Welding is the concept of joining two metals through some external procedures and the concept which stood as basic for welding is lap welding. Then after, this domain observed huge progression with the usage of metals such as bronze and copper. To the clear, this progression was driven by human enhancements in the invention of multiple instruments. In the 20the century, there comes the scene of electricity and this prompted the discovery of various technologies in the welding procedure. The invention just not stick to one kind of welding and invented modern welding processes and the one today we would like to discuss is submerged arc welding.
What is Submerged Arc Welding?
Definition: Submerged arc welding is the general kind of welding technique that consists of the development of arc in between the operating metal and perpetually fed electrode. This type is considered as increased productivity of welding and operated through the mechanical procedure and just confined to horizontal fillet welding location whereas with an increased deposition range. Most of the metals used for this process are minimal alloy range steels, nickel-dependent alloy materials, carbon steels, and stainless steel materials. The crucial characteristic of this process is deep saturation which allowed the technique to be employed in many industries.
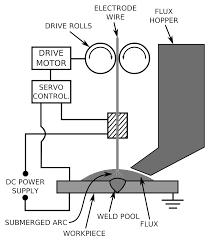
Submerged Arc Welding Process
Few of the features of this kind are:
- This process can be operated either through alternating or direct current.
- It can deliver enhanced output by the addition of non-conducting wire inside the welding pool where this can increase the output almost by 20 percent.
- Preferably appropriate for circumferential and longitudinal but welding’s necessary for the construction of vessels and pipelines.
- When welding is performed in parallel-perpendicular or in the leveled position, the fillet welding’s can also be done.
Equipment of Submerged Arc Welding
The equipment necessary for the submerged arc welding is dependent on the type of procedure such as semi-automatic or automatic. The equipment for the automatic type is
- Power resource
- Wire feeder
- Controlling system
- Flux feeding apparatus
- Welding head and
- Moving carrier
Power Source
Either alternating or direct can be used as a power supply. Direct current is provided through a rectifier and transformer whereas the alternating current is provided through a transformer. The current necessary for the equipment ranges from 200 Amp to 1000 Amp. Generally, welding is performed on thick metal plates and for one wire the current ranges in between 600-900 amperes while for double wires, the current ranges in between 800-1200 amperes.
In DC activity, the positive terminal has a connection with the electrode and the negative terminal is used for the increment of deposition rates. Through this power source, the output will be constant voltage and the arc is self-regulating.
In AC operation, the output will be constant current but the arc is not self-regulating. The output arc can be regulated through the sensation of arc voltage and by controlling the speed of wire feed.
Welding Gun
In the manual type of SAW welding, the angle of the gun is maintained at 450 from the vertical edge. In single-wire, a welding gun is positioned at 900 to the metal piece. Whereas in double wire operation, a welding gun is placed at an angle of 60-800. The positioning of the welding gun in these positions will decrease the interruption of the welding pool.
Flux Handling
Flux material has to be maintained in closed containers under dry environment, whereas open containers are to be stored in a dampness environment. For thin welds, the flux is arranged in a small hopper on top of the welding gun and in thicker welds, flux is arranged in huge hoppers and supplied with compressed air.
Shielding apparatus
Not like the other welding approaches, this shielding arc welding is a tidy procedure that creates output having no dirt and spatter at the time of welding. For minimal time welding joints, normal apparatus can be enough. Welding joints involve the steps of chipping and grinding, and for these goggles, defending shoes and gloves are required. Special care has to be taken when the management of storage hoppers.
Working Principle of SAW
The submerged ac welding working principle can be defined as below:
The welding procedure starts with the deposition of flux on the welding joint. In the cooling condition of the flux, it behaves like an insulator. Movement in the arc can be initiated by the movement of the tool through the workpiece. The heat which is created by the flux will soften the granular flux material. The flux moves into a complete conduction state when it is completely melted. This starts the current flow to the electrode via the molten flux which allows being in contact with the external environment. The left and undissolved flux will be considered as wastage and removed after the completion of the entire process.
By a constant speed level, the electrode will move towards the joint to get connected to it. When this connection is moderately automatic, then the connection moves in line with the welding top position, whereas in automatic SAW, there has to be a separate drive to allow the welding position to be at the top. By the assistance of the self-adjusting concept, the arc length is maintained at constant, When there is a reduction in the arc length, then the arc voltage and current levels will get increased. Opposing this scenario, when the length of the arc is more than the specified length, then the arc voltage and current levels will get decreased.
Advantages/Disadvantages
Few of the submerged arc welding advantages and disadvantages to be discussed are as follows:
Advantages
- Increased deposition rates
- Welding joints can be done for heavy materials too
- Appropriate for both interior and exterior applications
- There will be only a minimal amount of arc light and fumes which is good for employees
- Almost 90 percent of the produced flux can be reused and recoverable
- Welding joints done through SAW are completely effective, ductile and resistant to corrosions
- Single time welding can be enough for thick metal sheets
Disadvantages
- This method needs supporting strips while welding on thicker metal sheets
- Constrained for few nickel alloys and steel-based materials
- Utilization of flux is somewhat complicated
- Slag and flux residuals might impose some kinds of health concerns to the workers
Submerged Arc Welding Applications
- It is employed to weld carbon, steel, aluminum, titanium, and minimal alloy materials.
- It holds the ability to create welding joints for corrosion sturdy metals, heat-resistant steels, and other carbon steels.
- Even SAW is implemented for monel and nickel weldings
- Utilized especially for down hand welding place where the plate thickness ranges in between 5-50mm.
- Used in the industries of welding pipes, structural manufacturing, vessel manufacturing, storage tanks, and ship buildings
- Three and nine grades of wires and fluxes, in specific amalgamations, are utilized for SAW of basic steels, average tensile steels, lesser-alloyed or HSLA steels, tubes and stainless steels to implement in multiple domains.
FAQs
1). Why is submerged arc welding referred to as submerged?
SAW got its name as submerged because the welding joint and arc are submerged underneath a layer of flux.
2). What is the main purpose of submerged arc flux?
The flux is used for welding a kind of small insulative material that is composed of multiple small particles.
3). What is the strongest type of weld?
TIG is considered as the strongest kind of welding joints.
4). How spot welding is done?
This procedure makes use of two molded copper alloy electrodes to strengthen current at one spot and then correspondingly clamp the metal pieces collectively.
This is the whole concept behind submerged arc welding which explains the concepts of its working, equipment used for welding joints, its applications, and benefits. This is the most suggested type of welding joint and can be easily employed in various industries. So, know more about what are the other equipment used in submerged arc welding?