Generally, Power plants require steam for the purpose of heating. Hence, this purpose is fulfilled by the boiler, where the steam is produced by boiling water. Basically, the steam is produced by boiling water beyond its boiling point where it changes its state from liquid to vapor and this vapor is known as steam. So, for the production of steam, we require water and steam. To produce steam we need a boiler where available water is heated by means of some fuel such that steam is produced. In this article, we will discuss what is a steam boiler, classification, types, advantages, and disadvantages.
What is a Steam Boiler?
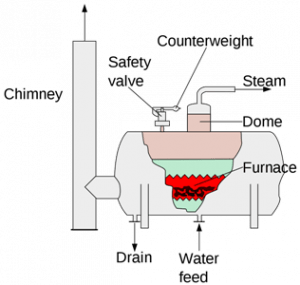
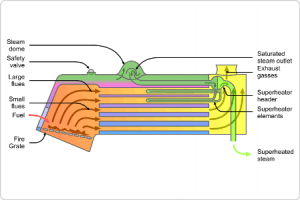
Definition of a Boiler: A boiler is a closed insulted case where heat is generated inside by the combustion of coal, which is then transmitted to water for the production of steam is known as a Boiler. This produced steam is utilized for the production of electricity in Power plants by running turbines. The figure below depicts the view of a Steam Boiler.

Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Working Principle
Boiler works on the principle of combustion of Fuel. The boiler depends on the process of combustion where heat is generated by the burning of fuel. In order that the combustion takes place, it needs some requirements. They are
- Fuel (burn Oil or Natural gas)
- Air (oxygen is required for combustion process)
- Heat (To increase the temperature of the Air mixture)
Without these requirements, combustion will not take place.
How Steam is Produced?
For the production of steam we need two basic requirements they are heat and water. Heat is generated by the combustion of fuel. The heat generated by the fuel is used to produce steam. Production of steam is better understood by the following figure.
Steam Generation
The Construction of Boiler Should Meet Certain Requirements
- The boiler should be in a closed case.
- The casing should be insulated in order to prevent the exposure of heat to the atmosphere.
- A draught fan should be arranged to escape combustion gases.
- The produced steam should be used effectively; there should not be any heat loss.
Due to the difference in temperature heat will be transferred naturally from one object to the other.
Different Types of Heat Transfers
- Radiation
- Convection and
- Conduction
- Radiation is the amount of heat transmitted by the sun to the earth. The sun radiates energy in the form of electromagnetic waves which is absorbed by the earth as heat. Depending upon the number of electromagnetic waves received by the earth it gets warmed up. Different types of heat transfers are shown in the figure below.

Convection Conduction Radiation
- Convection is the transmission of heat within a liquid where the mixing of two liquids takes place.
- In conduction, when one particular end is heating, heat is transmitted from that end to the other end.
Therefore, all these three types of heat transfer are involved in the operation of Boiler I,e heat is transferred from the burning of fuel (coal) to water.
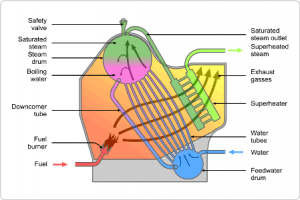
Steam Boiler Operation
- The Boiler basically consists of tubes which are arranged in series through which water will be flown. In the combustion area, heat is generated by the burning of coal where radiant energy in the form of electromagnetic waves is spread across the area.
- These electromagnetic waves in the combustion area come in contact with the tubes where they absorb the heat. This type of heat transfer is known as Radiation. The burning of coal produces some flue gases, whose heat is also absorbed by the tubes. The Operation of Steam Boiler is shown in the figure below.

Steam Boiler
- The conduction of heat takes place as the outer most part of the tube is heated, the innermost part also gets heated. The heat from the inner surfaces is transferred to the cool water in the tube.
