Piston pump has versatile applications due to robustness and highly efficient. Hydraulic pumps, processing technology, drilling, etc. are a few of the applications which use piston pumps. It is configurable for any kind of liquid and having a linear performance curve. Piston pumps are used to move liquids or compressed gasses. It is categorized as one type of hydraulic pump with robust and efficient performance. This article discusses an overview of the piston pump and its working.
What is a Piston Pump?
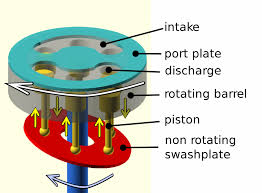
Definition: It can be defined as a machine that is used to displace liquids or compressed gases from one point to another. It is a positive displacement pump where a high-pressure seal reciprocates with the piston. These pumps are used where there is a requirement of high consistent pressure, like in water irrigation systems. Figure 1 shows the parts of the piston pump in detail. The principle of working is explained in the following section.
Piston Pump
Construction
As shown in the above figure, the piston pump consists of different parts. Each part is explained in brief
- Intake- This is part of the pump where the input is given. It may be liquid or high-pressure gas etc.
- Port Plate- This acts as the separating medium between the input port and output. The compressed gas or liquid is sent out through this medium.
- Discharge- This forms the output of the pump
- Rotating Barrel: This is a dynamic part of the pump, in which the pistons are inserted in their specific slots. When the barrel rotates, along with that the pistons rotate and displace the liquid or compressed gas.
- Piston- This forms the most important part of the pump. They are the interfacing medium between the nonrotating swash plate and the barrel. Pistons do have a spring-like system such that they reshape their size when the barrel revolves.
- Nonrotating Swash Plate- This is the interface for the external system and pistons. The pistons reshape themselves, get compressed when they come down under a force by the swashplate. The swashplate is a non-rotating part. It is fixed to the shaft.
- Shaft- The shaft is coupled to the rotating barrel and the swashplate. On the shaft, the complete assembly is housed.
Piston Pump Working Principle
The operating principle is explained in points below-
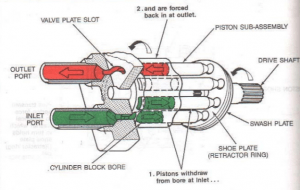
- The figure shown is for axial flow variable displacement piston
- The outlet port and inlet port are used intake and exhaust of the operating liquid or gas. These are placed in a casing made up of iron.
Piston Pump Working
The driveshaft is coupled to a swashplate and rotating barrel. The swashplate adjusts itself based on the position of barrel and pistons. As shown in the figure, we have two colors for the inlet and outlet port. When the barrel rotates, the piston which is placed upside, and pressed inside and similarly the piston which is place downsides, is pressed outside. There is an inclination in the position of the swashplate. The same position is reversed for the next cycle of operation such that the location of piston completely forms a cycle. This helps in gas or liquids to be displaced from one location to other i.e. from the input port to outlet port.
The pistons rotate along with the barrel in line with the position of the swashplate. The pistons are placed inside a cylindrical block. The movement of the pistons causes a difference in pressure, which causes suction of the inlet liquid or compressed gasses. The inclination in the vertical position of the swashplate is up to 10 to 15 degrees. Because of this reason, it is called, axial flow and variable displacement piston.
The motion of the piston is called reciprocating motion. The continuous motion i.e. suction and discharge by the pistons cause the displacement in the liquid or compressed gasses. When the angle decrease, we have less suction, and when the angle increase we have more. For that reason, it is called a variable displacement piston. The variable displacement depends on the swashplate angle.
