In 1860, the lighting equipment, as well as telegraphs, are protected using an electrical wire which is named as an electrical fuse. The first fuse was discovered by a scientist namely “Thomas Edison”. In an electric distribution system, the fuse is one kind of part. It is a safeguard device and it is used where a low melting thin material point is used. It works as a protective device when an extra current beyond its allowable value is flown. The operation of fuse dependent on inverse-time characteristics, larger the current more instantly the fuse will blow off.
What is an Electrical Fuse?
An Electrical fuse is a protective device that uses a thin material inside it, which melts in the case of power failure. Thus, it protects the equipment from a huge current.
Material Requirements for an Electrical Fuse
- The selected material should have a low melting point, low Ohmic losses, and high conductivity and free from deterioration.
Electrical Fuse
- The thin material used is of an alloy of Lead and Tin (Lead 37% and Tin 63%) used for small rating fuses.
- For the above 10A rating fuses, copper wires are used.
Selection of an Electrical Fuse
The selection of fuse plays an important role in power systems. Depending upon the rated voltage, maximum current rupturing capacity and rated current suitable fuse is selected. The placement of fuse should also be considered for reliably protecting any section or element of an electrical circuit.
Construction of an Electrical Fuse
The fuse is made of a thin material that has a low melting point. The body of the fuse is made of ceramic material. A live wire is connected through the element of fuse for the continuous power supply. In the failure cases, the element of the fuse will melt leading to the break of power supply.
Working of an Electrical Fuse
- During normal operating conditions, the thin material’s temperature is less than the melting point. Thus, a normal current is carried out.
- When under fault conditions, the element of the fuse is subjected to a temperature above its melting point where it gets heated up.
- The thin material heated will melt such that the power supply is interrupted.
Classification of Fuses
Fuses classified mainly into two types. They are
- AC fuses and DC fuses.
The classification of fuses is explained by a flow chart which is shown below.
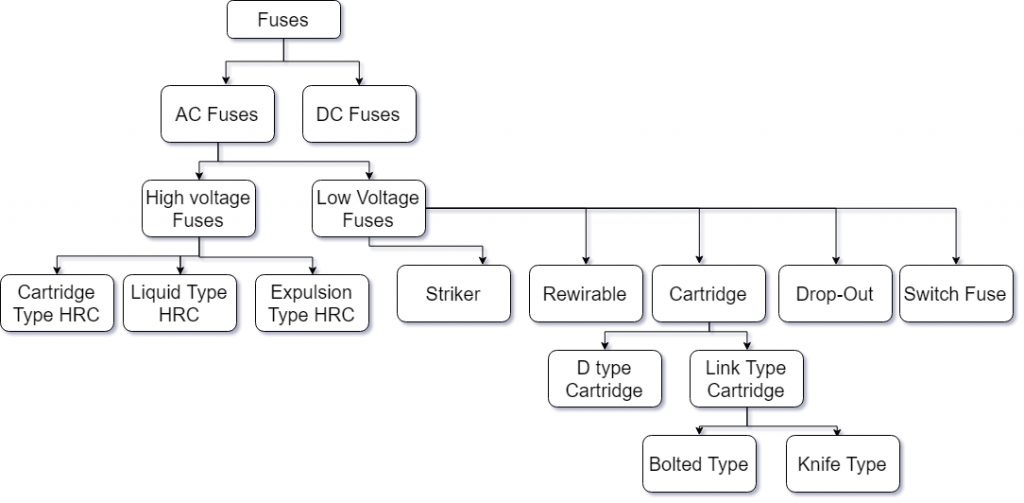
Classification_of_fuses.
DC fuses
DC fuses are of large size and require more maintenance. They operate for a constant voltage and due to this there will be arcing inside the DC fuses. This drawback will be overcome by the introduction of AC fuses.
AC fuses
AC fuses are of small size and require less maintenance compared to DC fuses. They operate by the alternating voltage with a varying frequency of 50 cycles per second. AC and DC fuses are further classified into HV and LV fuses.
HV fuses
HV fuses are Cartridge type, Liquid type, and Expulsion type.
Cartridge Type HRC Fuse
HRC means High rupturing capacity fuse. At the time of the fault, it disconnects the circuit very fast.
Construction of HRC Type Fuse
- It has a heat restraining ceramic body consisting of metal end caps. It has an airtight vacuum cartridge under which the element of a fuse is present.
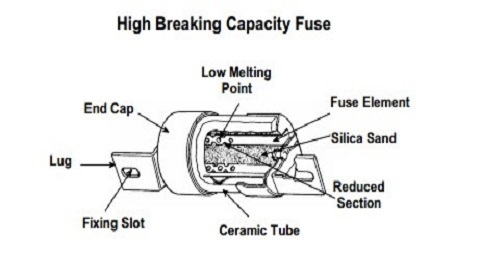
HRC Type Fuse
- The fuse element is surrounded by the filling powder I,e quartz powder.
- Fuse is made of silver connected to the end caps.
Working of HRC Type Fuse
- During normal operating conditions, the thin material’s temperature is less than the melting point. Thus, a normal current is carried out.
- When under fault conditions, the fuse element is subjected to a temperature above its melting point where it gets heated up. The quartz powder does not allow to increase temperature or when an arc is generated it immediately distinguishes the arc.
- HRC Fuse can withstand the heat generated by arc for a longer duration. Hence, it is called a High rupturing capacity Fuse.
Advantages of HRC Type Fuse
- Is has a High-speed response.
- It is Reliable, cheaper and it requires no maintenance.
Disadvantages of HRC Type Fuse
- Thin material needs to be replaced manually every time after each operation.
LV fuses are of Rewirable, Striker, switch, drop-out, and cartridge type.
Rewirable Fuse
The other name for rewirable fuse is Kit-kat fuse. It consists of two parts namely one is a base and the other is a fuse carries made of porcelain. The base is fixed and is connected to the line. The fuse carrier consists of a fuse element which is of a thin material that gets heated and melts when abnormal current flows through it. These are operated up to 500A for small loads. The rewirable fuse diagrammatical representation is shown below.

