A synchroscope is a device within an AC electrical power system that indicates the amount to which two systems like; power networks or generators are synchronized. These two systems should work at a similar frequency & the phase angle for the two power systems to be synchronized in between the systems should be zero. So these devices are useful in measuring & displaying the frequency variation and phase angle between two power systems. When these quantities are zero, it is secure to connect the two power systems. If we connect two unsynchronized AC power systems jointly then it causes high currents to supply, which will harm any equipment severely and is not protected by circuit breakers or fuses. This article provides brief information on Synchroscope, its working, and its applications.
What is Synchroscope?
A Synchroscope is an electronic device that is designed mainly to indicate if two generators, power networks, or any AC electrical power system is synchronized through each other. So this device verifies both systems’ operation to confirm whether they are functioning at a similar frequency or not. In addition, for these two systems to be synchronized, the phase angle must be zero as well. The phase sequence between two poly-phase systems must be similar. Thus, a Synchroscope is accountable for measuring & indicating the frequency & phase angle difference between two preferred power systems.
The synchroscope device is an essential device that plays a main role while the incorrect number between the two frequencies & phase angle causes severe injury to the systems that are not securely protected by fuses or circuit breakers. So this harm is because of the high current flow. This device can also show the speed of the incoming alternator whether it runs fast or slow.
Working Principle of Synchroscope
The Synchroscope device works by indicating the phase variation between two AC voltage signals from two different generators. This device displays the phase variation between the two signals & specifies whenever the two generators are within phase, which means their voltage signals are within phase through each other. Once the two generators are within phase lock, the synchroscope displays a stable reading that means the two generators are in synchronous and can be connected securely to a similar electrical power system.
Synchroscope Construction & Its Working
The synchroscope construction is shown below which includes two poles, connected across any two red & yellow phases of the incoming machine. From these two phases, the armature windings are supplied within the switchboard bus bars. This armature has two parallel windings. In this device, the resistance can be connected within series through one half winding whereas inductance is connected with the remaining half winding in series.
Here the inductance is given to move the flow of current through itself with 90 degrees related to the current within the provided resistance. These currents are provided to the two armature windings. So they generate a rotating magnetic field in combination with the field within the pole.
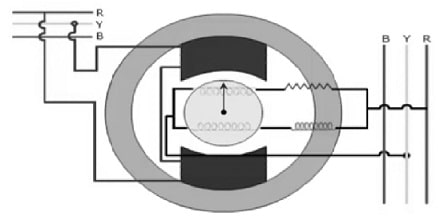
Synchroscope Construction
The pole’s polarity will exchange north-south based on changes in the yellow & red phases of the incoming machine. Here the rotary field responds with the poles & turns the rotor in a clockwise (or) anticlockwise direction. At the same time, the synchroscope pointer turns.
The synchroscope pointer’s direction of rotation can be determined by the frequency or speed of the incoming machine. Once the synchroscope pointer turns in the anticlockwise direction, then the incoming machine frequency is less. Similarly, if the synchroscope pointer turns in a clockwise direction, then the incoming machine frequency is higher.
Types of Synchroscope
There are two types of synchroscope; Electrodynamic type and moving iron type which are discussed below.
Electrodynamic Synchroscope
This type of Synchroscope is also called western Synchroscope which has an electrodynamic device & a three-limb transformer. In this type of synchroscope, the synchronization of static & dynamic techniques has been brought jointly to attain the right synchronization. In the dynamic technique, this type of Synchroscope is used while in the static technique, the system will require a lamp.
The central lamp in this device is responsible mainly for the lamb & the two external ones are accountable for the incoming machine & busbar voltages. The central limb gets the fluxes made through the external limbs. The received fluxes phasor sum turns into the next one within the central limb that results in the working of the lamp. In the central limb, the flux will make the lamp glow to its maximum range whenever the two voltages given by the external limb windings are within a similar phase. So this is precisely the opposite of whenever they are out of phase.
