Protection is the main concern while choosing any electrical device or appliance because when the power varies or excess current supplies, then it causes harm that results in a short circuit or an overload. So, it is necessary to integrate a device as a protection element to give over current protection to the device. The most common safety device used for protecting the circuit is a fuse which includes a metal wire/strip that dissolves whenever an over-current flow occurs by interrupting the current. At present, these protection devices have been replaced by an efficient circuit breaker called a miniature circuit breaker or MCB. This article provides brief information on a miniature circuit breaker or MCB.
What is an MCB or Miniature Circuit Breaker?
A miniature circuit breaker definition is; an automatically operated electrical switch that is used to avoid damage to an electrical circuit from excess electric current. These circuit breakers will trip during a short circuit or an overload condition to defend equipment against failure or electrical faults. Whenever the current supply exceeds a fixed level then it interrupts the current flow automatically and prevents damage from potential fire hazards to the electrical circuit.
The standard MCBs current ratings are; 1A, 5A, 2A, 10A, 16A, 25A, 20A, 32A, 50A, 40A & 63A. The MCB lifespan mainly depends on different factors like; the severity of trips, the frequency, the device quality, environmental conditions, etc. Usually, the lifespan of these devices is several decades with proper usage & maintenance.

Miniature Circuit Breaker or MCB
Construction of MCB
The construction of a miniature circuit breaker includes different parts like contacts, mechanical latch, external casing, knob, solenoid, a bimetallic strip, and arc chutes which are discussed below.
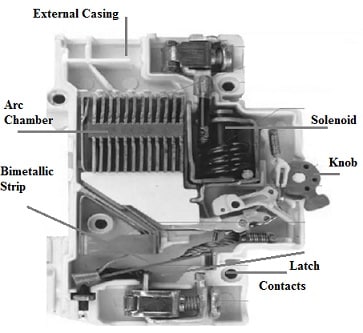
Construction of Miniature Circuit Breaker
The external casing is used to hold the entire internal components & guard them from dirt. This casing is made with insulating materials like; ceramics/plastic.
An MCB includes a set of contacts for each phase where one contact is fixed & the other contact is variable. This variable contact can be connected to the external knob which allows the opening & closing of the circuit breaker.
External knobs of MCB mainly help in manually turning ON & OFF the device.
A latch in the MCB is connected in such a way that it holds the contacts below spring tension on the ON position.
The bimetallic strip of MCB simply provides delayed overload protection by detecting the prolonged current flow which is higher as compared to its rated current.
The Solenoid of the circuit breaker helps in protecting short circuits by opening the mechanical latch. Whenever the current throughout the coil goes beyond a particular value then the solenoid will get activated, usually above 3 times its rated current. So solenoid is not triggered by overloads.
Arc chutes of MCB help in splitting as well as quenching arcs. This allows arc extinction throughout short circuits & on-load breaker openings.
Working Principle of Miniature Circuit Breaker
Miniature circuit breaker or MCB works on the thermal magnetic tripping mechanism principle, which merges both thermal as well as magnetic elements for detecting the electrical faults, occurring within the electric circuit.
The thermal element within the MCB is a bimetallic strip that protects from overload conditions. Whenever the temperature rises, it attains a specific point where the thermal element gets bent to trip the circuit breaker. A magnetic element in the circuit breaker is a solenoid coil that is utilized for protection from short circuit conditions. Once a high current is supplied throughout the circuit then this coil generates a magnetic field to trip the circuit breaker & interrupts the flow of current.
MCB Circuit Diagram
The circuit diagram of MCB is shown below which is designed with magnetic element, lane, contact open, latch, bimetal element, and load. The working of this circuit is, whenever there is a maximum flow of current throughout the MCB components, particularly the bimetallic strip then its temperature will increase when it gets heated and it causes the bimetallic strip to drive against the trip bar, thus it will unlatch the latch & breaks this circuit. So, the device is easily protected from overcurrent or overload. So the MCB has to be manually turned ON to restore the flow of current. When there is a sudden flow of large current, the solenoid comes into action as a substitute for the bimetallic strip. So the solenoid discharges the latch to break the circuit & provide safety.
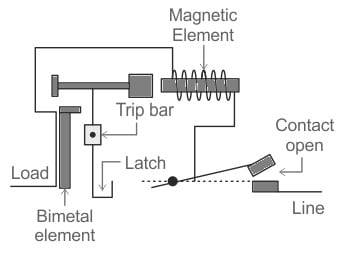
MCB Circuit
Types of Miniature Circuit Breaker
MCBs are available in different types like Type A, Type B, Type C, Type D, Type K, and Type Z which are discussed below.
Type B MCB
Type B MCBs are common type circuit breakers. Whenever the power exceeds five times the recommended limit in this circuit breaker then trip occurs. These are used in light commercial & residential applications wherever connected loads are mostly lighting fixtures and domestic appliances including resistive elements.