- Thus, water gets mixed up, and the cooler water is turned into hot water. The hot water beyond its boiling point changes its state from liquid to vapor. This type of heat transfer is known as convection. This is how steam is produced in a boiler.
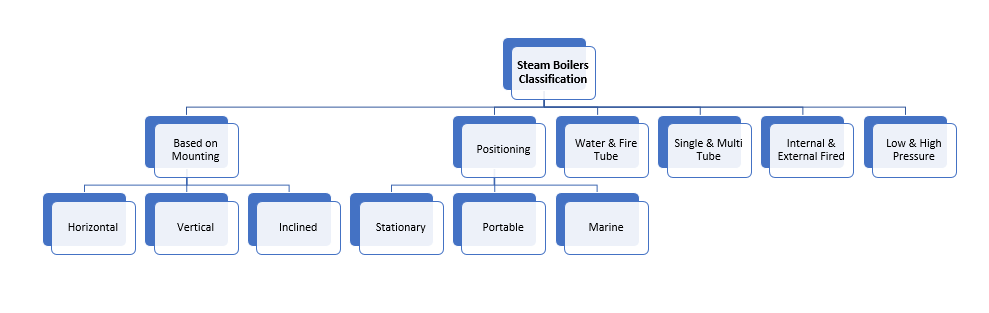
A Steam Boiler is Classified into Different Types Based on the Following
- Based on mounting I,e horizontal, vertical and inclined positions
- Whether the boiler is stationary, portable and marine
- Water tube and fire tube
- Single tube and multi-tube
- Internally fired and externally fired
- Fuel is natural or artificially circulated
- Fuel can be liquid, solid or gas.
- Low pressure and high pressure.
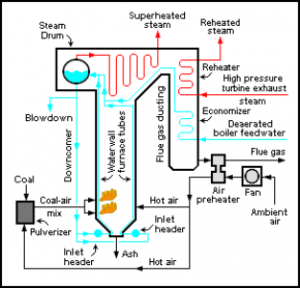
Water Tube Boiler
A water tube boiler is used for producing high-pressure steam. water tube boiler is shown in the figure below
Water Tube Boiler
In the water tube boiler, water will be flown inside the tube and fire is surrounded outside. So, it creates high-pressure steam.
There are different types of high-pressure boilers. They are
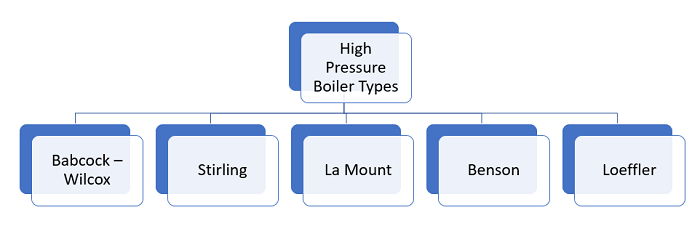
- Babcock – Wilcox
- Stirling
- La-mount
- Benson and
- Loeffler Boiler.
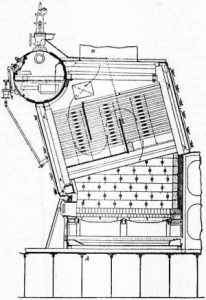
Babcock – Wilcox and Stirling
Babcock – Wilcox and Stirling type uses natural circulation where the heat will be transmitted through the natural circulation process. Thus, it does not require any artificial medium to circulate. Babcock – Wilcox Boiler is shown in the figure below.
water tube Boiler Babcock Wilcox
Babcock – Wilcox, and Stirling type also uses Natural draught fan, where the exhaust is sent to the atmosphere through natural draught fans.
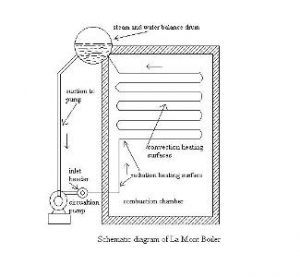
La – mont, Benson, and Loeffler boilers
La – mont, Benson, and Loeffler boilers require forced circulation and artificial draught fans. These boilers operate at high pressures. So, the production of steam in these boilers is high. As the steam production is high the efficiency of these boilers is also high. The high-pressure La-mont water tube Boiler is shown in the figure below.