Piston Pump Types
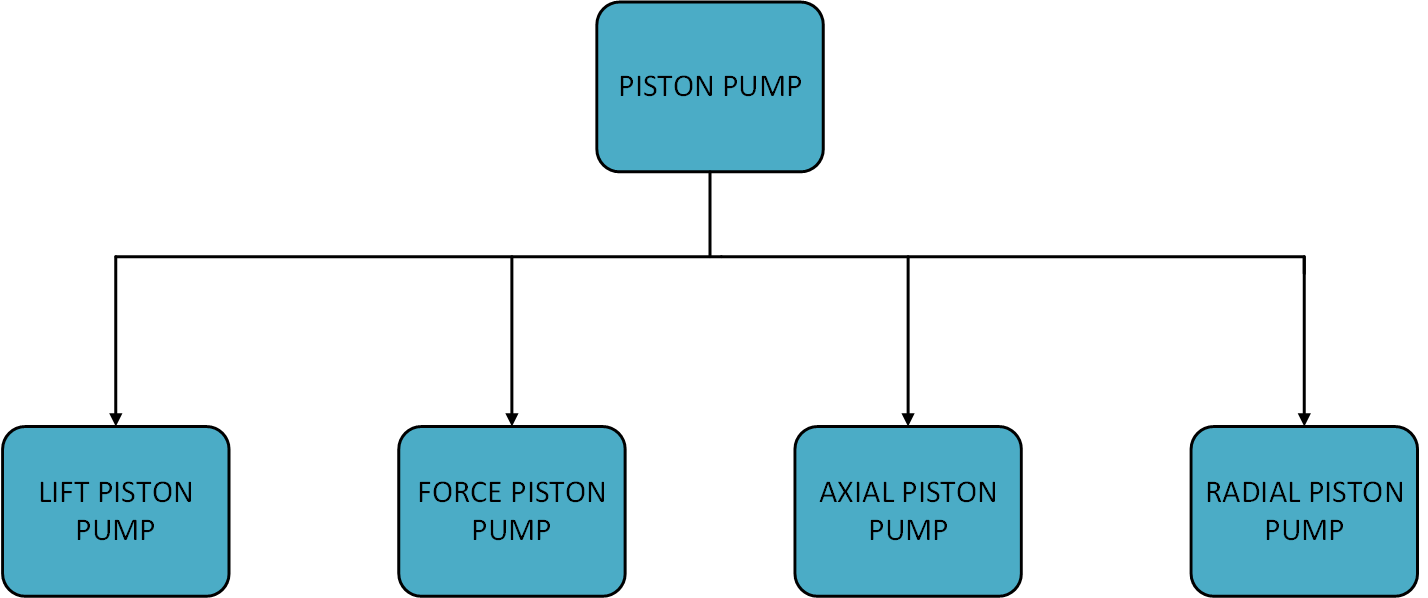
The different types of piston pumps are
Piston Pump Classification
- Lift Piston Pump- In this type of pump, the piston displaces the compressed gas or liquid with the help of a control device called a valve. The valve is placed just below the inlet port as shown in figure
- Force Piston Pump- The name force has been given based on the action piston. The piston can upstroke the fluid with force or opening of the valve, and similarly downstroke the liquid or compressed gases.
- Axial Piston Pump- The name axial has been given based direction of liquid or compressed gas to be exhausted. In this case, it is parallel to the axis of piston, hence the name axial has been given.
- Radial Piston Pump – In this piston pump, the flow of liquid is made radial, i.e. it flows outwards the piston.
Specifications
Like any other machine, this pump has its own specifications. Different parameters to be specified for a pump are operating temperature, head of the pump, rate of flow, power rating, current specification, horsepower, volume stroke, pressure, etc.
Piston Pump Applications
Due to its robustness, it has versatile applications. A few of them are mentioned as- High-pressure cleaning, water hydraulics, oil hydraulics, process technology, water injection, water cutting, drilling service, industrial, commercial, hydraulic pressure testing, etc.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of piston pumps are given as
- The working force in a piston pump can be controlled without moving the flow rate
- The performance of the pump is not affected by the rate of flow and pressure of the liquid or compressed gas
- In this pump, as compared to the vacuum pump, the range of pressure is wide.
The disadvantages of the piston pump are:
- Due to its assembly piston pump is heavy and bulky.
- They are capable of handling only lesser flower rates
- The flow is pulsating
FAQs
1. What does piston mean?
It is a disc or a cylindrical structure, which is placed inside a tube or metal cylinder. The piston can be moved up and down based on the movement of liquid or compressed gas
2. What is a hydraulic piston pump?
A hydraulic piston pump is the one where operating fuel is compressed gas. It has a number of applications due to its versatility.
3. What are the two types of piston pumps?
They are classified as axial flow and radial flow. One more category is lifted piston and force the piston
4. What is the most efficient hydraulic pump?
These are categorized as the most efficient hydraulic pumps.
5. Does a piston stop moving?
No, technically speaking for engine or for a pump under the running condition the piston never stops moving. It moves up and down based on the movement of liquid or compressed gas.
Hence we have seen the circuit diagram, operating principle, and classification of piston pumps. These are one classification of hydraulic pumps that are believed to be the most efficient ones. Due to its robustness and less maintenance, these are some of the most preferable hydraulic pumps. They have the advantages of axial and radial flow, a wide range of pressure. It has the easiness of control of flow as the control does not depend on head pressure and rate of flow. Here is a question for you, what could be the maximum inclination of swashplate from its axis?