Fuse is the most widely used terminology in the field of electronics and electrical engineering. This is the type of protective device which functions to safeguard electric circuits from high and over current ranges. These days, there exist numerous fuse designs where each type has its own features and characteristics based on the usage of the application. The history of fuse was initiated with the concept that Breguet suggested the implementation of decreased section type of conductors to safeguard electric circuit and devices from strikes. There are multiple kinds of foil fusible components that are utilized for the protection of cable during the period of 1864. Thomas Edison in the year 1890 got the patent rights for a fuse at a part of the electric distribution network. So, the one prominent type of fuse is the HRC fuse. This article now explains this concept in a more detailed way.
What is HRC Fuse?
HRC is abbreviated as High Rupturing Capacity Fuse where it is included with a fuse wire inside it. This device holds the S.C current carefully for a corresponding period of time. At this time, when the fault is detached, it will not be blown off whereas when it is not removed, it melts the circuit and removes it from the power supply. And because of this, the circuit remains to be at safe condition.
The generally used material for the construction of HRC fuse is glass, whereas other materials are also used. These can also be constructed and designed using various chemical mixtures and this depends of multiple factors. The outer compartment is completely airtight where it eliminated atmosphere interaction with the fuse components. The HRC fuse diagram is shown below:

HRC Fuse
Construction
The construction of HRC fuse is done using a high heat-resistant component such as ceramic where metal finished are caps are attached to this body. Through silver-current, the ceramic body and metal caps are connected.
The inner section of the fuse is filled with a powder material which is made up of materials like chalk, plaster of Paris, marble, quartz, and many others. The noise creates a substance that does not get overheated within the range of current. The generated heat will fade away the dissolved substance. The chemical reaction which happens between the silver vapor and filled powder will produce a high-end resistance substance where helps in reducing the arc present in the fuse.
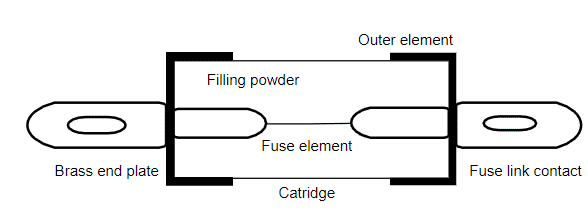
HRC Fuse Construction
Either silver or copper is generally utilized in fuses because of their minimal resistance. The HRC fuse generally consists of either two or more compartments that are connected using a tin substance. The melting point of a tin substance is nearly 24000C which is at a lesser extent when compared with the melting point of silver which is 9800C. So, the melting point of tin protects the fuse from short circuits and overcurrents.
Working Principle of HRC Fuse
The working of HRC fuse can be explained as below:
In general circumstances, there will be no required amount of heat generation for its dissolution. When there is more current passage ahead of the specified limit, then the fault current causes the melting of the fuse substance before it gets close to the edge. When the device is in an overload condition, the fuse will not be melted whereas in this condition it persists for a longer time period then a substance like eutectic will meltdown and breaks the fuse.
The thinner sections of the device will melt quickly in a minimal space when the fuse is present in short circuit conditions. This breaks down the eutectic substance. So, the HRC fuse holds a specific reason to offer certain constraints internal to the fuse element.
This is the basic working of the HRC fuse.
Different Types
There are mainly three types of HRC fuses which are
- NH fuse
- Din
- Blade contact
NH Fuse
This type of fuse offers both short circuit and overload protection even for a medium and minimal range of voltages. They even provide backup safety for starters which are present in motors and other devices opposing the devices to move into overload and short-circuiting conditions. These are minimal in size, weight and have small dimensions also.
Din Fuse
These are available in various current levels which are mostly utilized for multiple purposes having their performance at various temperature levels. These fuses are also present in numerous voltages which can be even employed for transformer safety also for no Low-Voltage conditions which mean backup protection. These din fuses have better clearing ability of perfect lesser over current having short-circuit behavior. The other applications of these are in gas-covered switchgear, air, transformers, air, and feeder sectionalizing.
Blade Type of HRC Fuse
These are also called plug-in or spade fuses which are available in plastic material and two metallic caps to fit into the socket. These fuses are employed in automobile devices used for S.C and wiring safety. These are also less in size, weight and have minimal cut-off current. Also available in various sizes and designs having various rating capacities those are printed on the top position.
