An Electron (e–) is a subatomic particle with a negative electric charge where the atom is made with three particles like protons, electrons & neutrons. All these three particles can form the nucleus of an atom. Every electron carries 1 unit of negative charge like 1.602 x 10-19 coulomb & it has an extremely small mass like 9.10938 x 10-31 kg as compared with a proton and a neutron. An Electron belongs to the first invention of the lepton particle family. Generally, these are considered elementary particles because they don’t have known substrates or components. This article discusses an overview of electron flow–working.
What is Electron Flow?
The electron flow is an electric current that flows from the negative terminal to the positive terminal because electrons are negatively charged so they are attracted to the positive terminal. In the outermost shell of an atom, the electrons do not have a strong attraction force toward the protons. So these electrons can be pushed out from their orbits. Once a force is applied, it can move from one atom to another atom. So electron shifting is known as electricity.
There are two kinds of electron flow AC and DC. AC can be obtained from an electrical outlet in a home. In AC, the electrons flow in two directions like from the positive (+) to the negative (-) terminal & from the negative (-) to the positive (+) terminal. Direct Current (DC) can be obtained from various power sources like batteries & solar cells. In DC, the electrons flow in only a single direction from the positive terminal to the negative.
The electric current simply powers different devices like lights, computers & mobile phones. For the flow of electrons, the electromagnetic force is mainly responsible. The flow of current in an electrical circuit is measured in amperes.
Formula
The flow of charge throughout a circuit is known as electrical current. It can be defined as the number of coulombs of charge passing a point for each second where 1 Coulomb is equal to 6.25 x 10^18 electrons. Electric current is denoted with ‘I’ & its unit is amperes denoted with Amps or ‘A’. The electron flow formula is I = Q/t.
How Does Electron Flow Work?
The electron flow diagram is shown below. The flow within a circuit is from the negative terminal to the positive terminal because electrons are negatively charged, so they will attract to the positive terminal.
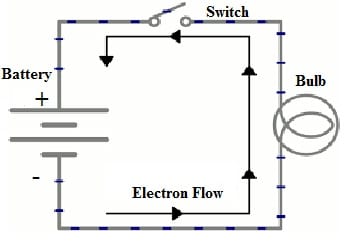
Electron Flow in a Circuit
Generally, an electrical circuit is the complete electrical energy path. In each circuit, a source of energy is required, so it is provided in most of the simple circuits through a battery. Once the electrons flow throughout the battery then they get energy, but once electrons flow throughout the bulb then they lose energy because it is changed into other forms like heat & light.
If there is a break within the circuit path, then electrons cannot flow & the bulb will go out. So, a switch within a circuit controls the flow. Once the switch is not closed, then there is no flow of current in the circuit because the circuit is incomplete. Once the switch is closed, the current flows because the circuit is complete. So by simply opening & closing the switch in the circuit, the light bulb is controlled by turning it on and off depending on the electrons flow.
Difference between Electron Flow Theory Vs Conventional
The difference between electron flow and conventional flow is discussed below.
Electron Flow | Conventional Flow |
| Electron flow is the new system that is used to explain the flow of electrons. | Conventional flow is the old system that is used to explain the flow of electrons. |
| The flow of negatively (-) charged particles is called electron flow. | The flow of positively (+) charged particles are known as conventional current. |
| The flow of electrons is from the negative terminal to the positive terminal of the battery. | The flow of electrons is from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the battery. |
| After the electricity discovery, electron flow is discovered. | This direction of conventional flow was assigned at the discovery of electricity. |
| It is the real direction of the current. | Conventional flow is an assumption to explain & analyze circuits simply |
| The different electrical rules like right-hand and left-hand would vary with this direction. | The symbols of various electrical components were designed depending on their direction like a transistor, diode, etc. |
Electron Flow in Diode
A Diode is an active electronic component that allows the current to supply only in a single direction. The diode is formed by sandwiching N-type & P-type semiconductors together & also a junction is formed at the intersection point. In this diode, P-side is known as the anode & the n-side is known as the cathode.
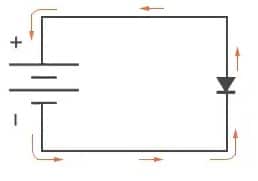
Flow of Current in Diode
Whenever the diode is connected in a forward-biased then it allows the flow of current throughout it. Similarly, when the diode is connected in reverse bias then it doesn’t allow the flow of current so it blocks the current. In forward bias, the potential at the anode terminal is higher as compared to the potential at the cathode. Similarly in reverse bias, it will be reversed.
Electron Flow in Capacitor
A capacitor is a two-terminal component that stores electrical energy within an electric field. These components are made with two metal plates with a dielectric material and these plates are separated by a dielectric material. The arrangement of these plates can be done parallel to each other.
Electrons do not supply throughout a capacitor but they accumulate on the negative (-) plate & deplete on the positive (+) plate. So this procedure continues if the voltage is applied & tapers off as the electric charge in between the two plates approaches the voltage applied.
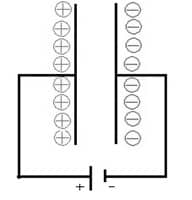
Flow in Capacitor
Which Way Do Electrons Flow?
The electrons flow from the negative (-) terminal to the positive (+) terminal of the cell.
How Do Electrons Flow in AC Current?
In an AC circuit, electrons flow in two directions from the positive (+) to the negative terminal (-) & from the negative (-) to the positive terminal (+).
Do Electrons Flow From Anode to Cathode?
The flow of current direction internally is from anode to cathode & thus the flow of electrons is from cathode to anode.
Thus, this is an overview of electron flow – working. The difference between electron flow and current direction is; the current direction is taken in opposition to the electron flow direction only because of the convention. Here is a question for you, what is a conductor?