We might often come across situations of facing damage to electronic devices. This happens because of multiple scenarios like atmospheric changes (lightning and thunders), voltage breakdowns, and utilization of heavy devices such as compressors. These all interruptions might enforce destruction to the electric equipment. And the one device which comes into a scenario to protect from this condition is Surge Protector which is also termed as a surge suppressor. The initial surge protector was established in the year 1950 by the General Electric company. Initially, selenium rectifiers are used in these kinds of devices and then with carbon piles. Now, we shall have a discussion on what is a surge protector, its operation, and its advantages.
What is a Surge Protector?
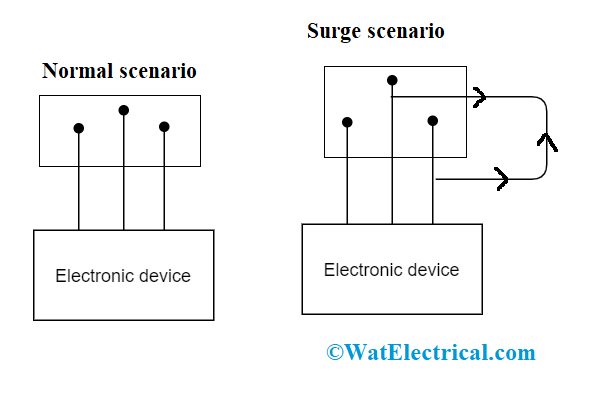
Definition: It is the device which protects computer and other kinds of electric devices form increased voltages or transient voltages. In general, for the office and household applications, the maximum amount of required power is 120 volts, when the voltage range exceeds this, it is termed as transient voltage. Voltage spike, which is the transient condition lasts for a maximum of 30 microseconds and reaches to the range of 1000 volts. These voltage spikes can cause destruction to wiring protections and other damages too.
So, a transient surge protection device handles to regulate voltage levels provided by the electronic devices either by obstructing or shorting the current path to the threshold level. The obstruction is performed through the usage of inductors that prevent a rapid change in the current levels. In a few cases, surge protectors can also use various devices to limit current levels.
basic-surge-protector-operation
How Does Surge Protector Work?
In general, a surge protection device is constructed of a senor, latch or unlatch circuit and a controller. A voltage sensor has the purpose of handling line voltage, the controller manages the level of sense voltage and determines when the signal voltage end for the latch or unlatch circuit. And the latch or unlatch circuit is a kind of regulated power switch that holds the ability of either connecting or disconnecting the line voltage. So, the construction of this surge protector seems to be some difficult and little expensive too.
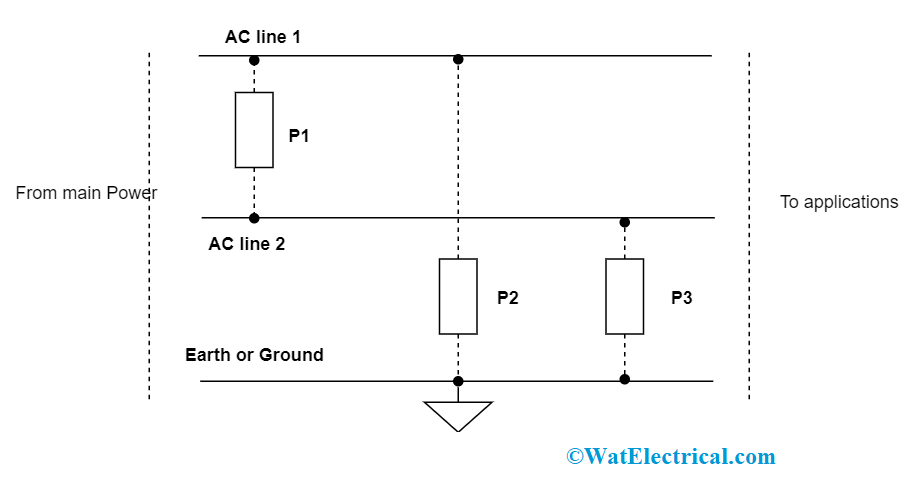
There exists another type of surge protector where it clamps the increased voltage levels rather than allowing power failure or voltage breakdown. This construction is mostly employed as internal surge protection like in SMPS. This kind of protection device can handle nearly 1000 volts. The below surge protector circuit diagram clearly explains the procedure:
circuit-diagram
The protector device (P1) which is across the AC Line 1 and 2 is termed as differential mode surge suppression. P2 and P3 are termed as common mode surge protectors. The purpose of P1 is to lock down voltage surge that occurs at AC lines 1 and 2, this is termed as disparity as it is implemented in between two hot wiring connections. Whereas, P2 and P3 are used to clamp voltage surge levels that occur in between hot wire and ground and this is termed as a common mode.
