The first compact commercial circuit breaker was launched by Stotz in 1923 which combines both the thermal & magnetic protection functions. After that, his team developed a circuit breaker device to replace a fuse. This device has a component, once it is heated it will enable a disconnecting device and once it is cooled, then it is turned on again. There are many companies that have been developing circuit breakers continually which range from single-pole CBs to the four-pole CB. These are available in many types and sizes which are used from residential to big industries applications. This article discusses an overview of a circuit breaker, its working, and its applications.
What is Circuit Breaker?
A circuit breaker definition is; an automatic switching device that is used to switch, break & carry current in standard conditions & in some particular time period. This electrical device is mainly designed for protecting different electrical circuits from short circuits or overload damage. The main function of the circuit breaker is to notice a fault & interrupt the flow of current throughout the CB operation. The circuit breaker diagram is shown below.

Circuit Breaker
Working Principle of Circuit Breaker
Circuit breaker (CB) includes two significant components fixed & moving contacts where these contacts touch each other & carry the current in standard conditions once the circuit is closed. Once the CB is closed, then the contacts like electrodes connect each other in the force of a spring.
The CB arms can be closed or opened in the normal operating condition to switch & maintain the system. The circuit breaker is opened only when pressure is applied to a trigger. Once any fault arises on any element of the system, then the circuit breaker’s trip coil will get energized & the moving contacts move away from each other through some mechanism, so the circuit gets opened.
Circuit Breaker Circuit
The circuit breaker in the following circuit is used to develop an automatic ON or OFF system that defends the power system once a short circuit or overload occurs. In the following circuit, there are many parts along with a CB like a bus bar, current transformer, relay coil, trip circuit, and no contact of the relay coil. The circuit breaker in this system is connected between the load and the Bus-bar.
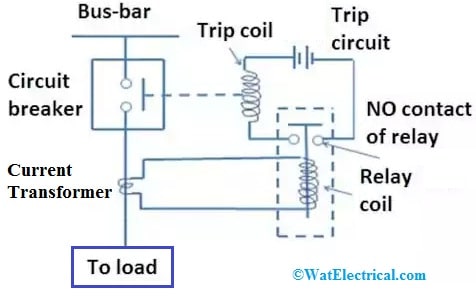
Circuit Breaker Circuit
In the above system, the current transformer provides an extreme electrical signal to the relay. Whenever an extreme current flow occurs within the circuit, the relay gets a signal from the current transformer & becomes active. Once the relay gets active then it closes the trip circuit. So a battery in the trip circuit is connected & for the circuit being closed the current starts flowing.
Thus, the trip coil will become magnetized & the contact which is moving within the circuit breaker will detach from the power line. So the whole circuit can be detached from the power system. The circuit breaker protects the whole power system in this manner.
Classification of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers are classified into two types AC circuit breakers and DC circuit breakers.
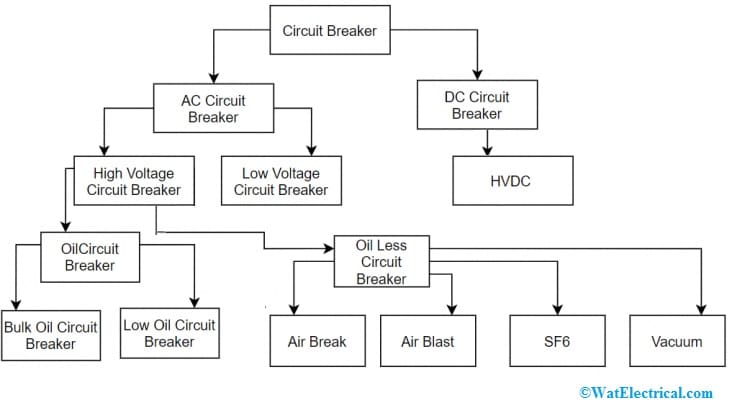
Classification of Circuit Breaker
AC Circuit Breaker
AC circuit breakers are more common as compared to DC circuit breakers. These CBs will not have a steady rate of voltage and they have the ability to move from side to side. Once extreme current is noticed, the circuit will be disconnected from the main power source for protecting the wiring system from overheating. AC circuit breakers are used in residential units.
AC CBs are available in two types the low voltage & the high voltage CB. A low CB is defined as a CB which has a voltage value below 1000V whereas a voltage value above 1000V then it is called a high voltage CB. Further, high-voltage circuit breakers are available in two main types the oil circuit breaker & the oil-less circuit breaker.

