In general, the steam or gases in the power plants can be produced through the fuel burning. A chimney in the plant can be used to release the gases into the atmosphere. These gases are very harmful to the environment as we ll as living organisms once they absorb because they include harmful particles. Because of these harmful gases, health issues will occur to human beings and other organisms. So these pollutants can cause global warming by polluting the environment. So, in order to overcome these issues, a filter should be used before releasing these gases from the industries into the environment. Thus, the filter which is used to filter these gases is known as Electrostatic Precipitator. This article discusses an overview of an Electrostatic precipitator which includes its operation, working principle, and its applications.
What is an Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP)
An ESP is a device for the cleaning of dust particles from the harmful flue gases that are exposed out from the boiler of a steam power plant.
Basically, the steam generated in the boiler of a power plant utilizes hot flue gases for the production of electricity. The hot flue gases after utilization will be expelled out through a chimney provided by an induced or forced draught fan. These hot flue gases contain harmful carbonate particles which affect the lives of human beings. SO, an ESP is placed before the chimney to filter out harmful particles from the flue gases before they are exposed out to the environment.
Working Principle of ESP
An ESP works on the principle of the corona discharge effect. A high DC voltage is applied across the two plates or electrodes. The negatively charged plate attracts the dust particles which are further attracted by the positively charged electrode by the process of Ionisation. Corona discharge is shown in the figure below.
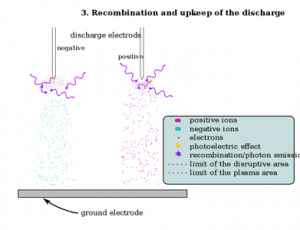
Corona discharge
Consider an example, Observe the pollution difference between two power plants with and without ESP installation.
A power plant without an electrostatic precipitator is shown in the below figure.

Before Using ESP
A power plant using an ESP is shown in the below figure.

After using ESP
An ESP involves four basic processes for its operation. They are
- Corona discharge
- Electrostatic attraction
- Dust particle collection, and
- Removal of these collected dust particles.
Components
- High voltage supply source and control system
- Mesh
- Gas Distribution System
- Hopper
- Collecting plate
- Discharge Electrode
- Hammering or Rapping system
High voltage DC supply is given to the electrodes for the corona discharge to take place.
Mesh is used as both pre-filter and post-filter for the collection of dust particles. Pre-filter collects the dust before sending flue gases to the ionization process. Post-filter is used to filter out the dust particles if any found after the ionization process.
The gas distribution system is employed for the proper passage of flue gases through the pre-filtration and ionization process.
Hopper is used to collecting the dust particles collected by the collecting plate.
The collecting plate is a positively charged electrode that collects the dust particles by the attraction principle which are ionized by the highly negatively charged electrode.
The discharge electrode is a highly negatively charged electrode which ionizes the dust particles which are made to pass through it.
Hammering is done on the collecting plate at periodic intervals to collect these dust particles in the hopper.
Construction and Working of an Electrostatic Precipitator
A high voltage DC supply is given to the electrodes, one will be positively charged and the other will be negatively charged. The dust particles from the boiler are fed to the ESP. The ESP has a pre-filter placed at the front portion. The dust particles will undergo a pre-filtration process before undergoing precipitation. The Electrostatic Precipitator working is discussed below.
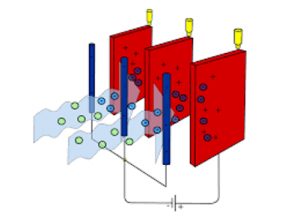
ESP
After Pre-filtration the particles will be subjected to experience a highly negatively charged bypassing the dust particles through the negatively charged electrode placed after the pre-filter. Due to the high negative charge, the dust particles will be ionized. Due to the attraction principle, the ionized negatively charged particles will be attracted by the Positively charged electrode.
This positively charged electrode acts as a collecting electrode whereas the negatively charged electrode acts as an emitting electrode. By the process of hammering (Rapping system), the collected dust particles will be dumped inside a hopper placed at the bottom of ESP. The mechanical Rapper system image is shown below.
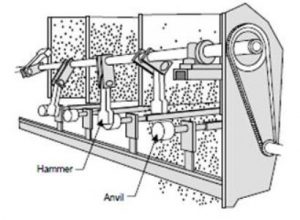
Mechanical Rapper
The remaining gas particles will be subjected to post-filtration where any other particles will be filtered out. The clean gas will be sent to the chimney to expose out.
Different Types of Electrostatic Precipitators
- Plate
- Dry
- Wet, and
- Tubular
Plate Type
In plate type, two plates or electrodes are arranged vertically through which these gases will be passed horizontally. Due to the principle of corona discharge, the dust particles will be attracted to the positive plate by the electrostatic attraction.
Dry Type
Dry-type ESP is used where the dust particles to be filtered should be of dry nature. It is used in the cement industry for the handling of ash. The harmful dust particles from the ash will be filtered out using dry type ESP.
Wet Type
Wet type ESP is used where the dust particles to be eliminated should be of wet nature. It is used in oil refineries where the fuel used is of liquid nature.
Tubular Type
Tube type ESP is used where the dust particles to be expelled out should be of adhesive nature. Here, the electrodes used will be of a tubular type which is given high voltage. These are arranged in different shapes like circular or hexagonal. The gases to be filtered are passed either upwards or downwards through these tubes.
Advantages
- Its initial cost is less
- Less maintenance
- Helps in protecting the environment
- Efficiency is high
- Works well compared to other separators
- Easy to operate
- Highly reliable
- Large dust particles can be easily eliminated.
- Approximately 90 percent of dust can be cleaned.
- Air Pollution can be minimized.
Disadvantages
- More running costs
- Cost compared to other devices is high
- Requires large area
Applications
- Used in power plants, pulp industries, metallurgical industries, and oil refineries.
- Used to remove the fungus in medical industries.
- Used to remove harmful particles in the chemical industry.
Therefore, this article includes an overview of an Electrostatic Precipitator. We can conclude that an ESP is a device that plays a crucial role in the process of dust elimination in a power plant. Basically, it is a filter used for the filtration of dust particles before they are exposed to the environment. In the above information, it also includes the use of ESP, working, advantages, and disadvantages. Here is a question for you, what is the working model and design of ESP?