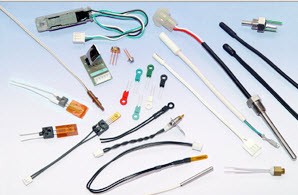
Types of Temperature Sensors
The most commonly measured physical parameter is temperature whether in process industry applications or in laboratory settings. Exact measurements are critical part of success. Exact measurements are needed for many applications such as medical applications, materials research in labs, studies of electronic or electrical components, biological research, and geological studies. Most commonly, temperature sensors are used to measure temperature in circuits which control a variety of equipment’s.
There are different types of temperature sensors used in the market today including resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), thermocouples, thermistors, infrared sensor , and semiconductor sensors. Each of them has a particular operating parameters. These sensors come in different varieties, but have one common thing: they all measure temperature by sensing a change in the physical characteristic.
What Is a Temperature Sensor?
Temperature Sensor
A temperature sensor is a device, usually an RTD (resistance temperature detector) or a thermocouple, that collects the data about temperature from a particular source and converts the data into understandable form for a device or an observer. Temperature sensors are used in many applications like HVand AC system environmental controls, food processing units, medical devices, chemical handling and automotive under the hood monitoring and controlling systems, etc.
The most common type of temperature sensor is a thermometer, which is used to measure temperature of solids, liquids and gases. It is also a common type of temperature sensor mostly used for non-scientific purposes because it is not so accurate.
Types of Temperature Sensors
There are different types of temperature sensors that have sensing capacity depending upon their range of application. Different types of temperature sensors are as follows:
- Thermocouples
- Resistor temperature detectors
- Thermistors
- Infrared sensors
- Semiconductors
- Thermometers
Thermocouples
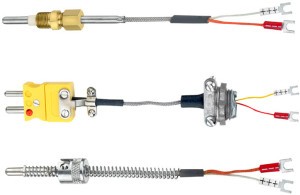
Thermocouples
Thermocouple sensor is the most commonly used temperature sensor and it is abbreviated as TC. This sensor is extremely rugged, low-cost, self-powered and can be used for long distance. There are many types of temperature sensors that have a wide range of applications.
A thermocouple is a voltage device that indicates temperature by measuring a change in the voltage. It consists of two different metals: opened and closed. These metals work on the principle of thermo-electric effect. When two dissimilar metals produce a voltage, then a thermal difference exists between the two metals. When the temperature goes up, the output voltage of the thermocouple also increases.
This thermocouple sensor is usually sealed inside a ceramic shield or a metal that protects it from different environments. Some common types of thermocouples include K, J, T, R, E, S, N, and B. The most common type of thermocouples is J, T and K type thermocouples, which are available in pre-made forms.
The most important property of the thermocouple is nonlinearity – the output voltage of the thermocouple is not linear with respect to temperature. Thus, to convert an output voltage to a temperature, it requires mathematical linearization.
Resistor Temperature Detector (RTD)
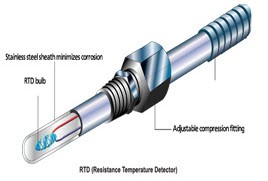
Resistor Temperature Detector (RTD)
RTD sensor is one of the most accurate sensors. In a resistor temperature detector, the resistance is proportional to the temperature. This sensor is made from platinum, nickel, and copper metals. It has a wide range of temperature measurement capabilities as it can be used to measure temperature in the range between -270oC to +850oC. RTD requires an external current source to function properly. However, the current produces heat in a resistive element causing an error in the temperature measurements. The error is calculated by this formula:
Delta T=P*S
Where, ‘T’ is temperature, ‘P’ is I squared power produced and ‘S’ is a degree C/mill watt
There are different types of techniques to measure temperature by using this RTD. They are two wired, three-wired and four-wired method. In a two-wired method, the current is forced through the RTD to measure the resulting voltage. This method is very simple to connect and implement; and, the main drawback is – the lead resistance is the part of the measurement which leads to erroneous measurement .
Three-wired method is similar to the two-wired method, but the third wire compensates for the lead resistance. In a four-wired method, the current is forced on one set of the wires and the voltage is sensed on the other set of wires. This four-wired method completely compensates for the lead resistance.
Thermistors

Thermistors
Another type of sensor is a thermistor temperature sensor, which is relatively inexpensive, adaptable, and easy to use. It changes its resistance when the temperature changes like RTD sensor. Thermistors are made from manganese and oxides of nickel, which make them susceptible to damages. So, these materials are called ceramic materials. This thermistor offers higher sensitivity than the resistor temperature detectors. Most of the thermistors have a negative temperature coefficient. It means, when the temperature increases the resistance decreases.
Thermometers

Thermometers
A thermometer is a device used to measure the temperature of solids, liquids, or gases. The name thermometer is a combination of two words: thermo – means heat, and meter means to measure. Thermometer contains a liquid, which is mercury or alcohol in its glass tube. The volume of the thermometer is linearly proportional to the temperature – when the temperature increases, the volume of the thermometer also increases.
When the liquid is heated it expands inside the narrow tube of the thermometer. This thermometer has a calibrated scale to indicate the temperature. The thermometer has numbers marked alongside the glass tube to indicate the temperature when the line of mercury is at that point. The temperature can be recorded in these scales: Fahrenheit, Kelvin or Celsius. Therefore, it is always desirable to note for which scale the thermometer is calibrated.
Semiconductor Sensors
Semiconductor Sensors
Semiconductor sensors are the devices that come in the form of ICs. Popularly, these sensors are known as an IC temperature sensor. They are classified into different types: Current output temperature sensor, Voltage output temperature sensor, Resistance output silicon temperature sensor, Diode temperature sensors and Digital output temperature sensor. Present semiconductor temperature sensors offer high linearity and high accuracy over an operating range of about 55°C to +150°C. However, AD590 and LM35 temperature sensors are the most popular temperature sensors.
IR sensor

IR sensor
IR sensor is an electronic instrument which is used to sense certain characteristics of its surroundings by either emitting or detecting IR radiation. These sensors are non-contacting sensors. For example, if you hold an IR sensor in front of your desk without establishing any contact, the sensor detects the temperature of the desk based on the merit of its radiation. These sensors are classified into two types such as thermal infrared sensors and quantum infrared sensors.
Thus, this is all about different types of temperature sensors. The cost of the temperature sensor depends on the type of work it is intended for. However, the accuracy of the sensor will decide the price. So, the cost depends on the accuracy of the temperature sensor. Present temperature sensors intended at reducing the cost as well as efficiency.
Photo Credits:
- Types of temperature sensors by atcsemitec
- Thermocouples by tutco
- Resistor temperature detectors by thermometricscorp
- Thermistors by ussensor
- IR sensor by meas-spec