
Types of Inductors
There are various types of inductors are available in the market based on its ratings and sizes and ratings. Their physical sizes differ from small sizes to the enormous transformer, based on the AC frequency being used and power being handled. An Inductor is one of the basic electrical components used in much wider application areas namely signal controlling, voltage stabilization, noise elimination, automobile operations, power electronic equipment, etc. At the present time, the designing improvement technique of an inductor enhances major performance on rest of the circuit.
Different Types of Inductors
An inductor is also termed as a coil, reactor, or choke, is a two-terminal electrical component used to build various electrical and electronic circuits. An inductor is used to store energy in the form of a magnetic field. It consists of a wire, generally twisted into a coil. When a current flows through it, energy will be stored temporarily in the coil. An extreme inductor is equivalent to a short circuit for DC and allows a reverse force to AC that depends on the frequency of the current.

Types of Inductors
A diverse electronic component used in an extensive range of applications needs various kinds of inductors. These are available in different sizes that include the wire wound and also multilayer inductors. Different sorts of inductors are power supply line inductors, high-frequency inductors, or power inductors, inductors for general circuits. Separation of the inductors is based on the kind of the core used as well as winding.
How Inductor Works?
An inductor is frequently referred to as AC resistor. It opposes the changes in the current and stores energy in the type of the magnetic field. These are very simple in assembly, comprising of the copper wire coils wounded on a core. This core might be air or magnetic. The applications of different types of inductors include in advanced applications like WPT (wireless power transfer).
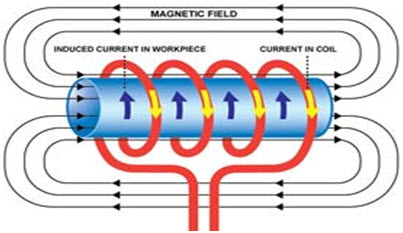
How Inductors work
Working of Inductor
Magnetic cores may be E-type or toroidal cores. Materials such as ceramic, powered iron, ferrite, are used for this core. The coil-carrying the electric current produces the magnetic field around the conductor. Additional magnetic lines are generated if the core is located inside the coil offered high permeability of the core is used.
The magnetic field stimulates EMF in the coil which results in a flow of current. According to Lenz’s law, the induced current resists the cause, which is the applied voltage.
Hence inductor opposes the variations in input current that guides to change in the magnetic field. This decrease of the current flow due to the induction is named inductive reactance. This will boost if the number of rolls in the coil is improved. It also stores the energy as magnetic field through charging and discharging processes and releases the energy while switching the circuit. Application areas of inductors include analog circuits, signal processing, etc.
Please refer to this link to know more about Electrical Inductors MCQs
Air Core Inductor
In air core inductor, the core is completely not present and gives high reluctance pathway for the magnetic flux, thus less inductance. These types of inductors have superior coils to generate higher flux densities. The applications of Air Core Inductor include in high-frequency applications such as TV and also radio receivers.

Air Core Inductor
Ferro Magnetic or Iron Core Inductors
Ferro Magnetic or Iron Core Inductors have high inductance property due to their higher magnetic permeability. These types of inductors are high power inductors but incomplete in higher frequency capacity due to the current losses namely eddy and hysteresis. The best example of these types of inductors is transformer designs.
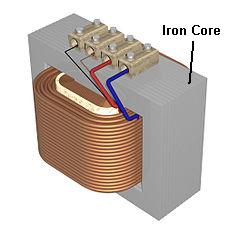
Iron Core Inductor
Ferrite Core Inductors
These are the different types of inductors which offer advantages of decreased cost and low core losses at high frequencies. Ferrite is a metal oxide ceramic based on a mixture of Ferric Oxide Fe2O3. Soft ferrites are used for the core construction to reduce the hysteresis losses.

Ferrite Core Inductor
Toroidal Core Inductors
In toroidal core inductors, a coil is wounded on a toroid circular former. Flux leakage is very low in this type of inductor. However special winding machines are required to design this type of inductor. Sometimes ferrite core is also used to decrease the losses in this design.

Toroidal Core Inductor
Bobbin based Inductors
In Bobbin based Inductors, the coil is wounded on the bobbin. Bobbin wound inductor designs vary widely in terms of power rating, voltage and current levels, operating frequency, etc. These are mostly used in switch mode power supplies and power conversion applications.

Bobbin Based Inductor
Multi-Layer Inductors
A multilayer inductor includes two conductive coil patterns which are set in two layers in the upper part of a multi-layered body. The coils of this inductor are connected electrically in a successive manner in series to two more conductive coil patterns inclined in the lower part of the multi-layered body. The application of multilayer inductors includes mobile communication systems and also noise suppression applications.
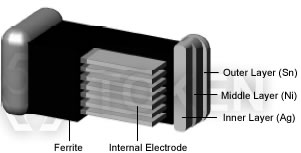
Multilayer Inductor
Thin Film Inductors
Thin film inductors are entirely different from the usual chip-type inductors which wound with copper wire. In this type of inductors, minute inductors are shaped using thin-film processing to make the chip inductor for high-frequency (ranges from about nano Henry) applications.

Thin Film Inductor
I hope this article has been useful and intriguing. So here is a basic question for you – What is the function of inductors in electrical circuits? Please give your answer in the comment section below. You also feel free to share your perceptions about this article and ideas.