The moving iron instrument is the most commonly used ammeter & voltmeter used at power frequencies in laboratories or switchboards. These types of instruments are designed in such a way to measure voltage & current to the accuracy required in most engineering works. As compared to any other types of AC instruments with the same accuracy & ruggedness, these are not expensive. So this article gives brief information on a moving iron instrument – working with applications.
What is a Moving Iron Instrument?
The instrument which has the moving iron used to measure the current or voltage flow is called the moving iron instrument. The working principle of moving iron instruments mainly depends on the iron movement attracted by the magnetic field to it & repulsion among them. Here, the magnetic field is generated by the current within the coil. The attraction force in this instrument mainly depends on the magnetic field’s strength.
The magnetic field is induced by the electromagnet whose magnetic field’s strength mainly depends on the magnitude of the current supplies throughout it. The moving iron instrument diagram is shown below.

Moving Iron Instrument
This moving iron instrument can be used as a voltmeter or an ammeter. If this instrument is used as an ammeter then it has less number of thick wire turns and if this instrument is used as a voltmeter then it has more thick wire turns. So this instrument simply supports both AC & DC.
Construction of Moving Iron Instrument
The moving iron instrument uses a moving element like a plate or soft iron vane. The vane is arranged in such a way that it moves freely within the magnetic field of the inactive coil. This coil is simply excited by the current/voltage whose magnitude is to be measured.
This instrument utilizes an electromagnet like the inactive coil. This electromagnet is not a permanent magnet where the strength of this magnetic field enhances or reduces through the magnitude of the current flow throughout it.
Working of Moving Iron Instrument
The moving iron instrument uses the stationary coil of aluminum/copper wire which functions like an electromagnet once current flows throughout it. The magnetic field strength induces through the electromagnet is directly proportional to the current flowing throughout it.
The vane of the iron/plates supply throughout the coil increases the stationary coil’s inductance. Here inductance is the conductor’s property which enhances their electromotive force once the unstable current supplies through it.
The electromagnet will attract the iron vane which passes throughout the coil and looks to reside in the minimum reluctance lane. The vane passes throughout the coil and will experience a repulsion force that is caused by the electromagnet. This force increases the coil inductance’s strength and this occurs due to the reluctance & inductances being inversely proportional to each other.
Types of the Moving Iron Instruments
These instruments are classified into two types attraction type and repulsion type which are discussed below.
Attraction Type Moving Iron Instrument
The attraction type moving iron instrument working principle mainly depends on magnetic attraction, because it attracts an iron piece once arranged close to a magnetic field. Here, this magnetic field is generated through an electromagnet.
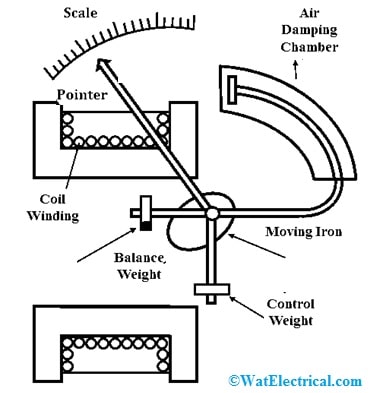
Attraction Type Moving Iron Instrument
This type of moving iron instrument includes a flat fixed coil with a slight opening. A moving iron in this instrument is designed with soft iron that is mounted on a spindle. Here, the coils are wounded with a no. of turns which depends on the instrument range. The pointer in this instrument is mounted on a spindle that includes a graduated scale used to show the deflection.
Once coil winding is coupled across the supply to be measured, then a magnetic field will be set up. So, the magnetic field’s intensity is higher within the coil as compared to the outside intensity thus low reluctance will exist within the coil. When the moving iron attempts to occupy the low reluctance position, then it is moved & attracted to the fixed coil. Once the iron piece gets moved, then the pointer in the instrument also moves to illustrate the deflection. So, this instrument achieves the equilibrium position once the deflecting torque is balanced by the controlling torque.
Repulsion Type Moving Iron Instrument
The repulsion type instrument includes two vanes otherwise iron plate where one vane is permanent & another vane is movable. In this type of instrument, the fixed vane is connected to the coil and the movable vane is placed on the spindle. So this spindle simply carries the pointer to move on a scale.
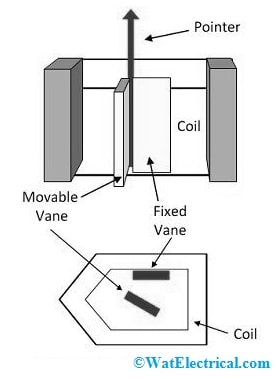
Repulsion Type
At first, the current does not flow throughout the coil so, the two vanes within the instrument will get touched each other & the pointer will be at zero position. Once current is supplied throughout the coil, then the magnetic field will be set up & two vanes get magnetized by similar polarities. At one end, north poles are generated in both the vanes, and at the other end, south poles are generated. Because of this, a repulsive force exists in between two vanes & the movable vane attempts to move away from the fixed vane.
