A device that transforms the form of input electrical energy to an output mechanical energy. Basically, there are two types of electrical motors they are the DC and AC type. The DC type machines are normally used in small applications whereas the AC type has its importance in a wide range of applications. Because the AC machines have more advantages compared to that of DC machines. In this article, we shall discuss what is AC motor, construction, working principle, types, speed control, and applications.
AC Motor
The machine that turns the class of input electrical form to an output mechanical form. Here, in this type of machine, the input given to the field winding is alternating. Hence, the name AC motor. The supply given to the field winding classifies its type whether it is AC or DC type machine.
Construction of AC Motor
It consists of a Frame or Yoke, stator, rotor, bearings, fan, shaft, and slip rings. The parts of an AC machine is explained below.

Parts of Motor
The frame is used as an outer protecting cover that is used to protect against environmental conditions. The frame also acts as an outer periphery such that the inner parts can be easily housed. The stable state section of the equipment is stator on which the stator winding is enclosed. The cross-sectional view of the AC machine is depicted below.

Cross-Sectional View
The rotor is the moving part that either move in clockwise or anti-clockwise depending upon thrust impelled on it. The bearings provide proper friction for the rotor to run smoothly. A fan is employed to remove the unwanted heat that gained during the running of the rotor. It is expelled out through the ventilation that is provided behind the machine. A shaft is provided to deliver the mechanical output as the rotor rotates. The slips rings are employed for a normal Ac machine where rotating armature stationary field winding is employed. In this situation, the slip rings allow the input alternating current to change continuously in the coils.
Working Principle of AC Motor
It works on the principle of Lorentz force equation I,e whenever a current-carrying conductor is placed in the magnetic field it exhibits some force in it. The working of a normal AC machine with the rotating armature and stationary field winding is shown in the figure below.
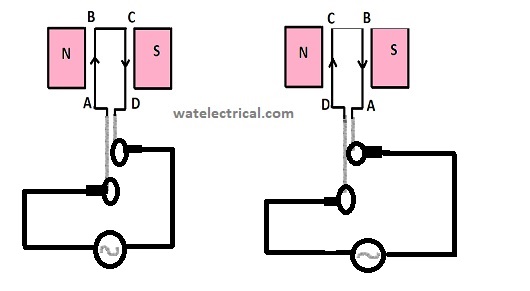
AC Machine Working Diagram
When alternating current supply is fed to the coil of the rotor, it experiences some force due to the law of the Lorentz force equation. Due to this force, torque will be developed in the clockwise direction that enables the rotor to rotate.
A normal AC machine has its field winding on the stator and armature winding rotor. But due to this the size of the motor increases and also due to commutator and brushes, the efficiency of the machine decreases. So, to avoid these problems, the proper arrangement is made for the housing of stator and rotor windings on the armature. This placement has great advantages compared to the rotating armature type. Almost all the industrial machines used are of stationary armature type. Let us discuss in detail these machines by studying the different types of motors.
Types
There are several varieties of AC machines based on the speed they are classified as a synchronous and asynchronous motor. The asynchronous motor is also known as an induction motor. It is a machine that runs at a constant speed I,e synchronous speed. But an asynchronous motor runs at a speed less than that of synchronous speed. The induction motor is further classified into single-phase, and three-phase induction motors.
The classification of the alternating type of motors is illustrated below.
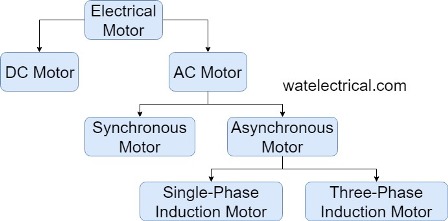
Classification of Motor
Working of Synchronous Motor
The stator winding is given a three-phase power supply such that a rotating magnetic field (RMF) is developed. This RMFrotates in the air gap and tries to interact with the field winding. The field winding is given a DC supply in the synchronous machine. The field winding develops a stationary magnetic field. The rotating magnetic field and the stationary magnetic field interact with each other. Due to the inertia of the rotor, the rotor is unable to achieve unidirectional torque. So, the synchronous motor is not a self-starting machine. To avoid this, an initial rotation is provided. When an initial rotation is given, the stator and rotor poles get interlocked with each other. Further, the machine develops unidirectional torque that allows the rotor to rotate continuously.
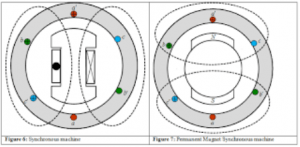
Synchronous Machine
Working of a Single-phase Induction Machine
When a three-phase power supply is given to the stator winding of the machine, RMF will be developed. The RMF interacts with the short-circuited rotor conductors. Due to this, an emf is induced in the rotor bars according to the principle of mutual induction just like a transformer. But the rotor cannot develop the unidirectional torque because the main winding produces a two-directional torque. The flux produced by the main winding develops two fluxes which oppose each other. To produce a unidirectional torque, an auxiliary winding with a capacitor is arranged at a phase displacement of 90 degrees with the main winding. Due to this arrangement, the opposition force is canceled out and an additional force greater the existing force is developed. This makes possible for the rotor to develop unidirectional torque and the rotor runs smoothly. The working of a single-phase induction machine is displayed below.
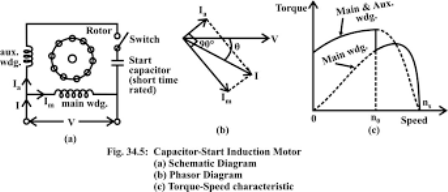
Single Phase Induction Motor
Working of a Three-Phase Induction Machine
The performance of this motor is alike to a single-phase machine. But, the construction is quite different the stator winding is displaced at an angle of 120 degrees and a balanced current is allowed to flow in the windings. This makes possible for the windings to develop a rotating magnetic field. This Rmf due to the three-phase develops a unidirectional torque. Hence, it can act as a self-starting machine.
Three Phase Induction Machine Working
Waveform
Applications
- It is used in mixer grinders, pumps, and household appliances.
- Used in industries.
Consequently, we had a summary of what is AC motor. It is a machine that changes the form of alternating electrical energy input to an output of mechanical energy. We also analyzed its construction, working, types, speed control, and uses. Here is a question for the readers, How the speed of an AC motor can be controlled?
Leave a Reply