The armature is a part of the motor that plays an important role in its operation. It is wound with a number of coils around it that forms a magnetic circuit. This circuit is responsible for the production of flux which in turn develops the required torque. This is the reason why it is considered as the heart of any rotating device because it is the source for the production of flux in any machine. So, let us discuss in detail about the importance of armature in this article. In addition, we shall also discuss its function, method of controlling the speed, and applications.
Armature
The collection of core, commutator, and brushes is considered as an Armature. In this, the winding is placed in the slots which are teeth type. It can be either used as a stationary part or as a rotating part. It is used as a rotating part in DC type machines I,e the motor and the generator. Similarly, it is used as a stationary part for ac type machines I,e in synchronous and induction type motors. Compared to the rotating type, a stationary type has more advantages. A stationary type is more efficient than a rotating type. The diagram of the armature is shown in the figure below.
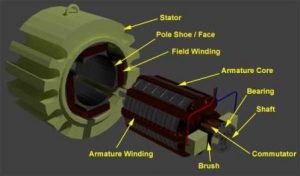
Parts of the core
The commutator is used for the collection of current from the winding and these commutator segments are connected to the brushes by some adjustable springs. The brushes collect the current from the commutator segments and deliver the power obtained to the load.
Components of Armature
- The armature is the combination of armature core, armature winding, the commutator, and the brushes. The components of the armature are shown in the figure below.

Components of Armature
- The armature core is made of silicon steel laminations to reduce eddy current and hysteresis losses. It holds the armature winding I,e it provides mechanical support to the winding. It consists of teeth and slots in which the winding is housed. It provides a low reluctance path for the main field flux. The armature winding is responsible for the production of armature flux.
- A commutator consists of some segments that collect the current from the armature. It is responsible for the conversion of alternating to direct current.
- Brushes are attached to the commutator with some adjustable springs. These are responsible for the collection of the current from the commutator.
Function of Armature
It produces a flux that is used for the development of power inside the machine such that the motor is able to rotate. The winding wound on the core is given current through a DC supply. This current-carrying winding as under the influence of the magnetic field develops a force that develops a rotational torque. This torque enables the machine to rotate. Similarly, in AC machines a stationary type is used that is given initially a three-phase supply. This current-carrying stationary winding develops a rotating magnetic field (RMF). This RMF interacts with the stationary field winding flux and develops a torque to rotate the rotor.
It produces flux that opposes the field produced by the main fielding. Due to this opposition, some effects will be produced. Those are the cross-magnetizing and de-magnetizing effects. One distorts the magnetic field and the other weakens the magnetic field. These oppositions can be overcome by means of using either compensating winding or interpoles.
Armature Control Method
Basically, an armature is provided with resistance this helps in limiting the excess current. To control the speed of the motor, apart from the inbuilt winding resistance, a controlling resistance should also be added. The relation between the speed of the motor and the back emf of a motor is given by
N α Eb – Ia.Ra
N α Eb – Ia.Ra – Ia.Rc
N α Eb – Ia. (Ra + Rc)
We know that the speed of the motor is directly proportional to the back emf. By varying the emf we can able to control the speed of the motor. By increasing the resistance, we can able to decrease the emf such that speed can be varied. The figure that represents the speed control is shown below.
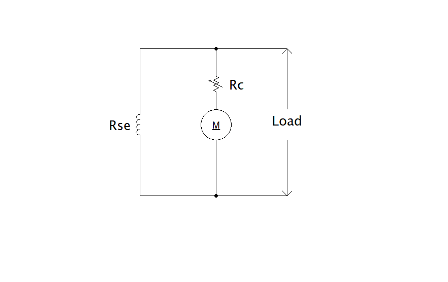
Speed Control
Applications
- Used in every machine for the production of torque.
Thus, in this article, we had an overview of what is an armature. It is simply a power generating device used inside the machine for the production of rotating torque. Apart from this, we had also studied its definition, function, how to control its speed, and its applications. Here is a question for the readers, what is the use of commutator in any machine?