In the current world, we have been observing huge global energy catastrophes because of massive energy demands and the availability of only a few resources. This crisis happens because non-renewable resources are getting exhausted and renewable sources are not appropriately utilized. This creates a quick demand for searching alternate options for energy generation. And one of the options in microbial fuel cell technology. The thought of using microbes for electricity generation was started in the early 20th century by Michael Potter in 1911. This article deals with the explanation of what is MFC technology, how it works, what are the components involved, and its applications.
What is a Microbial Fuel Cell?
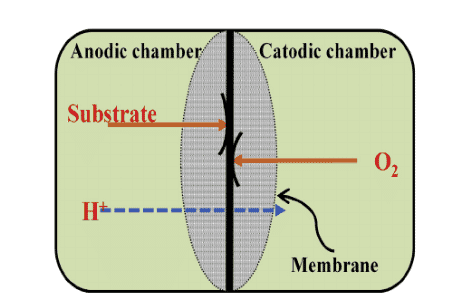
An MFC is considered a device that is used for the conversion of chemical to electrical energy using microorganisms. These cells are constructed either by bioanodes or biocathodes or both. In many of the microbial fuel cells, both the anode and cathode sections are separated by a membrane because in anode oxidation happens and in the cathode, reduction happens.
The MFC can also be termed as a bioelectrochemical fuel cell that produces current by transferring electrons generated from oxidation on the anode to the oxidized compounds on the cathode using an additional electric circuit. It was known that the demonstration of the first MFC took place in the 20th century where it was utilized as a mediator which means that it was employed as a chemical that transmits electrons from bacteria to the anode.
Later on, in the 21st century, these fuel cells were also utilized for wastewater treatments.
Design of Microbial Fuel Cell
An MFC has two designs where each of these works on different mechanisms. Every mechanism is dependent on the organisms that are used, wastewater source, and others.
The designs are
- Single Chambered
- Double Chambered MFC
Double Chambered MFC
In the double-chambered MFC, there are two chambers where these two are connected using a bridge that is made of either sodium or potassium salt. In this, salt agar is used as a bridge other than using dyes because dyes are considered as poisonous together with the microorganisms which are active electrochemically. Here, one container has wastewater or else water with microbes and the other container has salt/aerated wastewater/aerated water.
The container which has wastewater is kept at an anaerobic state which means there is no oxygen supply to the container and the caps are air sealed and have an opening slot only for methane and other kinds of gases generated by organisms. And the other container is completely kept at an aerobic condition where helps for oxygen generation for aerated/aerated wastewater.
As states that both the chambers are connected together by salt agar. The composition of salt agar is
1% of NaCl or KCl
2.5% of Agar
This composition can be done as per the necessity, or the size required for salt agar. In both anode and cathode sections, a graphite electrode is used. The construction of microbial fuel cells in double-chambered design is shown as follows:
Single Chambered MFC
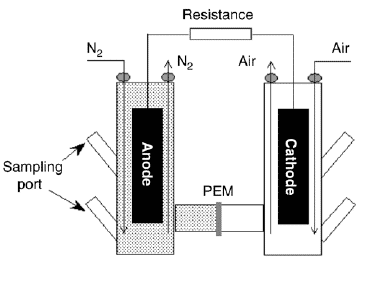
This single-chambered MFC has two single containers that consist of two internal containers. These internal chambers are designed by a semi-permeable coating that allows for electrons transport. When compared with dual-chambered MFC, single-chambered MFC holds more efficiency. Here, the generation of electricity happens through a non-mediated approach by utilizing wastewater.
As there exists no salt bridge or dye for electron carriers, the efficiency in transportation of electrons is more and ions loss is very minimal. This single MFC needs the anodic section, and it has to be kept at an anaerobic state and then the cathode is moderately dipped in the fuel cell so that some part of the cathode gets exposed to oxygen.
Here the cathode and anode materials that are used are graphite and copper. And the substance which is used for constructing the entire container is polystyrene and copper is totally dipped into the cell and from this current generation takes place through a wire connection. The below picture shows the single-chambered MFC construction.
Single Chambered Microbial Fuel Cell
How do MFC’s Work and Generate Electricity?
The working of microbial fuel cells takes place by letting bacteria operate as they need which means they undergo oxidation and reduction of organic particles. The respiration process of bacteria is fundamentally considered a redox process where the movement of electrons takes place. When there is electron movement, some potential is generated for utilizing EMF in order to perform some operation.
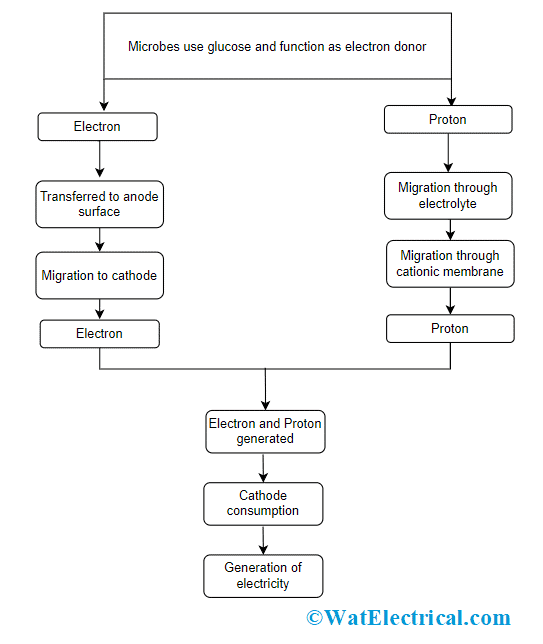
Electricity Generation Process in MFC
As MFC contains anode and cathode sections partitioned by a membrane, microbes that are at the anode undergo oxidation and generate protons and these protons move through the membrane to reach the cathode. And the protons which move from the anode to the external circuit generate electricity. The logic behind this is gathering the electrons released by microbes as they undergo respiration.
