Electricity is incredibly useful everywhere but a lot of people die or injured at home or in industries due to electrical accidents. These accidents can be prevented by installing residual current protection devices in the consumer unit of the house. So these devices can save lives by guarding you & your family against electric shock & provides some protection from fire. This device turns off the electric power supply in a fraction of a second if you get an electric shock. So, consumer units with RCDs provide you with the best protection because they generally cover all the sockets, wiring & appliances within your home. This article discusses an overview of a residual current device or RCD – working with applications.
What is Residual Current Device?
A Residual Current Device or RCD is a safety electrical device, used to turn off the electricity in 10 to 50 msec if an electrical fault occurs. This safety device is mainly designed to protect from the electrocution risks & fire caused by earth faults. As compared to standard circuit breakers (CB), RCD is more advanced & it works by simply monitoring the electrical current flow between live & neutral conductors. RCDs are also known as GFCIs (ground fault circuit interrupters) and RCCBs (residual current circuit breakers).

Residual Current Device
Residual Current Device Working Principle
An RCD working principle is to monitor the balance of current flow throughout the live & neutral wires with a differential current transformer. If there is a leakage current between these two wires then there is a problem within the circuit, so the RCD will turn off the power.
The working of the residual current device follows as;
The working principle of RCD mainly depends on one fact i.e; when the same current flows within the live wire will return always throughout the neutral wire until there is no leakage current to earth. If there is a leakage, then the current flow will take another way to earth through your body, so you will get an electric shock.
The RCD uses a current transformer. Once there is no leakage current, then the generated magnetic fields by the flow of current within the coils cancel out. But, if there is a leakage current, then generated magnetic fields by the live wire are disturbed which creates an imbalance. This imbalance will activate the switch & trips the residual current device, turning off the power supply.
Residual Current Device Circuit Diagram
The RCD or residual current device comes under circuit breakers which are used to detect current & disconnect any unbalanced current in a circuit when there is any fault takes place. The circuit diagram of the residual current device is shown below.
The RCD circuit can be built with a current transformer, test button, relay, and load. The current transformer includes three windings like a primary winding that contains line current, a secondary winding that contains neutral current) which generates equivalent & opposite fluxes when both currents are equivalent and finally sensing winding. Whenever a fault as well as both the currents in the windings changes, then it creates out-of-balance flux and generates the differential current that supplies throughout the sensing coil that is connected to the relay.
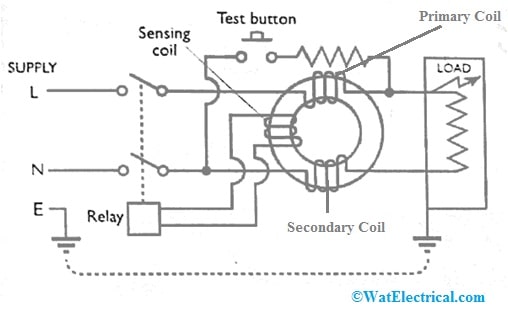
Residual Current Device Circuit
The RCD in the above circuit is connected between the neutral supply & line conductor on the load side. So it helps the circuit once it is turned ON/OFF live supply. Once the test button in the circuit is pressed then current flows throughout the circuit based on the provided resistance in the circuit. So this current supplies throughout the RCD line side coil with load current.
However, when this circuit avoids the neutral side coil of the residual current device, then there will be an unbalance between the neutral side & line side of the coil of the device. Thus, the RCD trips to detach the supply even in typical conditions. So, this is how the circuit tests the reliability of RCD.
Residual Current Device Operation
The RCD generally operates with Kirchhoff’s law. In any kind of circuit, an incoming current is identical always to the outgoing current always. An RCD compares & analyzes the variation within the magnitudes of the current supply across the neutral & the phase wires.
Generally, the flow of current to the load throughout the live wire is always the same as the current returning back throughout the neutral wire. Once any electrical fault occurs because of the leakage on the live wire, the returning current toward the neutral line is decreased. So this causes a variation of current between the incoming & outgoing wires which is known as the Residual Current. This current is mainly used in RCD to detect an electrical fault. When this residual current is noticed, then instantly the RCD will activate to trip & break the circuit. In RCDs, a push button is used to test the reliability of the device anytime by the user.
So in this process, whenever a test push button is pressed, it avoids a small amount of current across the live side of the RCD circuit. This position causes a difference to activate the neutral side of the RCD device, and then it forces the RCD to cut off & trip the circuit so that it confirms the reliability working of the device.
Residual Current Device Types
There are different types of residual current devices which are discussed below.
Fixed RCD
Fixed RCDs or mains RCDs are installed permanently in the fuse box or consumer unit to provide protection to individual circuits or groups of circuits. This RCD provides the maximum range of protection because it protects all the wiring, the sockets on a circuit & any connected devices.

Fixed RCD
Socket RCD
Socket residual current device is mainly built to utilize with individual outlets. These types of RCDs are normally used in domestic, construction & industrial sites. Socket RCDs provide convenience wherever it’s hard to find a fixed RCD. The protection of this RCD is provided normally as a temporary measure & is not intended for a stable installation.

