A capacitor motor is a single-phase induction motor that has two windings; the main winding and auxiliary winding. The main winding gets energy from the power line directly whereas a secondary winding like auxiliary winding gets energy throughout a capacitor. This kind of motor has some benefits like higher starting and running torque. The currents within this motor’s two windings will differ in phase & producing torque. There are three kinds of single-phase induction motors based on the starting technique used; capacitor start, capacitor run, and capacitor-start capacitor-run motor. This article provides brief information on a capacitor start motor, working and their applications,
What is a Capacitor Start Motor?
The capacitor start motor definition is; the motor which uses a capacitor to start is known as capacitor start motor. This is a single-phase induction motor that uses a capacitor within the auxiliary winding circuit to generate a better phase difference between the current within the main & the auxiliary windings.
The performance of this motor can be influenced by different factors like; the type of capacitor, size, load conditions, and the frequency & voltage of the power supply. These types of motors generally exhibit moderate starting current, good efficiency in full-load conditions, and high starting torque. These motors are obtainable in 120 W to 750 W power ratings. The capacitor start motor power factor typically ranges from 0.6 lagging to 0.8 leading.

Capacitor Start Motor
Working Principle
The working principle of this motor involves a starting coil & a capacitor. This motor is simply designed with two windings; the main winding & an auxiliary (or) starting winding. The main winding is connected directly to the power supply & produces a magnetic field whereas the starting winding is arranged electrically 90 degrees apart from the first winding, This winding is simply connected to the power supply through a capacitor.
These two windings are arranged within the stator & the capacitor is simply connected with the starting winding in series. So this combination will create a phase shift between the current supplies within the two windings which results in a rotary magnetic field that starts the rotation of the motor.
Features
The features of a capacitor start motor include the following.
- The power rating of this motor lies between 120 Watts & 7-5 kW.
- This motor develops a very high starting torque that is from 3 to 4.5 times the complete load torque. To get a high starting torque, the two following conditions are significant; the starting winding resistance value should be low and the value of the Starting capacitor should be large.
- The starting winding of this motor gets heat less quickly & is suited well to applications that involve either prolonged or frequent starting periods.
Capacitor Start Motor Circuit
A capacitor-start induction motor circuit is shown below which is designed with a stator, a start switch, a capacitor & a rotor. The stator of this motor is a stationary device that has two windings; the main & the auxiliary. It forms the exterior part of the motor. The rotor in this device is a rotary device and is typically squirrel cage type. The start switch in this circuit separates the start winding & the capacitor whenever the motor attains about 75% – 80% of its complete speed. The capacitor in this circuit is connected in series through the start winding & makes a phase difference between the currents within the two windings.
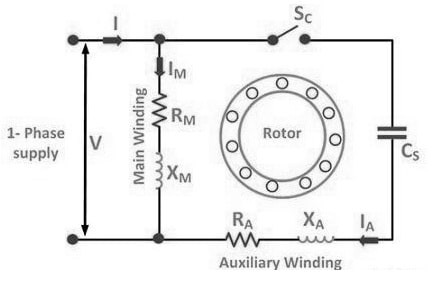
Capacitor Start Motor Circuit
Working
Whenever the stator windings in this circuit are energized from a single-phase supply, then two windings carry two dissimilar currents. There will be a 90-degree time-phase difference as well as 90 90-degree space difference between the two currents. These currents will generate a rotary magnetic field that turns ON the motor.
The two windings in this circuit are connected simply in parallel throughout the motor starting. In this circuit, a start capacitor will stay long enough to quickly bring the motor up to a fixed speed, generally about 70 to 80 % of the complete speed.
After that, the auxiliary winding in this circuit is separated from the supply frequently through a centrifugal switch & this motor remains power-driven through a single winding which creates a pulsating magnetic field.
In this design, the auxiliary winding can be considered as a starting winding, because it is used only in motor startup. If the centrifugal switch in this circuit is broken, then this motor will not function correctly. When this switch is open always, then the start capacitor is not an element of this circuit, thus the capacitor motor does not turn ON. Similarly, if the switch in this circuit is closed always, then the capacitor is always within this circuit, thus the motor windings will burn out. If this motor does not begin, then the capacitor is the problem far more likely than the switch.
