An Electrical Generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. This machine is further classified into two other kinds based on the power supply i,e ac and dc. The basic difference name a generator as an ac or dc is its input power supply. If the supply to the machine is single directional then it is Dc and it is vice-versa if it is alternating. The internal operation differs with this input supply. Let us discuss in detail considering all the aspects that make this machine function. In AC, we use slip rings that are used for the production of alternating current. Initially, in either of the machines, the generated voltage or current is an alternating one. In this article, we shall discuss what is an AC Generator, construction, working, how EMF is induced, parts, and applications.
What is an AC Generator?
Definition: This is a machine that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy giving an output of alternating current or voltage. It works on the principle of faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. The direction of current in an Alternating Current generator is found by using fleming’s right-hand rule. A four-pole single-phase generator is shown in the figure below.
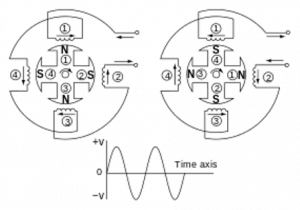
Generator with Four Poles
Construction
Parts
It consists of Yoke, permanent magnets, a coil or loop wound with wires, pole core, armature core, pole shoe, slip rings, and brushes. The Yoke is a frame that acts as a protecting cover for the generator. All the components rest inside the Yoke. Magnets are used for the production of the magnetic field inside the air gap. A coil made of four-wire AB, BC, CD, and DC is placed inside the magnetic field. The schematic diagram of this machine is shown in the figure below.
Parts of the machine
Pole core consists of pole shoe which is used to house the windings. The core of armature is used to rest the armature windings. The armature is responsible for the production of armature flux. The slip rings are used for the operation to be performed smoothly. These are attached to the brushes through the current passes. Slip rings run smoothly between the brushes which avoid the twisting of wires.
Working
It works on the principle of Faradays’s law of electromagnetic induction. Whenever a conductor cuts the lines of magnetic flux an EMF will be induced that causes the current to flow in the conductors. For a better understanding of the working of the Alternating Current Generator, consider a simple loop generator placed under the influence of a magnetic field. The loop placed inside the magnetic field is named as ABCD as this loop is an attachment of wire AB, BC, CD, and DC. This loop is rotated by using an external shaft which is generally a prime mover. The working of an Alternating Current Generator is shown in the figure below.
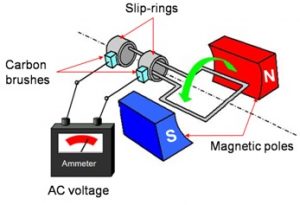
Alternating Current Generator
The lines of magnetic flux will be from left to right from Pole ‘N’ and ‘S’. When the loop is rotated it cuts the magnetic flux thus, developing an EMF. The developed EMF causes the current to flow in the conductors. This current direction is found by using fleming’s right-hand rule in generators.
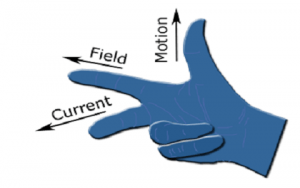
Fleming Right Hand Rule
Fleming’s right-hand rule states that the three fingers middle, fore-finger, and thumb are positioned perpendicular to each other. The representation of Fleming’s Right-hand rule is shown in the figure below.
Here, as the loop rotates, the current inside the wire AB is found by applying this rule. The current flows inside the wire AB for half cycle. As the loop rotates, the current inside the wire AB reverses for the other cycle. The same thing happens in the other wires too I,e in BC, CD, and DC. Therefore, the current direction changes for every half-cycle as the loop rotates. The working of the Alternating Current Generator considering two cases is shown in the figure below.
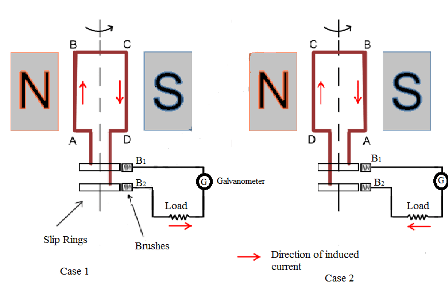
Working Alternating Current Generator
The loop end is connected to slip rings and is responsible for the movement of the wires as the loop rotates. The slip rings are connected to the brushes, the current passes from the slip ring to brushes and then to the load. These slip rings are used to slip smoothly because they are attached to the brushes in order that there is no twisting of the winding.
As the current changes for every half cycle in the loop. Therefore, at the load end, we can observe the current to be alternating by using a galvanometer. Thus, this is how the Alternating Current generator generates alternating current or voltage.
Types
There are two types of AC generators. They are
- Induction or asynchronous generators
- Synchronous generators
Induction Generators :
Also known as Asynchronous Generators, these are a type of Alternating current generators that operates on the same principle as that of a normal generator. The working principle is just similar to a transformer the difference is a transformer is a static device whereas the Induction generator is a rotating device. The speed of the Induction generator is less than the synchronous speed so, it is termed as an asynchronous generator. These are generally used in small machines like mixer grinders, and as large machines used in Industries. The Induction Generator is shown in the figure below.

Asynchronous Generator
Synchronous Generator :
This is also a type of Alternating Current Generator which rotates at synchronous speed. These are generally used in power plants because of its high efficiency. This generator also works on the principle of faradays’ law of electromagnetic induction. An Emf is induced due to the motion of the conductor inside the magnetic flux. The synchronous generator is shown in the figure below.
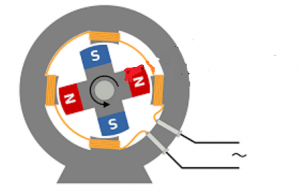
Synchronous Generator
Advantages of AC Generator
- The design is simple.
- Less maintenance.
- Losses are less
- Less size.
Applications
- These are used in power plants for generation and also during transmission, and distribution.
Thus, in this article, we had an overview of an Alternating Current Generator. It is a type of generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. It gives an output of alternating current or voltage. Apart from this, we had also studied construction, working, types, advantages, and applications. Here is a question for the readers, what is the difference between the AC and the DC generator?
Leave a Reply