loads & speeds.
The disadvantages of induction generator include the following.
- This generator has lower efficiency, demand of reactive power & the requirement for an exterior power source to begin the generation procedure.
- It cannot produce reactive volt-amperes.
- It is not appropriate for separate and isolated operations.
- It cannot give protection to the voltage levels of the system
- This generator has less efficiency.
- It cannot produce reactive power.
- The induction generator operation needs a synchronous machine for supplying the reactive power near to it.
Applications
The applications of induction generator include the following.
- These generators can be used with an alternate energy source like a windmill for extensive power generation.
- These generators help in supplying power to the loads within remote areas.
- These are used widely within wind turbines because of their capacity to operate at changeable speeds & handle the conditions of fluctuating wind.
- These are used frequently in small-scale hydroelectric power plants for converting the energy from mechanical into electrical energy from water turbines.
- These generators are used by Industries with extra mechanical energy like steam plants & gas turbines to change this energy into electrical power mainly for grid supply or self-consumption.
- These are used in remote areas wherever grid connection is not possible.
- These can be utilized with renewable energy sources & energy storage systems to provide a consistent power supply.
What is the Difference between Synchronous and Induction Generator?
The synchronous generator supplies both active & reactive power whereas the induction generator supplies active power only & monitors reactive power mainly for magnetizing.
Is the Induction Generator Self Start Generator?
It is not a self-start generator, thus it is required to excite the stator through an external polyphase source to generate the rotary magnetic field.
Why Capacitor is used in an Induction Generator?
In an induction generator, the capacitor acts like a reactive power source, so it provides reactive power to the induction generator.
What is an Induction Generator and How it is Different from an Induction Motor?
An induction generator is a type of AC electrical generator that works by using induction motor principles to generate electric power. These generators simply operate by rotating their rotors mechanically faster than synchronous speed. The induction motor uses electricity while the generator generates electricity.
What is a Grid Connected Induction Generator?
Whenever an induction generator is connected to the grid, then the system supplies reactive power for operating the generator.
Thus, this is an overview of an induction generator, construction, working, types, circuits, differences, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. Induction generators have versatility & robustness, so frequently used within wind turbines & some micro hydro installations because of their capability to generate very useful power at unstable rotor speeds. These generators are electrically and mechanically very simple as compared to other types of generators. Here is a question for you, an induction generator is also known as?