Type B MCB
In this type of circuit breaker, the magnetic release operates in between 3 & 5 times its complete load-rated current, so it instantly trips whenever the current throughout this circuit breaker is 3 to 5 times the rated current. If you have 10A-based Type B MCB, then it trips between 30A to 50A magnetically. Type B MCBs are applicable in industrial units and residential areas. So these types of MCBs are considered to be the most sensitive and used in residential areas where fluctuations and current surges are less intense.
Type C MCB
Type C MCB frequently trips at surges that exceed 5 to 10 times the capacity of power. For instance, A C10-type MCB simply trips at full load current in between 50A & 100A. The Type C MCB functions are; the circuit’s protection & control against short circuits, overloads & protection for inductive & resistive loads through low inrush current.

Type C MCB
The loads which are connected to this circuit breaker are mainly inductive like fluorescent lighting or induction motors. These MCBs are applicable strategically in devices that have high power utilization necessities and also in industrial & commercial units. Type C MCBs are used in lighting, small transformers, control circuits, coils, pilot devices, etc.
Type D MCB
Type D MCBs are the least sensitive circuit breakers which trip between 10 & 20 times full load current. The main functions of this type of MCB are; protection & control of the circuits against short-circuits & overloads; Type D MCBs are used in specialty commercial or industrial devices wherever current inrush is extremely high like; X-ray machines, transformers, large winding motors, and many more.

Type D MCB
Type A MCB
Type A MCB is the most sensitive circuit breaker which is designed to trip immediately whenever the current surpasses 2 to 3 times the rated current. These are the most sensitive circuit breakers which are limited to the most delicate gadgets. These types of MCBs are designed mainly for highly sensitive device protection.

Type A MCB
Type K MCB
Type K MCB trips whenever the current attains 8 to 12 times the rated current whereas the operating time is below 0.1 second. Type K MCBs are suitable for motor and inductive loads through high inrush currents. The main functions of this circuit breaker are; protection & control of the circuits like transformer, auxiliary circuits, and motors, against short-circuits & overloads. These circuit breakers offer protection for damageable elements within the overcurrent range and they also give the best protection for two cables & also lines.

Type K MCB
Type Z MCB
Type Z MCB simply trips in between 2 to 3 times full load current and these are responsive highly to short circuits. So these MCBs are used for providing protection highly to sensitive devices like semiconductor devices. The main functions of this MCB are; it protect and control of the circuits against short-circuits, long-duration, and weak overloads.