RCD Socket
Portable RCD
Portable RCD is a plug-in RCD and it is used with socket outlets once working with electrical equipment outdoors or wherever there is no permanent RCD protection. These RCDs can be used by anybody like professionals because it is an important safety devices for anybody who is working with electricity.

Portable RCD
Type AC RCD
Type AC RCDs are general type RCDs that are most frequently connected in dwellings. These are mainly designed to detect alternating currents & protect equipment that is capacitive, resistive, or inductive without any electronic components.
These types of residual current devices do not have a time delay & work immediately on imbalance detection. The suitable circuits of RCDs are electric showers, hobs, ovens, tungsten lighting, immersion heater, and tungsten lighting. Type AC RCDs can detect & react to only AC sinusoidal wave current.

Type AC RCD
Type A
Type A RCDs are mainly used for AC & also for residual pulsating DC up to 6 mA. This kind of RCD is specifically designed to use in single-phase class 1 electronic load. These RCDs are used for protecting different circuits like inverters, induction hobs, Class-I IT equipment, power supplies for Class-II equipment, lighting equipment like LED drivers & dimmers, charging equipment in an electric vehicle, etc. These types of RCDs are also appropriate for Type AC applications.

Type A Residual Current Device
Type F
Type F residual current devices are specially designed for providing protection to circuits wherever 1- phase variable speed drivers are used. These are used for frequency-controlled appliances & equipment which include AC controllers with variable speed drives, Class-I power tools, dishwashers, washing machines, tumble driers which include synchronous motors. Type F RCDs are also applicable for Type A & Type AC applications.

Type F Residual Current Device
Type B
Type B RCDs are mainly used for loads with 3-phase rectifiers like PV systems, variable speed drives, medical equipment & EV charging station. Type B RCDs are used for single & three-phase equipment like inverters, UPS, lifts, PV systems, escalators, industrial machines, welding equipment, and charging equipment of electric vehicles with smooth residual DC current above 6 mA. Type B RCDs are also suitable for Type A, Type F & Type AC applications.

Type B Residual Current Device
Advantages
The advantages of the residual current devices include the following.
A residual current device is a life-saving machine that is used to protect you from getting an electric shock when you touch a bare wire.
- RCDs also protect from electrical fires.
- These devices protect different equipment by reducing the hazard from an electric shock.
- It protects against both residual current & earth faults.
- Once the rated sensitivity of the circuit is exceeded, the circuit will be detached.
- RCDs have a test button that is used to verify if the system is working.
- It protects the circuits from voltage variations.
The disadvantages of the residual current device include the following.
- By using RCDs, over-current faults & shot circuits are not noticeable. For this, it should be used always in combination with an MCB.
- If the current supplies from phase to GND then it can protect effectively from electric shock.
- If the current supplies from phase to phase then it does not guard against electric shock.
- A small amount of current is directed frequently to the earth once there is an unexpected shift within electrical loads.
- An RCD cannot remove all risks of fire or electric shock. Especially, an RCD will not only notice overload conditions, phase-to-phase short circuits, or phase-to-neutral short circuits.
- RCDs do not defend from overload current. These are mainly designed to defend once the variation between neutral current & live current is different. But, an overload current cannot be noticed.
- These devices do not defend from line-neutral shocks because the flow of current within them is balanced.
- RCDs do not guard against overheating that hits if cable conductors are not correctly screwed or tightened at the terminals.
- The RCDs have some unwanted tipping because whenever there are unexpected changes within the electrical load, there is a small flow of current to the earth, particularly in the old machines.
Applications
The applications of residual current devices include the following.
- RCDs are extremely significant in providing real-time safety for circuits within high-voltage commercial setups & industries.
- An RCD is used to prevent you from a fatal electric shock when you touch a bare wire.
- RCDs will turn off the electricity if there is any electrical fault occurs.
- An RCD protects from the electrocution risks & fire caused by earth faults.
- An RCD monitors your installation of wiring permanently to notice any leaking current.
- The RCD is used to switch the current flow immediately once current leaking toward the earth is noticed with electrical equipment.
- These are used in electrical installations.
Is an RCD the Same as a Circuit Breaker?
The RCD is a safety switch and the circuit breaker is a fuse. The main difference between these two is; an RCD protects people from electrical accidents & the circuit breaker protects electrical systems & wiring in your home.
Where are Residual Current Devices Used?
Residual current devices are installed in the consumer unit to provide safety to individual circuits or groups of circuits. A fixed RCD provides the maximum range of protection because it guards all the sockets & wiring on a circuit as well as any connected devices.
Do all Circuits Need RCD Protection 18Th Edition?
All the circuits rated 32A or at least 30mA earth leakage requires RCD protection under the new 18th Edition.
Know more about Single Phase Inverter MCQs.
Thus, this is all about an overview of a safety device like a residual current device or RCD that is very helpful in protecting you from electric shock by simply detaching the circuit once it notices an imbalance among live & neutral wire currents. This device is used for shock protection & also electric fire prevention. Here is a question for you, what is a circuit breaker?