AC Circuit Breaker
Oil Circuit Breaker
The circuit breaker which works by using oil for arc extinction is called an oil circuit breaker. Further, this circuit breaker is sub-categorized into two types bulk oil & low oil type CB.

Oil CB
Bulk Oil Circuit Breaker
This type of CB utilizes transformer oil like an arc extinction medium. The oil in this circuit breaker also works like an insulator in between the CBs’ two conducting parts. This CB rating ranges from 25MVA @ 2.5KV – 5000 MVA @ 230KV.
Low Oil Circuit Breaker
In this type of CB, the oil is used through blast action for arc extinction. Here the major oil function in this circuit breaker is to disrupt the formation of an arc & it is not utilized for protecting the live elements of the earth.
Oil Less Circuit Breaker
An oilless circuit breaker is again classified into four types air brake, air blast, Sulphur hexafluoride & vacuum circuit breaker.
Air Break Circuit Breaker
The arc within this circuit breaker is initiated & destroyed in the static air where the arc moves. The breaking capability of this circuit breaker is around 500 MVA, so used in the low voltage range of up to 15KV. These types of CBs are classified into three types based on the air breaking methods like plain air break, arc chute, and magnetic blowout type.
The contacts in the plain air circuit breaker are made in horn shapes. In the arc-chute type, low & medium voltage-based circuits are utilized for the interruption of the arc whereas, in the magnetic blow type, the magnetic field is used as an arc interruption medium.

Air Break CB
Air Blast Circuit Breaker
This type of CB utilizes an air blast to blow out the arc. The compressed air in this circuit breaker is stored in the tank form & discharges throughout the nozzles to generate a high-velocity jet to extinguish the arc. This CB has been used for low voltage up to 15 kV & breaking capacities of 2500 MVA. These are also utilized in outdoor switchyards mainly for 220kV lines. These CBs are classified into two types axial blast and cross blast CB. The air within the axial circuit breaker flows longitudinally within the arc direction whereas in the cross-blast type, the flow of air will be at the right arc angle.

Air Blast CB
SF6 Circuit Breaker
The SF6 circuit breaker is also known as the sulfur hexafluoride circuit breaker. This type of circuit breaker utilizes SF6 gas to extinguish the arc. Here this gas has huge arc extinguishing properties & as compared to other arc quenching media like air or oil, it is also better.

SF6 Circuit Breaker
Vacuum Circuit Breaker
The contacts within this circuit breaker are connected to the vacuum interrupter which is sealed permanently. Once the contacts are divided within the high vacuum then the arc can be extinguished. These types of CBs are cheaper, have a long life, available in less bulky, and need less maintenance.

Vacuum CB
DC Circuit Breaker
The circuit breakers which are used within DC power distribution systems to protect from potential hazards & over current are known as DC circuit breakers. These types of circuit breakers perform different functions like interrupts the current flow once it goes beyond a predefined threshold, protecting different electrical components, avoiding electrical fires, etc. These circuit breakers are used in solar PV power generation, storage systems of battery energy, power distribution systems, DC charging systems of vehicles, and many more.

DC Circuit Breaker
HVDC Circuit Breaker
The HVDC circuit breaker is a type of DC circuit breaker that is used for high-voltage direct current interruption. This circuit breaker has nearly 33KV of voltage breaking capacity & 2KA of current. This CB uses either air blast or oil as a quenching medium. The main drawback of this circuit breaker is that the direct current is unidirectional, so in the DC system, there is no zero point. In this circuit breaker, the fault current must be decreased to zero with some external techniques.