Type Z MCB
Single Pole MCBs wiring through a Double Pole MCB
The wiring diagram for single-pole MCBs with a double-pole MCB is shown below. This wiring is mostly used in the Distribution Board of household wiring. Generally, the distribution board is connected after the energy meter from where the power supply is separated or supplied to every individual room.
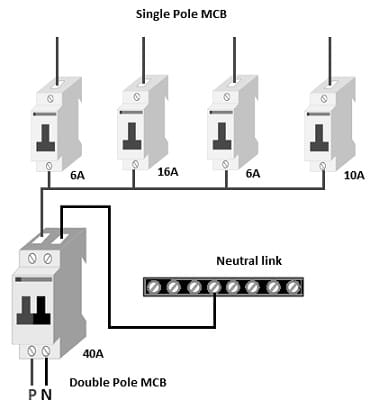
Miniature Circuit Breaker Wiring Diagram
Here double pole MCB is used as an input. By turning off the power supply, the whole house will be switched off. Here every single pole MCB’s output goes to different rooms of the home. This wiring supplies only fans, lights, and small electrical equipment. Separate double MCBs are used only when washing machines, AC & refrigerators are used for them.
So in this connection, every single pole MCB may have the same or a different current rating based on the necessity. The most significant thing is that the double pole MCB’s current rating must be higher than the current ratings of the sum of all single-phase MCBs. Here all rooms’ neutral is coupled to the neutral link & the phase of every room can be connected through individual miniature circuit breakers.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of a miniature circuit breaker include the following.
- MCBs are very sensitive in detecting changes within the current flow.
- These circuit breakers respond very quickly against overload & short circuits because of their sensitivity.
- These can be reused because there is no requirement to change any electric wire.
- Its maintenance & replacement cost is less.
- These are more reliable safety devices and are also simple to use.
- MCBs turn off the electricity connections automatically & supply can be again resumed very easily.
- These are very safe from electricity.
- MCBs provide a good interface.
- It identifies the specific fault areas within the circuit.
- Its performance is better in case of faulty circuit identification & earth leakage.
- MCB has a time delay characteristic, so it works more properly in the surge current case.
The disadvantages of miniature circuit breakers include the following.
- The MCB cost is more.
- It is applicable for small current-carrying applications like the protection of home wiring.
- In the MCB circuit, the auxiliary contact does not take place.
- They provide limited current protection against other electrical hazards like lightning strikes or voltage surges.
- These circuit breakers have limited overcurrent rating which means they protect only circuits up to a particular amperage.
- MCBs are very sensitive devices that trip because of small changes within the current flow.
- These circuit breakers need to be changed whenever they trip because they cannot be reset.
- For high-power appliances, MCBs provide limited protection.
Miniature Circuit Breaker Applications
The applications of miniature circuit breakers include the following.
- A miniature circuit breaker is a significant device used for the safety & efficient working of electric machines.
- MCBs are used in various electrical appliances which are used for domestic and industrial purposes.
- These are used to check & protect the appliances connection constantly like heaters, fans, lights, etc.
- These circuit breakers perform various functions like isolating switches against faults, local control switches, and installation of overload protection devices or specific types of appliances/equipment.
- A miniature circuit breaker is an outstanding solution for buildings, commercial areas & homes with less equipment.
- These circuit breakers help protect homes from overload.
- These devices play a key role in the effective electricity distribution across all the house lighting systems.
- These circuit breakers help in maintaining the safety & quality of light bulbs.
- These devices provide an impressible security mechanism in large-scale & small-scale as well industries.
What is MCB and its uses?
MCB is an electromechanical device that helps in protecting an electrical circuit against overcurrent flow. These circuit breakers are used as isolating components in industrial, commercial, and domestic settings.
Can you use Type C MCB in Domestic?
The Type C MCB is used in domestic appliances, wherever the current load is medium. This MCB trips off whenever the current flow is 5 to 10 times above normal.
What are Type D circuit breakers used for?
Type D circuit breaker is used in heavy-duty industrial & commercial devices where extremely strong current surges occur occasionally like; X-ray machines, welding equipment, UPS units & large motors.
Thus, this is an overview of an MCB or miniature circuit breaker which is an automatic switch that turns off the circuit automatically during abnormal conditions like faulty or overload conditions. At present, MCBs are used instead of a fuse within a low-voltage electrical network because MCBs are very sensitive to overcurrent as compared to a fuse. Here is a question for you, what is fuse?