Pumping industry became extensively prominent from 1982 itself and there onwards there have been multiple enhancements and inventions. One of the developments which stood as the great invention is positive displacement pumps and their types. Enhanced environmental knowledge gave a real development to pumps having no shaft seals. The trend of electronics and computers even entered into the scope of pumps in the aspect of variable speed drives. Pump choosing software has fastened the process of pump selection along with multiple scenarios. Of all these, the one that we are going to have our discussion is “Gear Pump”.
What is a Gear Pump?
A gear pump comes under the category positive displacement pump which has a continuous delivery rotary pump. With the help of gear meshing, mechanical energy is converted into fluid energy and this creates void suction. Space which is in between the gear meshing pull in the high-level of viscous liquids by letting them flow towards the wall surface and then to the output. This pump works effectively for an extended level of viscous liquid like oil because it does not need any priming.
Gear Pump Design
In general, a gear pump is designed either with two or more rotational gears internal to the casing section having more tolerance. To allow correct fluid transmission, inlet and outlet positions are made with proper casing. Depending on the casing construction, a gear pump is of two types. And they are
- Internal gear pumps
- External gear pumps
Choosing of the gear pump is based on the essential factors. In the case of these pumps, a liquid displacement per each gear teeth revolution is known by:
Q = ʃ0zt0Vndt
Where flow fluctuation (ŋ) = Vmax – Vmin
And here ‘Q’ corresponds to fluid displacement
‘Z’ corresponds to the number of associated teeth
‘Vn’ corresponds to the liquid flow rate
‘t0’ corresponds to the time taken for teeth revolution
‘Vmax’ and ‘Vmin’ correspond to the maximum and minimum flow rates
‘Vav’ corresponds to the average flow rate
Working Principle
The gear pump working principle can be explained as follows:
When there is a revolution of toothed wheels inside of the casing section, air will get wedged in between and throughout the teeth which creates space. This shows a result of a positive up direction lift of the liquid on the way to the suction pump. The pump continues to pull in the air until it initiates to receive liquid through the inner section.
The liquid will be pulled into it at the level of atmospheric pressure; prior to being trapped in-between the space of two wheels. Gradually the viscous liquid will be pulled in the direction of output and then pulled towards the out. The pump functions effectively also in the inactive state but operates more actively when it got primed in before.
Added protection in the scenario of valve relieving is fitted in the gear type revolving pump so as to expel any kind of destruction either for the pipeline or pump. The relieving valve will decrease the additional pressure during emergency thus safeguarding the entire equipment.
gear-pump-construction
Types
There are mainly two gear pump types and those are of
- Internal
- External p
Internal Gear Pump
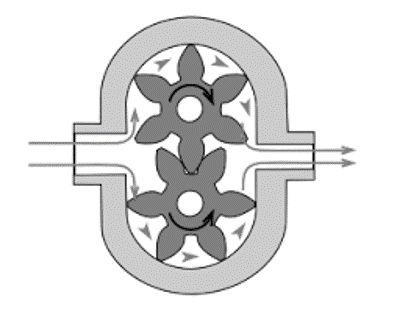
This pump functions on a similar principle but here the interlocking gears are of dissimilar sizes and one revolving internal to the other gear. The bigger gear which means the rotor is termed as the internal gear and the teeth is on the inner side. Inside the rotor, there is minimal gear. The teeth of these two gears are interlocked in one position.
When these gears emerge from the mesh on the inlet side of the pump, they will create extended volume. Then the liquid is flown into the cavities and surrounded by the gear teeth as the two gears stay to revolve opposing the partition and the casing sections. When the gear’s teeth are interlocked on the pump discharge side, then the fluid volume will get decreased and the liquid is drawn out.
internal-gear-pump
External Gear Pump
Here the two gears are of similar size where these are interlocked by other individual shafts. In general, motor drives initial gear and the second one is driven by an initial one. In a few situations, the motor drives both the shafts. Bearings that are on the casing side will support the shafts.
When these gears emerge from the mesh on the inlet side of the pump, they will create extended volume. Then the liquid is flown into the cavities and surrounded by the gear teeth as the two gears stay to revolve opposing to the casing section. When the gears’ teeth are interlocked on the pump.
Applications
The gear pump applications are stated as below:
Mostly, gear pumps are employed for an extended level of viscous liquids like resins, oil, foodstuffs, and paints.
- These are utilized in the applications where precise dosing is necessary.
- As the gear pump output is not much influenced by pressure, it can be even applied in the applications where there is an unbalanced supply.
The classification of gear pumps also have their specific applications:
External Gear Pump Applications
- Chemical blending and compounding
- Used in lube and fuel oils
- Polymers and solving agents
- Caustic and acidic fluids
- Hydraulic, farming and engineering applications
- Polymer metering and chemical extracts
Internal Gear Pump Applications
- Used in surfactants and soaps manufacturing
- Pigments, inks, and resins
- Used in food products like animal feed, cocoa butter, corn soups and in many
Gear Pump Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages are
- Streamlined maintenance
- Minimally susceptible to cavitation’s
- Manageable results
- Manage a wide range of viscous fluids
The disadvantages are
- Produces loud sound at the time of gears interlocking
- Fluids need to free from abrasives
FAQs
1). What is the difference between the internal and external gear pumps?
The difference between these gear pumps lies in the rotor and idler gear sizes.
2). Can gear pumps run dry?
Yes, gear pumps can be operated as because they are self-priming
3). What is meant by gear ratio?
It is defined as the ratio of turns that the output shaft made per one rotation of input shaft.
4). What is an external gear pump?
An external gear pump is the PD pump which functions with two similar and interlocking gears where those are supported by two individual shafts.
5). What is a positive displacement pump?
A PD pump is the one that has enlarging and shrinking cavities on the suction and discharges sides.
So both the types of gear pumps are extensively used in many applications and there benefits and drawbacks hold the ability to be implemented in many ranges of industries. Moreover, simple maintenance and minimal susceptibility to issues enhance the operation of gear pumps. Know more about the concepts of what are the other characteristics of the gear pump?