HVDC CB
Difference between Overcurrent, Overload, and Short Circuits
The difference between overcurrent, overload & short circuits are discussed below.
|
Overcurrent |
Overload |
Short Circuit |
| It is the condition wherever extreme current supplies within the circuit because of overload & particularly short circuits. | An overload is a condition wherever the load uses current as compared to the rated or normal current. | It is an electrical circuit used to allow a flow of current to supply along an unintended lane. |
| An overcurrent is caused by the circuit overloading or a short circuit, an arc fault/ground fault. | Overload occurs when various heavily rated appliances are utilized together. | A short circuit occurs because the flow of current within the circuit suddenly increases & also overloads, |
| Over-current can cause extreme heat generation, equipment damage, and fire risk. | An overload can cause the overheat of the circuit wiring, which could dissolve the insulation of wire & lead to a blaze. | Short circuits can cause damage to the circuit, and these are responsible to cause electrical burns, electrocution & fires. |
| Overcurrent can be reduced by using circuit breakers, electrical fuses, etc. | Overload can be reduced by increasing the power supply from the generation side. | Short-circuit can be reduced by increasing the inductive reactance observed at the fault location. |
How to Select a Circuit Breaker?
The circuit breaker selection can be done based on the different factors which are discussed below.
- The circuit’s current rating & voltage level.
- The type of faults in the circuit.
- The ecological conditions.
- The circuit breakers installation location.
- The service life as well as maintenance requirements of CB.
- The cost & its availability.
Some guidelines to select a circuit breaker include the following.
- SF6 or oil circuit breakers are chosen for high voltage (> 72.5 kV) based applications because they have high insulation strength & breaking capacity.
- SF6 or vacuum CBs are chosen for medium voltage (1 kV – 72.5 kV) based applications because they have low noise levels, high reliability, durability & low arc energy.
- Miniature or air CBs are selected for low voltage (< 1 kV) based applications because they have high-speed operation, their maintenance & installation cost is less.
- SF6 or oil circuit breakers are selected for outdoor-based applications because they are resistant to pollution & corrosion.
- Air or vacuum CBs are selected for indoor-based applications because they are very secure to operate and very compact.
- Vacuum or air circuit breakers are selected for frequent switching-based operations because they have low wear & tear of contacts.
- SF6 or vacuum CBs are selected for the protection of the generator because they handle asymmetrical faults & also high transient currents.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of circuit breakers include the following.
- It can be used without replacement for many times.
- It is operated automatically/manually for switching.
- It gives careful protection & separation of various power system parts.
- It interrupts high fault currents without producing dangerous flames or gases.
- It decreases the fire hazard risks as well as power outages caused by different faults.
- These CBss replace fuses.
- These are extremely reliable.
- These devices are more functional.
- It gives protection to the circuit from damage caused by extreme currents.
- The CB can be reset when it operates through a switch.
- It is very easy to reset.
The disadvantages of circuit breakers include the following.
- Circuit breakers are very expensive.
- These are complex as compared to fuses.
- They need normal maintenance.
- It needs to be tested to make sure the correct functioning
- It doesn’t work when electrical or mechanical faults occur.
- These circuit breakers may cause voltage surges in switching operations.
- Its installation & repair is costly.
- Circuit breaker reacts slowly as compared to fuses.
Applications
The applications of circuit breakers include the following.
- Circuit breaker protects generators from overloads, short circuits, reverse flow of power, etc.
- They protect different kinds of transmission lines from lightning strikes, faults, switching surges, and many more.
- They protect feeders, distribution transformers, and induction motors from overloads, faults, under-voltage, etc.
- Circuit breakers protect industrial equipment like compressors, pumps, and many more from an imbalance of phase, overloads, faults, etc.
- These are very useful in protecting commercial buildings from power surges, faults, overloads, etc.
- They protect rail vehicles from short circuits, overloads, faults, etc.
- A circuit breaker protects the circuit from overload, short circuit, or overcurrent.
- It interrupts the flow of current after protective relays notice a fault.
Thus, this is an overview of circuit breakers, their working, their classification, and their applications. In any electrical system, a circuit breaker is a very significant device that operates either manually or automatically. These devices are used to defend an electrical circuit from any injury occurred by short circuits or overload. Here is a question for you, what is MCB?