
Switch Mode Power Supply Circuit
Power supply is an electronic circuit that is used for providing the electrical power to appliances or loads such as computers, machines, and so on. These electrical and electronic loads require various forms of power at different ranges and with different characteristics. So, for this reason the power is converted into the required forms (with desired qualities) by using some power electronic converters or power converters.
Electrical and electronic loads work with various forms of power supplies, such as AC power supply, AC- to-DC power supply, High-voltage power supply, Programmable power supply, Uninterruptable power supply and Switch-mode power supply.
What is Switch-mode power supply?
The electronic power supply integrated with the switching regulator for converting the electrical power efficiently from one form to another form with desired characteristics is called as Switch-mode power supply. It is used to obtain regulated DC output voltage from unregulated AC or DC input voltage.

Switch mode power supply
Similar to other power supplies, switch-mode power supply is a complicated circuit that supplies power from a source to loads. switch-mode power supply is essential for power consuming electrical and electronic appliances and even for building electrical and electronic projects.
Topologies of Switch Mode Power Supply
There are different types of topologies for SMPS, among those, a few are as follows
- DC to DC converter
- AC to DC converter
- Fly back converter
- Forward converter
Switch Mode Power Supply’s Working Principle
The working of a few types of switch-mode power supply topologies is as follows:
1. DC to DC Converter SMPS Working Principle
In a DC-to-DC converter, primarily a high-voltage DC power is directly obtained from a DC power source. Then, this high-voltage DC power is switched at a very high switching speed usually in the range of 15 KHz to 50 KHz.
And then it is fed to a step-down transformer which is comparable to the weight and size characteristics of a transformer unit of 50Hz. The output of the step-down transformer is further fed into the rectifier. This filtered and rectified output DC power is used as a source for loads, and a sample of this output power is used as a feedback for controlling the output voltage.With this feedback voltage, the ON time of the oscillator is controlled, and a closed-loop regulator is formed.
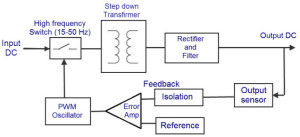
DC to DC converter SMPS
The output of the switching-power supply is regulated by using PWM (Pulse Width Modulation). As shown in the circuit above, the switch is driven by the PWM oscillator, such that the power fed to the step-down transformer is controlled indirectly, and hence, the output is controlled by the PWM, as this pulse width signal and the output voltage are inversely proportional to each other.
If the duty cycle is 50%, then the maximum amount of power is transferred through the step-down transformer, and, if duty cycle decreases, then the amount of power transferred will decrease by decreasing the power dissipation.
2. AC to DC Converter SMPS Working Principle
The AC to DC converter SMPS has an AC input. It is converted into DC by rectification process using a rectifier and filter. This unregulated DC voltage is fed to the large-filter capacitor or PFC (Power Factor Correction) circuits for correction of power factor as it is affected. This is because around voltage peaks, the rectifier draws short current pulses having significantly high-frequency energy which affects the power factor to reduce.
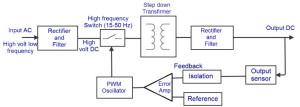
AC to DC converter SMPS
It is almost similar to the above discussed DC to DC converter, but instead of direct DC power supply, here AC input is used. So, the combination of the rectifier and filter, shown in the block diagram is used for converting the AC into DC and switching is done by using a power MOSFET amplifier with which very high gain can be achieved. The MOSFET transistor has low on-resistance and can withstand high currents. The switching frequency is chosen such that it must be kept inaudible to normal human beings (mostly above 20KHz) and switching action is controlled by a feedback utilizing the PWM oscillator.
This AC voltage is again fed to the output transformer shown in the figure to step down or step up the voltage levels. Then, the output of this transformer is rectified and smoothed by using the output rectifier and filter. A feedback circuit is used to control the output voltage by comparing it with the reference voltage.
Please refer to this link to know more about Regulated DC Power Supply MCQs
3. Fly-back Converter type SMPS Working Principle
The SMPS circuit with very low output power of less than 100W (watts) is usually of Fly-back converter type SMPS, and it is very simple and low- cost circuit compared to other SMPS circuits. Hence, it is frequently used for low-power applications.
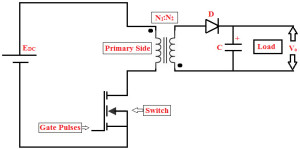
Fly-back Converter type SMPS
The unregulated input voltage with a constant magnitude is converted into a desired output voltage by fast switching using a MOSFET; the switching frequency is around 100 kHz. The isolation of voltage can be achieved by using a transformer. The switch operation can be controlled by using a PWM control while implementing a practical fly-back converter.
Fly-back transformer exhibits different characteristics compared to general transformer. The two windings of the fly-back transformer act as magnetically coupled inductors. The output of this transformer is passed through a diode and a capacitor for rectification and filtering. As shown in the figure, the voltage across this filter capacitor is taken as the output voltage of the SMPS.
4. Forward Converter type SMPS Working
Forward converter type SMPS is almost similar to the Fly-back converter type SMPS, but in the forward converter type, a control is connected for controlling the switch and at the output of the secondary winding of the transformer, and the rectification and filtering circuit is complicated as compared to the fly-back converter.
It can be called as a DC to DC buck converter, along with a transformer used for isolation and scaling. In addition to the diode D1 and capacitor C, a diode D2 and an inductor L are connected at the output end. If switch S gets switched ON, then the input is given to the primary winding of the transformer, and hence, a scaled voltage is generated at the secondary winding of the transformer.
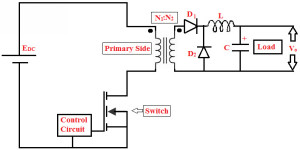
Forward Converter type SMPS
Thus, the diode D1 gets forward biased and scaled voltage is passed through the low-pass filter preceding the load. If the switch S is turned off, then the currents through the primary and secondary winding reach to zero, but the current through the inductive filter and load can not be change abruptly, and a path is provided to this current by the freewheeling diode D2. By using the filter inductor, the required voltage across the diode D2 and to maintain the EMF required for maintaining the continuity of the current at inductive filter.
Even though the current is diminishing against the output voltage, approximately the constant output voltage is maintained with the presence of the large capacitive filter. It is frequently used for switching applications with a power in the range of 100 W to 200 W.
Please refer to this link for SMPS MCQs.
Different types of topologies are there in which SMPS can be realized such as Buck converter, Boost converter, Self Oscillating fly-back converter, Buck-boost converter, Boost-buck, Cuk, Sepic. But only a few are discussed in this article, namely DC to DC converter, AC to DC converter, Fly-back converter and Forward converter. For more information regarding the types of switch-mode power supply and the types of SMPS with their working principles, feel free to write your comments for improving this article technically so that you can help the other readers to get awareness of SMPS.