The operation of the Single-phase induction motor can be done through a single power phase and used in domestic as well as industries. The main characteristic of this kind of motor is the same as that of a three-phase. This motor starts automatically (self) but a 1-phase Induction motor will not start automatically because it cannot expand starting torque. 3-phase expands starting torque through a rotating magnetic field. An AC motor starts through an exterior source however it needs an extra space of about 30% than a three-phase motor. We shall discuss what is a single-phase Induction motor, construction, working, types, starting methods, why it is not self-starting, advantages, and applications.
Single Phase Induction Motor Construction
These are the small rating motors, so these are called fractional KW motors. These are used for domestic purposes. The essential components of this motor are a rotor which is a rotating part, a stator winding which is stationary. It has got two parts one main winding and one auxiliary winding. The auxiliary winding is arranged at 90 degrees to the main field winding. The stator and rotor of this motor are shown in the figure below.

Squirrel Motor
Structurally this motor is the same as that of a polyphase with a squirrel cage rotor. The common difference between a one-phase and a Polyphase is the placement of the winding. Normally, one winding is placed on the stator of this motor which produces a stationary MMF with alternating time, whereas in a polyphase winding is displaced at an angle of 120° which produces a rotating MMF with stationary time.
These are the motors whose ratings are less and hence called Fractional KW motors and are used for domestic uses. It includes a frame where all the inner parts are mounted. The outer portion I,e frame is used as a protecting layer to avoid outside disturbances. The rotor which acts as the rotating device and stationary part is the stator. The main winding and auxiliary winding are displaced by an angle of 90 degrees I,e both the windings are arranged perpendicularly. The diagram for the stator & rotor is illustrated in the below diagram. The construction of the three-phase and one-phase motor resembles the same but it differs in the placement of the winding. In three-phase, the windings are arranged with a phase displacement of 120 degrees. This allows the motor to generate a rotating magnetic field in the air gap with time remaining stationary. The three-phase winding diagram is shown in the figure below.
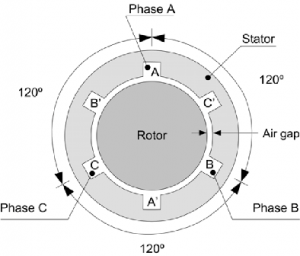
Three Phase Winding Diagram
Working Principle of Single Phase Induction Motor
This type of motor is given a one-phase supply to the main winding place on the stator. Due to the current in the winding, some magnetic fields will be developed in the air gap. Emf will be induced in the rotor conductors according to the principle of electromagnetic Induction. As the conductors the placed in the magnetic field some emf will be induced in the conductors. Due to the Lenz law, as it opposes the cause which produced it. Due to the change in current in the main winding, the rotor conductors tend to experience a force that allows the rotor to rotate.
The net rotating magnetic field (RMF) induces a current in rotor conductors due to electromagnetic induction. So, the current-carrying conductors influenced by this RMF will produce a force according to Lorentz law and the rotor begins to rotate in the same direction as that of RMF. The winding diagram is shown in the figure below.
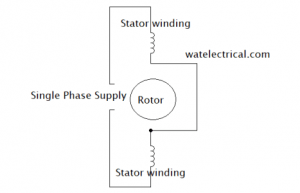
Winding Diagram
It works on the principle of double field revolving theory where the current passing through the main winding will produce a fluctuating magnetic field. The rotor will keep on rotating in the same direction because the fluctuating field is equivalent to the sum of two oppositely rotating magnetic fields this concept is known as a double-revolving field theory.
Please refer to this link to know more about Single Phase Induction Motor MCQs
Please refer to this link to know more about Poly Phase Induction Motor MCQs
Double Field Revolving Theory
It operates based on the double field revolving theory. This theory explains why the motor is not self-starting.
When supply is given to the stator, stator flux (Фm) is developed due to the current flow in the winding. According to the double field theory, the stator flux is divided into two components, which is equal to half of the magnitude I,e (Фm/2) and opposite in direction. One is represented as a forward component (Фf) and the other as a reverse component (Фr).
The stator flux is an alternately varying magnetic flux and components divided are explained at different conditions. At 0°, the two components will be in opposite directions. The torque produced by the forward component is positive and the torque produced by the reverse component is negative. So, the net torque is zero the rotor is given initiation in both directions at starting. At 90°, the two components will be in the same direction I,e they aid each other to produce a positive torque. The rotor can rotate during the running conditions. This is the reason why it is not self-starting. Hence, the rotor is given some initial rotation for the movement.
Equivalent Circuit
The single-phase induction motor’s circuit diagram is given below.
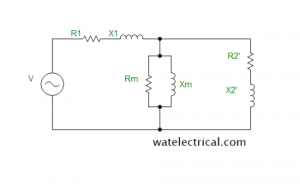
Equivalent circuit
Based on the double field revolving theory equivalent circuit is developed. Due to the double field revolving theory, the alternating stator flux is divided into two components namely, forward field and backward field respectively. The circuit diagram of this motor at the starting condition is illustrated below.