rewirable_fuse
Switch Fuse
Switch fuse is used for small and medium level voltage purposes. It acts as a switching device for the domestic householders whenever a fault has occurred. It trips the circuit and protects the equipment from damage.

Switch Fuse
Striker Fuse
In striker fuse, the striker is a pin which is used as an external tripping circuit. This pin is extended out from the fuse base which acts as an external indicator.
Drop-out fuse
Drop-out fuse normally called DO fuse. These are used for the protection of the transmission lines and are operated at 11KV,22KV, and 33KV voltages and up to 1200 A ratings. The drop-out fuse diagram is illustrated below.

Drop out fuse
LV Cartridge Type
The other name for the Cartridge type is the totally enclosed type. LV cartridge type is further classified as D type, and Link Type.
D-type
In D-type, the fuse element will be inside the cartridge surrounded by two metal end caps. D type cartridge fuse is illustrated below.

Cartridge D Type
Link-type
Link-type fuse is classified as a blade and bolted types
Blade and Bolted Type
Blade and bolted type are also considered as plug-in type fuses. These fuses consist of a plastic body from which two metal blades will be used as contacts for the operation. Blade type fuse image is displayed below.

blade_type
The most commonly used blade type fuse is the knife blade type fuse.
Knife blade Type Fuse
- Knife type fuse is a type of cartridge fuse where it has two blades at both ends making contact with the fuse.
- Knife type is used at a place where the amount of fault current is more. Such huge currents cannot be controlled by normal fuses. So, there is a need for developing a high rating fuse which sufficiently controls the huge current. For this reason, knife type fuse is developed where it can able to distinguish arc produced by huge fault currents.
- Knife type fuses are used in substations where it can control a large amount of current.
- Knife type fuse can be operated up to 400A.
Construction of a Knife-blade Type Fuse
- Knife type fuse consists of two blades that are placed in a hinged jaw. The two blades are inserted into the contacts with live wire to pass an electric current.
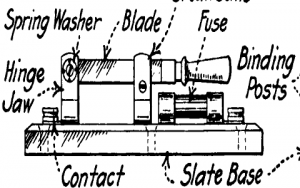
Knife-Type-Fuse
Working of Knife Type Fuse
- During normal operating conditions, the thin material’s temperature is less than the melting point. Thus, a normal current is carried out.
- When under fault conditions, the fuse is subjected to a temperature above its melting point where it gets heated up. The working of Knife type fuse is shown in the figure.

Working-of-Knife-type-Fuse
- There are different rows of holes are present inside a knife type fuse, the centered holes are the smallest ones.
- When the temperature exceeds the limit, knife type blade melts over these points. When that happens usually an arc is generated across the holes. But the arc will also generate even more heat. So, it operates the next set of holes on both sides. If still there is an arc it goes to the third set until the fault current is eliminated.
BS Type Fuse
- There are different standards to be followed before constructing any fuse. Similarly, Bs type is also a standard fuse where BS is the standardization similar to IEC (International electro-technical commission).
- The difference between IEC and BS is, IEC published by international electro-technical commission whereas BS published by British standards.
- In countries like England, most of the industries use BS standard fuses like BS88. The basic BS type standard 13A fuse is shown in the figure.

BS-Type-Fuse
- The British standards e.g BS1361 cover both service fuses and J-type fuses.
- BS type fuses are developed for easy and safe operation and they can be operated up to 100A.
Advantages of Fuses
- Fuse provides the cheapest means of protection.
- Fuse requires no maintenance.
- It limits current without noise, flame, gas or smoke.
- It requires less time to operate.
- It is smaller in size.
Disadvantages of Fuses
- Manual operation is required for re-wiring or replacing thin material.
- It consumes time for replacing thin material.
- Current-Time characteristics might vary.
Please refer to this link to know more about Electrical Distribution System MCQs, Electric Illumination MCQs, Transmission Line MCQs, Protective Relay MCQs.
Thus, this article gives a brief information about what is a fuse, material required for fuse, selection of fuse, its operation, working and types of fuses. Here is a question for you, what is the application of knife type fuse?