Types of MFC
There are various types of microbial fuel cells, and this section explains clearly each type of MFC.
Mediated MFC – Here, the type of microbial cells which are used in an electrochemically inactive nature. The transfer of electrons from microorganisms to electrodes takes place with the mediators like neutral red, thionine, humic acid, and others. Many of the mediators are pricey and they are poisonous too.
Mediator-free MFC – The MFC’s used for electrons transfer has the nature of electrochemically active and the MFC’s used in this type can be Aeromonas, Shewanella putrefaciens, and many others. Few types of bacteria hold the ability to transfer electrons through pili which is present on their outer layer.
The MFC’s can function in wastewater and generate electricity from specific plants and oxygen. A few of the plant types can be algae, rice, lupines, cordgrass, and others.
Phototropic Biofilm – This type of MFC employs a phototrophic biofilm anode which consists of photosynthetic orgasms like candyanophyta and Chlorophyta. Using the process of photosynthesis, the MFC’s generate organic metabolites and provide electrons.
Soil-based MFC – The functionality of soil-based MFC follows the same as general MFC where soil functions as an anode and the anodic elements are proton exchange membrane and inoculum. The location of the anode is at some depth in the soil whereas the cathode location is on top of the soil, and it is exposed to the atmosphere.
In general, soils abound with various kinds of microbes along with electrogenic bacteria required for MFCs. Also, microbes that exhaust oxygen exists in the soil and these operate as oxygen such as costly PEM components so that the redox ability of the soil diminishes with more depth.
In addition to these, the other types of MFCs are
- Ceramic membrane
- Nanoporous membrane
- Microbial electrolysis
Components of Microbial Fuel Cell
This section explains on what are the necessary and optional components needed in MFC and what are the materials used for the components.
| Component in MFC | Materials | Necessary or Not Obligatory |
| Anodic Compartment | The materials used in the anodic section are glass, Plexiglas, and polycarbonate | Necessary |
| Cathodic Compartment | The materials used in the cathodic section are glass, Plexiglas, and polycarbonate | Not obligatory |
| Anode | The materials that are utilized as an anode are carbon paper, graphite, Pt black, graphite felt, reticulated vitreous carbon (RVC), carbon cloth, and Pt | Necessary |
| Cathode | The materials that are utilized as a cathode are carbon paper, graphite, Pt black, graphite felt, reticulated vitreous carbon (RVC), carbon cloth, and Pt | Necessary |
| Electrode Catalyst | The materials that are utilized as electrode catalysts are polyaniline, Pt, MnO2, Pt black, and Fe3+ | Not obligatory |
| Proton exchange system | As a proton exchange layer, the materials that can be used are ultrex, nafion, and polyethylene. poly | Necessary |
Advantages and Disadvantages of MFC
The advantages of the microbial fuel cells are:
- MFC’s hold the ability to generate electricity from unused sources like wastewater and organic components.
- As the MFC procedure is not based on fossil fuels, it shows minimal impact like greenhouse gas emissions when compared with other types of fuels
- Utilizing high-cost catalysts like platinum can be avoided and this is an added advantage of MFC
- Helps in the recovery of valuable compounds from substances
- Shows effective transformation of the substrate to electricity
- Generates minimal carbon emissions
- A microbial fuel cell functions as an alternative for fuel source
The disadvantages of the microbial fuel cell are:
- MFC’s generate only a limited amount of power which can be in the range of 50 watts/m3
- Used in the applications only those function with fewer power requirements
- The minimal evolution rate of microbes
- Required high level of maintenance and functionality
- Shows poisonousness of the substance
- The membranes that are used in MFC are expensive, and also have minimal efficiency of transferring protons
- Delivers minimal power output
Microbial Fuel Cell Applications
There are a wide variety of applications of MFC. A few of those are discussed here:
- In power generation – The microbial fuel cells are used in applications that work with minimal power, whereas substituting batteries seems to be not practical like WSN. Wireless sensors offered by MFCs stand as examples to be utilized for remote conservations.
- Education system – Soil-dependent MFC’s function as educational tools because they show various scientific principles, and these can be prepared with multiple substances like soils and things that are present in the fridge. One of the examples of using MFC in the educational system is IBET which is the integration of biology, English, and technology.
- Biosensors – The electricity produced from MFC holds direct proportion with the organic substance content of wastewater utilized as fuel. The MFC’s also have the capability of calculating the concentration of solute present in wastewater. A BOD sensor of MFC type will offer realistic BOD values.
- Also utilized in aerobic digestion
- Used in bio-recovery applications
On the whole, this is all about microbial fuel cell. The article has completely focused on explaining microbial fuel cell technology, its components, working, design, types, and applications. Also know, what are the substrates utilized in MFC’s?