For normal transient level, P1 is used and for extreme transient voltage level, P2 and P3 are used.
Surge Protector Types
Depending on the installation and protection capabilities, surge protectors are mainly classified as three types:
- Service Entrance
- Whole-Home
- Receptacle
Service Entrance Devices
These protector devices have extended durability where this shield from the damaging surges that come from the power grid. Many of the houses and apartment blocks have these installed. The wiring of these surge protectors is somewhat complicated and this needs extensive experience in either connecting or disconnecting from the major feed. Also, the cost of installation of these devices is less. Service entrance protectors are also termed as Type 1 protectors.
Whole-Home Devices
In similar to the construction of Type 1, whole-home protectors have the same, but these can be installed by the user itself. The design and configuration of these devices hold the capability of either protecting a single circuit or many circuits in the entire house. Depending on the model, this type can safeguard both smaller and larger surge levels.
Receptacle Devices
Receptacle surge protector devices are the most implemented type when compared with others. The installation and implementation of this type is so streamlined so that many people go with this only. The crucial feature of this is its power strip, where this safeguards many circuits from the transient voltage levels and also it can be shared across multiple minimal power devices. This is also termed as Type 3 protector where it basically transfers additional power to earthing wire.
Other than these, the other types of surge protector devices are:
- Selenium voltage protector
- Quarter wave coaxial surge compressor
- Series mode of surge arrestors
- Lighting arrestor
Advantages & Disadvantages
The following are the crucial surge protector advantages & disadvantages:
Advantages
- The essential and crucial of this device is the protection of circuits from transient voltage levels
- Manage the voltage ranges and safeguards electric equipment from being damaged
- Circuit boards installed inside the device where the excessive power absorption happens here itself
- Easy installation
- Affordable pricing
- Maintenance, restoration, and additional costs are minimal
Disadvantages
- For a few construction models, the maintenance and installation is somewhat complicated
- They can protect the devices only to some extent (for specified range). The after the specified range, they might not withstand and this may cause damage to the circuit.
Applications
The surge protector applications are as below:
- Implemented in cellular networks and towers
- Solar and wind power services
- Employed in railway systems and in dams
- Hydroelectric power plants
- Telephone applications
- TV receiver systems and in speakers
FAQs
1). What does a surge protector do?
This is the device designed to safeguard from the voltage surges and eliminate circuit damage.
2). Does a surge protector protect against lightning?
A far distant lighting spikes can be protected through surge protectors, whereas direct lighting can’t be protected.
3). What makes a good surge protector?
A good and high voltage protector is the one which has nearly 6 to 700 joules of capacity then only it can trigger the additional voltage levels quickly.
4). Can surge protectors catch fire?
In some of the situations, these devices can catch fire especially when the circuit becomes over-heated.
5). Can a surge protector trip a breaker?
It can have two answers Yes and No. But mostly they won’t trip a breaker.
Know more about Oil Circuit Breaker MCQs.
This is the comprehensive information related to surge protectors. For both conventional and modern circuits, these devices are suitable to protect from transient voltages. Even the technological advancements are progressing, voltage breakdown is the most general scenario happening till today, So, in correspondence with this, surge compressors have a huge demand and being implemented in many industries. So, know the other concepts corresponding to these like how to choose the best surge protector device and how they can be installed?