Characteristics
A few of the characteristics of HRC fuse are as below:
Braking Ability
This is the property where the maximum range of current can safely be disrupted by the fuse. This has to be more than the potential range of SC current. Small fuses might have more disruption ratings when compared with the current rating. Fuses those are with minimal and fewer voltages are generally used for residential purposes and those have normal rating levels. Fuses that are utilized for commercial or industrial applications have more interruption ratings having some minimal voltage-current restricting increased interrupting fuses those are rated for 3,00, 000 amperes.
While fuse with increased voltage components which are with the range of 1,15,000 volts has a rating of entire apparent power that means in the range of megavolt amperes of the error level on the circuit. Few kinds of fuses are named like high rupture capacities, high breaking capacities, and those are usually filled with the same kind of material or with sand.
I2t Rating
It is the property that is correlated with the amount of energy that is allowed by the fuse when it is free up of electrical damage. This scenario is usually observed in S.C cases and the values get added to operate co-ordination investigations in electrical systems. The specifications of I2t are given themselves in the manufacturer charts and they will be different for every fuse family. For the synchronization of fuse functionality either with upstream or downstream devices, both clearing and melting I2t will be specified.
The melting value of I2t has a direct proportion to the total amount of energy that is necessary to initiate the fuse element melting. Whereas, clearing i2t has a direct proportion to the entire amount of energy that allows the fuse at the time of fault clearance. The energy is mainly based on the time and current for fuses along with the existing system voltage and fault ranges.
Current and Time Qualities
The rate of speed where the fuse blows is based on what amount of current will be flowed through the device and manufacturing material of the fuse. The device manufacturers will provide the graph of time vs current which is probably represented on a logarithmic scale which signifies the device, and this permits relation with the feature of defensive equipment both downstream and upstream directions of the fuse.
The functional time is not constant but diminishes when the current value is increased. The device is manufactured to have specific features of functional time when related to the current. A general kind of fuse might need to double its rated value of current to open in just one second. The selection of fuse is based on the load characteristics.
How to Interpret the Fuse Characteristics
As per the below depicted fuse characteristics figure, it was shown three fuses with the ratings of 60 Amps, 100 Amps, and 200 Amps. Let us consider a 60 Amps fuse for easy understanding. It is observed that when the amount of current flow through the fuse device is 350 Amps, then the melting of the fuse will start in 0.02 sec which is 20 milliseconds whereas when the current flow is 225 amps then the melting will be nearly at 50 milliseconds. So, with this, it can be known that fuse characteristic is in inverse time which states that when the current rate is higher, the melting time will be minimal.
Advantages
A few of the advantages of HRC fuse are:
- The HRC fuses are less in cost when compared with other types of fuses
- The construction and maintenance of the device is simple and easy
- No need of high-end maintenance is required
- Simple functional procedure
- The program is designed to work continuously
- It has increased breaking capacity
- During overload conditions, there will be perfect in-line characteristics.
Disadvantages of HRC Fuse
The disadvantages are:
- Once the device is blown out, it cannot be used for reusage.
- When any contacts are placed near to the HRC fuse, it creates overheating
- There will be the probability of increased interlocking
- After every operation, they have to be modified
- When heat is generated from the arc, it shows the impact on the switches that are connected
Applications
The applications of HRC fuse are explained as:
- High rupture capacity fuses are used to protect high rated voltage switch gears during short circuit conditions
- Employed for backup protection
- These devices are also implemented in motor stators.
- HRC fuses are even utilized for electrical devices like automobiles, transformers, motors, and many others.
Know more about Switch Gear and Protection MCQs, Regenerative Braking MCQs.
Know more about Switchgear.
On the whole, this is the concept of HRC fuse. These are mainly used for minimal voltage installation where those can be easily substituted. The devices offer increased speed functionality in S.C and over current protection. The devices even offer stability for industrial applications and semiconductors also. Finally, this article has provided a detailed description of HRC fuse definition, working principle, characteristics, advantages, drawbacks, and applications. Know about what are the main household applications of HRC fuse?