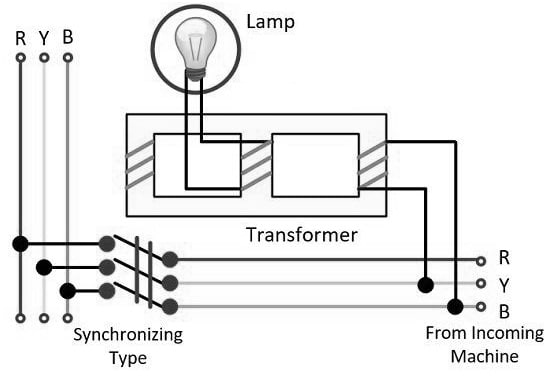
Electrodynamic Type
The dynamic part of this device has two significant parts that have been separated into a fixed coil. Here, the moving coil of this part has a pointer. The fixed coil is connected with a resistor that connects to the bus bar & there is an inductor coupled to it also. The terminal of the incoming machine is coupled to the moving coil through a capacitor. Once both voltages are within a similar phase, the two currents will be within quadrature to each other & no torque impacts the pointer & stays vertical. The pointer movement in this part indicates the incoming machine’s speed.
Moving Iron Synchroscope
The moving iron synchroscope is shown below which has two iron pieces located one above the other and separated through a brass piece over a common spindle. In this type of synchroscope, the fixed coil is coupled across the bus bar. Here, the two pressure coils are coupled across the incoming alternator terminals where one coil is coupled with a noninductive resistance ‘R’ in series. Similarly, another coil is connected with an inductive coil ‘L’ in series.
Once the incoming machine’s frequency is different from the bus bar frequency then the synchroscope device functions as a single-phase power factor meter & indicates the phase variation between the two EMFs.
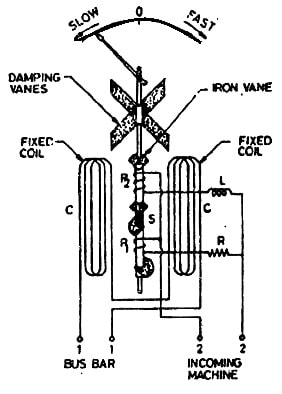
Moving Iron Type
Whenever the incoming machine’s frequency is not the same as the bus bar frequency then the spindle continuously turns at a speed within revolutions for every second equivalent to variation between the two system’s frequencies. The rotation direction mainly depends on whether the incoming machine working too slowly or too fast.
In this device, the displacement on the scale from the null position will induce the phase variation between the EMFs. Once the pointer at the center zero position is stationary then the paralleling switch must be closed.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of Synchroscope include the following.
- It is a very accurate device.
- This instrument verifies both systems’ operation to ensure they are functioning at a similar frequency.
- This device helps in measuring the frequency & phase angle variations between two AC systems. When these variations are zero, after that the two AC systems are connected as well as synchronized through each other.
The disadvantages of Synchroscope include the following.
- It is an expensive device.
- It does not show the phase sequence.
- Synchroscopes only work above a limited frequency range.
- When most synchroscope devices are connected to two systems’ single phase only, then they cannot guarantee that the phase sequence is right.
Applications
The applications of Synchroscope include the following.
- Synchroscope device is used in power plants.
- This instrument is used to indicate phase angle & frequency differences between two voltages.
- These can be utilized mainly for, disturbance recording, high speed protecive control & state measurement.
- It is used for measuring & indicating the phase angle & frequency difference between two preferred power systems.
- Synchroscope is used to confirm that the systems are synchronous or not while connecting a generator to paralleling multiple generators or the power grid. So this avoids disturbances & maintains constant power flow.
- This device is used for synchronizing two AC systems. So this synchronization is fundamental to ensure that the systems work at similar phase angles & frequencies.
- It performs like a conductor’s baton to coordinate the rhythm & two AC system’s timing.
How many pressure coils does the moving iron Synchroscope consist of?
The moving iron Synchroscope has two pressure coils.
What is a synchroscope and its types?
Synchroscope is an instrument used to display the relative frequency difference as well as the phase angle between the machine to be matched & the system voltage. These are available in two types analog and digital.
What is synchroscope describe the term synchronizing.
A synchroscope device In AC electrical power system indicates the amount to which two systems like power networks or generators are synchronized through each other. So this device was used for synchronizing a power plant of the factory by the power grid of a utility.
What does it mean if the synchroscope is turning in an anti-clockwise direction?
If the synchroscope pointer turns in an anti-clockwise direction, it indicates the frequency of the generator is lesser than the reference frequency.
Thus, this is an overview of the Synchroscope, its working, its types, and its applications. This is an electronic device used for synchronizing two AC systems. So this synchronization is essential to ensure that the systems work at similar phase angles & frequencies. Synchroscope is used to verify while a generator is connected to the power grid (or) paralleling several generators, whether these systems are synchronous or not. So this avoids disruptions & maintains constant power flow. Here is a question for you, what is an analog synchroscope?