A circuit breaker is one type of electrical switching device used to control & also protect the power system, either automatically or manually from any harm occurred by short circuits or overload. The main function of the circuit breaker is to obstruct the flow of current once the protective relays notice a fault like electrical fires, shocks, and the electrocution risk. These are classified into different types based on different factors, location of installation, and arc extinction medium. This article discusses an overview of a vacuum circuit breaker, its working, and its applications.
What is Vacuum Circuit Breaker?
The circuit breaker or CB that uses vacuum media mainly for arc quenching is called a vacuum circuit breaker. The dielectric strength of the vacuum is much better or has superior arc quenching properties as compared to other types of medium. The vacuum amount usually ranges from 10-5 to 10-7 torr. Generally, the vacuum is a force under atmospheric force wherever no gas is there. These circuit breakers are suitable for medium voltage power distribution that ranges from 22kV – 66 kV and are also used for protection and switching power systems. These circuit breakers replace oil circuit breakers & SF6 circuit breakers So these circuit breakers are necessary at incomers & interconnectors within a network.
Arc quenching is a process used to extinguish or suppress electrical arcs that occur in various electrical devices and systems. An electrical arc is a discharge of current through the air or other insulating medium between two conductive surfaces, typically occurring when there is a gap or breakdown in the insulation.
When an arc is initiated, it generates intense heat, light, and pressure. Arcs can pose significant safety hazards, as they can cause damage to equipment, result in electrical fires, and harm personnel. Arc quenching aims to interrupt or extinguish the arc as quickly as possible to prevent these risk

Vacuum Circuit Breaker
Properties
The vacuum circuit breaker or VCB has two main phenomenal properties which are discussed below.
- These two properties will make these circuit breakers very efficient, less costly, less bulky, and much high service life with less maintenance.
- This circuit breaker has a superior dielectric medium as compared to other insulating media. So the vacuum is better as compared to other media apart from SF6 & air which are used at high pressure.
- Once an arc is opened by simply moving the contacts separately within a vacuum, then an interruption will occur. So with the interruption of arc, their dielectric strength will be increased up to thousands of times as compared to other circuit breakers.
Construction of Vacuum Circuit Breaker
The construction of a vacuum circuit breaker is very simple as compared to other CBs which is shown below. These breakers are very popular because of the voltage ratings of up to 36 kV. In this circuit breaker, the covering part is made with an insulating material like porcelain, glass fiber unbreakable plastic, or glass but most of the time, glass material is used because it helps in observing from the outer surface. If the glass material of this CB is blurred then it indicates simply that the vacuum circuit breaker is dropping its vacuum.
The upper contact in the above diagram, the electrode is connected is fixed/welded whereas the lower contact is sealed by a stainless metallic bellow design like a moving object. The two metal end flanges support most of the CBs like outer insulating enclosure, fixed contact, metallic bellows & vapor condensing shield. This circuit breaker contacts have faces in large disc-shape that include spiral segments so that the arc current generates an axial magnetic field. In this circuit breaker, the separation between the two contacts is about 1 cm which is sufficient for a current interruption within a vacuum.
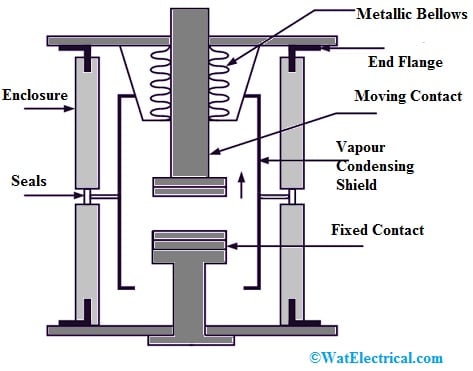
Vacuum Circuit Breaker Construction
Working
The vacuum circuit breaker working principle is to separate the contact once any fault occurs within the system & to extinguish the generated arc in the vacuum throughout the operation. Once any fault takes place within the system, then this vacuum circuit breaker simply releases its contact to separate the system as quickly as possible.
In the operation of a circuit breaker, the arc can be generated due to the ionization of metal vapors within the contacts. So this generated arc can be stopped or extinguished as electrons, ions & metallic vapors which are reduced within the contact surface to make a quick enhancement rate within the vacuum dielectric strength.
The vacuum circuit breaker working mainly depends on the energy stored mechanism within the closing spring. This spring can be prepared manually or electrically & it is automatically charged after the CB operation. Lastly, the tripping can be done once high voltage within the system is detected thus the contact breaking is done to separate the system.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of a vacuum circuit breaker include the following.
- The vacuum circuit breaker is available in small size, lightweight with a small operating mechanism.
- This circuit breaker has low action noise and small control power throughout the switch operation.
- The contact gap in this CB is about 10mm, simple mechanism, low closing power & long service life.
- This circuit breaker has a short arc extinguishing time, small arc energy, small contact loss, low arc voltage & various breaking times.
- These types of circuit breakers have exact superiority as compared to other types of breakers whenever the voltage is high & the current to be disrupted is low.
- The cost of this circuit breaker is low as compared to other interrupting devices mainly low fault interrupting abilities.
- It has small variable guide rod inertia.
- It doesn’t require any additional filling of the gas/oil.
- The unit of this circuit breaker is self-contained & compact.
- The vacuum CB has extra high acceptance.
- Once the arc is busted, the medium in between the fractures recovers rapidly & the medium used does not require to be changed.
The disadvantages of vacuum circuit breakers include the following.
- The vacuum production of this circuit breaker needs advanced technologies.
- Extra surge suppressors are necessary for the low magnetizing currents interruption within a certain range.
- The vacuum loss because of failure or transit damage will make the whole interrupter inoperable & cannot be set on-site.
- VCBs are too costly over 36 kV.
- The high technology is used within the vacuum generation.
Applications
The applications of vacuum circuit breakers include the following.
- The vacuum circuit breaker or VCB is used in various industrial applications as high-speed making switches.
- These types of circuit breakers are extremely suitable for the system which needs from 11V to 33 kV.
- These are used with static over the current relay to provide an overall permission time of below 40msecs on phase-to-phase errors.
- These are used in high voltage-based circuits and also in generators & electrical substations.
- These breakers are used to interrupt the double earth faults & phase currents
- These are used where a high-switching sequence is used.
- This is used in railway applications for electric supply switching & traction current.
- This CB is used for switching motor drives.
Where are vacuum circuit breakers used?
Circuit breakers are mostly used for switching & protect primary distribution stations, medium voltage range circuits, high voltage induction motor circuits, etc.
What is VCB and its function?
VCB is a vacuum circuit breaker is a type of circuit breaker and its main functionality is to disrupt the flow of current once any fault is noticed. In this CB, the arc quenching occurs within a vacuum medium.
Why do We Use VCB instead of ACB?
VCB is used instead of ACB in medium voltage range applications which range from 11 kV to 33 kV because ACB is used in low-voltage based applications which range up to 450V.
Know more about Circuit Breaker.
Thus, this is an overview of a vacuum circuit breaker, its construction, working, and its applications. The vacuum circuit breaker is the most consistent type of circuit breaker with inexpensive, no fire risks, less maintenance, low inertia, low arc energy, no gas generation, little maintenance, etc. Thus this is the most frequently used type of CB in high-voltage transmission. Here is a question for you, what is MCB?