Capacitor Start Motor Characteristics
The capacitor start motor’s Torque Speed characteristics are shown below. The capacitor start motor simply develops higher starting torque which is 3 to 4.5 times the complete load torque. There are two conditions necessary to get a high starting torque; the value of the capacitor should be high and the starting winding resistance value should be low.
The above Torque Speed characteristics illustrate that the starting torque is high. As compared to a split-phase motor, this motor’s cost is higher due to the presence of a starting capacitor & centrifugal switch. This motor can be upturned first by bringing this motor to a rest state and after that reversing one of the windings connections. Since the phase dissimilarity between both the starting & the running current is higher, and then it draws a low starting current.
Phasor Diagram
The phasor diagram of the capacitor start motor is shown below.
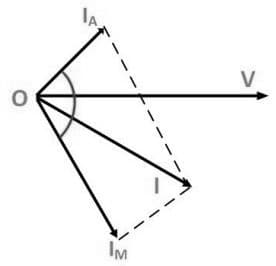
Capacitor Start Motor Phasor Diagram
- In this diagram, the ‘IM is the main winding current which is lagging the auxiliary current IA with 90 degrees. Therefore, a single-phase current supply is split into two 2-phases. The two windings of this motor are displaced separately with 90 degrees electrical & their MMFs are equivalent in magnitude however 90 degrees apart within the time phase.
- The capacitor start motor works as a balanced two-phase motor. When this motor reaches its rated speed, the auxiliary winding as well as the starting capacitor are automatically separated through the centrifugal switch which is provided on the motor’s shaft.
Advantages & Disadvantages
The advantages of a capacitor start motor include the following.
- These motors’ design is quite simple which makes them very easy to make & maintain.
- These motors are used in a wide range of applications due to low starting current & high starting torque.
- The capacitor used for this motor has the 7 microFarad to the 9 microFarad capacitance value that improves the motor performance after it starts running.
- The configuration of this motor works very well and it is obtainable in multi-kilowatt sizes.
- These motors simply produce a high starting torque that is appropriate for heavy-load starting conditions.
- These types of motors operate very efficiently through a single-phase power source and are suitable for commercial & domestic applications.
- The capacitor in this motor creates additional starting torque, normally 200 to 400% of the rated load. The starting current is normally from 450 to 575% of the rated current and is much lower as compared to the split-phase type because of the larger wire within the start circuit, so this allows simply reliable thermal protection & higher cycle rates.
The disadvantages of a capacitor start motor include the following.
- These motors are expensive due to the additional capacitor used.
- The capacitor used in this motor may need periodic replacement.
- These motors need maintenance.
- It is not appropriate for variable speed applications because of their starting mechanism.
- The size of the capacitor used in this motor is larger as contrasted to an electrolytic capacitor through similar ratings.
- These motors have less starting torque.
Applications/Uses
The applications of capacitor start motors include the following.
- Capacitor start motors are mainly used in driving high inertia loads wherever regular starts are necessary like; pumps, compressors, air conditioners, power tools, fans, and different types of industrial & domestic equipment.
- These motors are used in a broad range of belt-drive applications which include; large blowers, machine tools & small conveyors.
- These are used in various direct-drives (or) geared applications.
What is a Capacitor Start Motor used for?
Capacitor start induction motor is widely used for heavy-duty applications that need high starting torque like; pumps, conveyors & refrigerator compressors.
Can a Motor Run Without a Capacitor?
Different types of motors don’t need starter capacitors but Induction motors are the only ones that normally need starter capacitors.
Thus, this is an overview of a capacitor start motor, circuit, working, characteristics, phasor diagram, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. These motors are efficient & versatile and offer robust performance & high starting torque for a broad range of applications. The benefits of this motor like simplicity & efficiency will make these capacitors an outstanding choice for several commercial, industrial & domestic needs. When choosing this motor for a particular application needs to consider factors like; power supply, starting torque requirements, and maintenance. Here is a question for you, what is a capacitor?