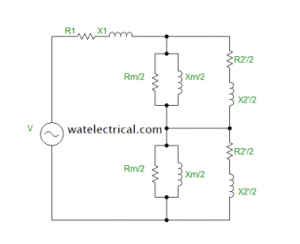
Equivalent Circuit at Standstill
The circuit diagram of this motor at the running condition is displayed below.
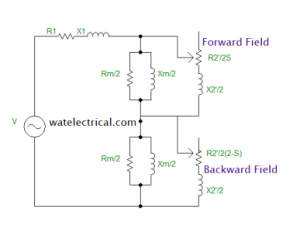
Equivalent Circuit at Running Conditions
Why Single Phase Induction Motor is not Self-Starting?
There are two oppositely rotating magnetic fields so torques produced by them will be equal and opposite. The net effect will be zero torque on a rotor so the rotor won’t start. If we rotate the rotor with some initial rotation then the torque produced will be higher than the other. So, there will be a net torque in the same direction of initial rotation, as a result, the rotor starts rotating in the same direction.
This is done by introducing an auxiliary winding with a capacitor. This produces some torque which gives rotor some initiation for its rotation.
How Single Phase Induction Motor is made Self-Starting?
The solution to Self-start the motor is if we are able to cancel any of the rotating fields then we will be able to start the motor. The auxiliary winding with a capacitor arrangement is used exactly for this purpose.
The auxiliary winding produces two oppositely revolving magnetic fields one of them will cancel RMF of main winding and other will it get added up. The resultant will be a magnetic field that revolves under specific speed such a magnetic field can give starting torque to the rotor.
Starting Methods
These motors are classified into different types depending upon the starting methods. They are
- Split phase
- Capacitor start capacitor-run
- Capacitor start
- Permanent Capacitor
- Shaded pole type
The required motors are selected depending upon required staring and running torque, starting and running currents drawn from the supply and duty cycle.
Split-Phase
Split phase motor stator winding consists of main winding and auxiliary winding which are displaced in space by 90 electrical degrees. With a one-phase supply, by phase splitting, we can get two currents with 90 degrees time angle which produces RMF that is able to rotate the rotor.
Capacitor Start
This motor is just similar to that of a resistance start motor it is an improved version of resistance starting. Starting winding with more number of windings is wound on the stator with a capacitor. This capacitor gives the starting initiation to the rotor to rotate.
Capacitor Start Capacitor Run
This motor is an improved version of the capacitor start motor. In the capacitor start, the capacitor is used only for the starting purpose. But here, it will be used both for the starting as well as the running conditions. Hence the name, capacitor-start-capacitor-run motor.
Permanent Capacitor
In this, the capacitor is used permanently there is no centrifugal switch to operate as it operates continuously and is also called a capacitor run motor. It has two stator windings which are placed at an angle of 90 degrees apart. The main winding is connected across the supply and the auxiliary winding can be connected with the supply in series.
Shaded Pole Type
It is a split-phase type motor and has salient poles with its own exciting coil. Some portion of the coil is put on by a shaded coil. When the coil is excited, the current gets induced in the shaded coil which produces a magnetic field I,e shaded pole flux. The shaded pole flux and main winding flux will be at an angle of 90 degrees and these two fields have satisfied the space and time displacement conditions. Hence, a rotating magnetic field is developed which enables the motor to rotate.
Please refer to this link to know about the detailed information regarding the type of single-phase induction motors
Advantages
- Used for small loads.
- Used for domestic purposes.
Disadvantages
- Capacitor-start motor has good starting conditions but poor running conditions because the capacitor is disconnected in running conditions. So, only the main field winding is connected to the motor under running condition.
Applications
- These are used for fans, blowers, centrifugal pumps, and office equipment.
- These are the lowest cost motors which are usually available at ratings ranging from 0.05 to 0.5 HP.
- Capacitor start motors are employed where there is a requirement hard to start-loads such as compressors, pumps, refrigerators, and air-conditioning equipment.
- Capacitor start capacitor run motors are employed where there is a requirement of high starting torque such as conveyors, compressors, pumps whose rating ranges from 0.125 to .75 HP
- Shaded pole motors are used in toys,
- Permanent split-phase motors are employed where there is a requirement of low starting torque such as for directly connected fans, blowers, and centrifugal pumps.
Therefore, this article discusses a piece of detailed information on a single-phase induction motor. It is one kind of machine which uses the electromagnetic induction principle. This motor is not a self-starting as well as it cannot expand RMF. It can be expanded through specific starting techniques to make the motor self-start by itself. And also, we have discussed its working, a theory of double field revolving, starting methods, benefits, disadvantages & applications. Here is a question for you, what is the main difference between single-phase & three-phase motor?