An Electrical Substation plays an important part of the electrical system as it acts a bridge in transferring the electricity from the power generation source unit to the end consumers by working to speed up or slow down the current when required. Substations include transformers, insulators and circuit breakers to help regulate power issues, changing the frequency, voltage, AC to DC, P.F and other characteristics. Substations play a key role in helping generate, transmit and distribute to homes a safe and consistent energy flow.
There are numerous types of electrical substations depending on its nature and power tackling capacities. Classification of Substations broadly falls under the following 4 categories based on various aspects
- Substation Types based on Application
- Substation Types based on Service
- Substation Types based on Operating Voltage Levels
- Substation Types based on Location/Design
Types of Electrical Substations based on Applications
The following is the classification of substations based on the application aspect.
1) Step-up Substation:
The step-up substations are linked to generating stations directly as generation is achieved in lower voltages. Hence, these voltages are needed to be stepped-up for economical transmission of electrical energy over greater distance. The step-up substation may have circuit breakers which are utilized for transmission and generation circuits in the case when required to be shut down. The specified voltages which are leaving the step-up transmission are to be analyzed through customer’s needs.
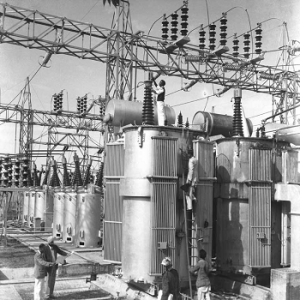
Step up Substation
2) Step-down Substation:
The step-down substations are linked with load centers as there is a requirement of different voltage levels for various loads. The step-down substations are capable to change the voltage levels of transmission to usually 69kv. The lines of the substation are then serving as a source to that of the distribution substation. Moreover, some of the power is tapped from the substation line to be used for industrial purposes in the way.

Step Down Substation
3) Primary Substation:
The primary grid substations are linked with bulk load centers alongside primary lines of transmissions. The voltages are stepped-down at various voltage ranges for purpose of secondary transmission.

Primary Substation
4) Secondary Substation:
The secondary substations are lined alongside secondary transmission lines adjacent to loads. The voltages here are further stepped-down for purpose of distribution.

Secondary Substation
5) Distribution Substation:
The distribution substations are located at the lace where voltages of primary distribution are being stepped-down. These voltages are for consumers to use for their actual loads. These substations are having high-voltage bearable wires and conductors having one neutral to ground and 4 live wires. The 3 phased voltage is of 34500 volts amid conductors and wires and the voltage is about 19920 volts in single phase when it is considered amid neutral to ground and conductor.
Depending on the type of equipment used / Configuration, the substations could be classified as

Distribution Substation
- Conventional – Outdoor type with air-insulated equipment
- Indoor type with air-insulated equipment
- SF6 Gas Insulated Substation
- Outdoor type with gas-insulated equipment
- Indoor type with gas-insulated equipment
- Composite Substation or Hybrid Substation combination of above two.
6) Mobile Substation:
The mobile substations are only for a dedicated purpose and are temporary in nature i.e. mainly for giant constructions. A mobile substation is supposed to fulfill power requirements of the under-construction structures. These substations are a source of temporary electrical supply and its maintenance is very easy. It has vibrant protection from blackouts, fires, weather disturbance, and sabotage etc.

Mobile Substation
7) Industrial Substation:
The industrial substations are also known as bulk substations and are traditionally referred to as distributive substation, however, these are for dedicated consumers only e.g. industries requiring bulk power to be supplied.

Industrial Substation
8) Mining Substation:
The mining substation is of a distinct kind and is needed to be designed carefully as an increased level of precautionary safety measures are to be taken for the operation of its electrical energy. This substation is dedicated for the control of electrical power supply from the surface to mine power station lying underground.
Types of Substations based on Service
Converter Substations–
As the name suggests, Converter substations contain equipment that changes the frequency of current from higher to lower and can also convert AC to DC or the reverse also.

Converter Substation
Switching Substations–
A key function of these switching station includes switching the power line without altering the voltages as they are placed in between the transmission lines. It also isolates the faulted portion of the systems and de-energize faulted equipment which helps the grid operate with stability.
Collector substations–
These substations are primarily used in distributed power generation projects like wind farms, hydroelectric projects etc where power flow from multiple power sources can be collected and distributed to the grid by stepping up the transmission voltage.
Types of Substations by Operating Voltage Levels
The substations classification below is based on the voltage levels they operate and may vary from region to region
- High Voltage Substations (HV Substations) – Involving voltages between 11 KV and 66 KV.
- Extra High Voltage Substations (EHV)– Involving voltages between 132 kV and 400 kV.
- Ultra High Voltage(UHV) – Operating voltage above 400 KV.
- Direct-current high voltage (dc HV) – ±250 kV, ±400 kV, ±500 kV

High Voltage Substations
Types based on Locality / Design
The following are types of substations based on locality.
- Outdoor Substation: The outdoor substations are constructed in the open air. These are also known as a 66KV substation, 132KV substation, 220KV substation, and 400KV substation etc. These days gas insulated substations are built for high voltage systems.

Outdoor Substation
- Indoor Substation: The indoor substations are generally of lower voltages and are built under a roof or closed compartment. These substations are also known as 11KV substations and 33KV substations etc.

Indoor Substation
- Pole Mounted Substation: The pole mounted substations are majorly distribution substations which are constructed on the structure of two, four, or sometimes six or more poles. In such substations, there is a need of mounting distribution transformers over poles alongside isolator switches. The single pole is also known as H pole and 4 pole structures are more relevant which are operating at 25KVA, 125KVA, and 225KVA.

Pole Mounted Substation
- Underground Substation: The underground substations are built in ground or subversive. These substations are built in congested places where building open air/outdoor substations are not possible. However, the design of such substations is very complex. The usual voltage level of such substation varies from 34500/19920 to about 4160/2400 volts.
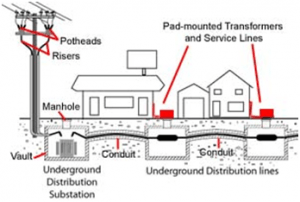
Underground Substation
Know more about Electrical Isolator.
Know more about SF6 Circuit Breaker MCQs, Electrical Tariff Question and Answers.
We have covered in detail the classification of substations based on the application, design, location, service, operating voltage levels etc. While there are many more terms like Grid Substations, Town Substations, Traction Substation etc these are more or less categorized based on the above categorization. Here is a quick question for your – What is the List of Electrical Substation Components?