Thus, the movable vane moves because of the repulsive force & the pointer on a spindle will show deflection. Once the controlling torque is equivalent to the deflecting torque then the pointer will stop deflecting. As a result, the total repulsion force mainly depends on the strength of the magnetization field produced by the coil. This magnetic field mainly depends on the supplied current. In this type of moving the iron instrument, torque control is provided through the damping torque as well as spiral springs which are provided through air friction.
Types of Repulsion Type Moving Iron Instrument
The repulsion type moving iron instrument is classified into two types radial vane & concentric vane or co-axial type which are discussed below.
Radial Vane Repulsion Type Instrument
If the repulsion type moving iron instrument has radial vanes then this instrument is called a radial vane repulsion type instrument. This instrument includes two vanes which are also known as iron strips. These vanes are arranged radially, where one vane is fixed & the other vane is movable.
The deflection torque in this instrument is directly proportional to the actual current within the coil to make the scale uniform so that readings of scale can be directly attained. These instruments are the most sensitive type.
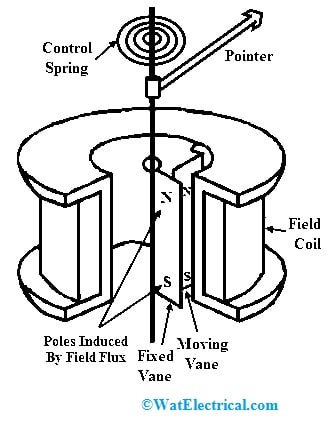
Radial Vane Repulsion Type Instrument
Co-axial Vane Repulsion Type Instrument
If the repulsion type moving iron instrument has coaxial vanes then this instrument is called a coaxial vane repulsion type instrument. In this type of instrument, the two vanes are arranged co-axially within the coil where one vane is stationary and the other vane is movable and rotates at the middle axis within the stationary vane. But, the deflecting torque on the pointer is directly proportional to the square of the current within the coil. So the scale in this instrument cannot be uniform because of the concentric vanes. These instruments are less sensitive as compared to radial-type instruments.
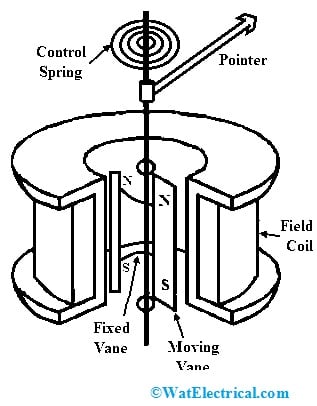
Co-axial Vane Repulsion Type
So, from the above information, we can conclude that the attraction type instrument will possess the least inductance as compared to the repulsion type instrument. So, voltmeters are entirely accurate over extended levels of frequency. Repulsion-type instruments are mainly utilized for economical purposes. By using these instruments, the linear scale can be attained very easily.
Deflecting Torque of a Moving Iron Instrument
In a moving iron instrument, the deflecting torque is given as
Td = (1/2)I^2(dL/dθ)
The controlling torque in these instruments is provided through spring. So, controlling torque due to spring is
Tc = Kθ
Where,
‘K’ is the constant of spring.
‘θ’ is the deflection within the needle.
The deflecting & controlling torque in equilibrium condition is equivalent to the following.
Deflecting Torque = Controlling Torque
Td = Tc
(1/2)I^2(dL/dθ) = Kθ
From the above equation, ‘θ’ can be written as
θ = (1/2)I^2/K(dL/dθ)
Advantages
The advantages of moving iron instruments include the following.
- This instrument is applicable for both AC & DC.
- This device has very less friction error due to a high torque weight ratio
- These instruments are available at less cost because it has less number of coil turns as compared to other instruments like PMMC.
- This is robust due to its very simple construction.
- It can resist overload for a moment.
- Applicable for high power & low frequency-based circuits.
- It is capable of giving accuracy within limits of both accuracies as well as industrial grades.
The disadvantages of moving iron instruments include the following.
- The scale is not uniform.
- The power utilization is high for a low range of voltage.
- The errors in this instrument can be caused because of the hysteresis within the iron & stray magnetic field.
- Change within frequency can cause very serious errors in AC measurements.
- The spring stiffness will decrease when the temperature increases.
- This instrument is nondirectional, so its accuracy is low.
- Power consumption is high.
Applications
The applications of moving iron instruments include the following.
- These instruments are mainly used as an ammeter, voltmeter & wattmeter which can work on both AC & DC.
- These are used for measuring alternating currents & voltages.
- These types of Instruments are used at power frequencies within laboratories.
- These MI instruments are extensively used in switchboards & labs.
Know more about Electric Traction MCQs , Dynamometer Type Wattmeter MCQs.
Please refer to this link for Moving Iron Instrument MCQs.
Thus, this is all about an overview of a moving iron instrument – working, types, advantages, disadvantages and its applications. Moving iron instrument is also known as an MI instrument and it is one kind of measuring instrument used to measure current or voltage. So, these instruments utilize a movable iron piece arranged within the magnetic field so that the pointer will deflect on the scale and thus called this instrument as moving iron instrument. Here is a question for you, what is an ammeter?