La-Mont Boiler
Fire-Tube Boiler
Fire-tube boiler used for producing low-pressure steam. A Fire tube boiler is shown in the figure below.
Fire Tube Boiler
In a Fire tube boiler, the fire will be inside the tube and water is surrounded outside. So, it creates low-pressure steam.
There are different types of low-pressure boilers.
- Cochran,
- Locomotive and
- Lancashire
Natural circulation is used in low-pressure boilers, the material which is used in this type is circulated naturally.
The exhaust gases which are released to the atmosphere is naturally exhausted by a natural draught fan except in Locomotive Boiler.
The internal firing process is preferred in this type where the combustion of fuel is fired internally in the boiler.
A stationary boiler is used except in scotch marine and Locomotive.
Cochran Boiler
It is a vertical, multi-tubular, internally fired, natural circulation boiler. The Cochran boiler is shown in the figure below.

Cochran boiler
Its shell is placed vertically (vertical type), consists of many tubes inside the shell (multi-tubular), The combustion of fuel takes place internally (internally fired), and the water will be circulated naturally without any pump (natural circulation).
It is a fire tube boiler (flue gases generated by the combustion of fuel that will be sent through the tubes surrounded by water).
Locomotive Boiler
It is a horizontal, multi-tubular, internally fired, natural circulation boiler. The locomotive boiler is shown in the figure below.
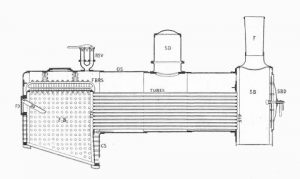
Locomotive boiler
Its shell is placed horizontally (horizontal type), consists of many tubes inside the shell (multi-tubular), The combustion of fuel takes place internally (internally fired), and the water will be circulated naturally without any pump (natural circulation).
It is a fire tube boiler (flue gases generated by the combustion of fuel that will be sent through the tubes surrounded by water).
Lancashire Boiler
It is a fire tube, horizontal, internally fired, and natural circulation boiler, stationary and low-pressure boiler. Since it is a low-pressure boiler steam production will be less. Due to the lower steam production, the efficiency of the boiler is also low compared to the water tube boiler. The Lancashire boiler is shown in the figure below.
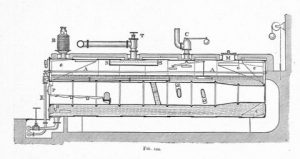
Lancashire boiler
Boiler Efficiency
- It is actually the proportion of heat transfer utilized to the total amount of heat produced by the burning of fuel.
- Boiler efficiency = W (h – hfw) C
Where W = weight of water evaporated into steam per one KG of the burning of fuel
C = Calorific value in KJ/KG
h = heat of the water
hfw = heat of feed water
Advantages of Boiler
- The design is simple.
- Construction cost is less.
- It requires less maintenance.
Disadvantages of Boiler
- Sludge (soft deposits of Ca and Mg salts) and scale (hard deposits of Ca and Mg salts) formation on the body of boilers.
- Due to impurities heat transfer is interrupted.
- Lowers safety.
- The danger of explosion due to overheating when heat transfer is interrupted.
- Boiler efficiency will be reduced
Applications of Boiler
- Steam Boilers are used in steam locomotives, portable engines, steam-powered road vehicles, Stationary steam engines, industrial installations, and power stations.
Thus, in this article, we have studied what is a boiler and how steam is generated and different types of heat transfers. We can conclude from this article that for the production of steam the construction of the boiler should meet certain requirements in order to produce maximum steam. Thus, in this way, we can increase the efficiency of the boiler. Here is a question for the readers what is the difference between the fire tube and water tube boiler.