Electrochemical and electrical sensors are usually one part of the measuring sequence. And this sequence generally comprises of a sensor, transmitter, and a cable. And the foremost classification of sensors is analog and digital. The digital sensor technology is more substantial in regard to its extensive reliability and exactness. Digital sensors are the contemporary replacements of analog sensors because of few drawbacks in the analog type of sensors. So, this article mainly focusses on the concept of digital sensors, their importance, and how they are classified?
What are Digital Sensors?
Digital sensors are the kind of electrochemical or electrical sensors where the information is converted to digital form and then transmitted. The output of a digital sensor is the distinct digital signal of the quantity which is being measured. And the measured quantities might be of conductivity, pH value, redox potentials, and many others. The output is in the form of 1’s and 0’s where ‘1’ represents ON condition and ‘0’ represents OFF condition. This corresponds that a digital signal generates distinct (non-continuous) values and the output is considered either as a single “bit”, (serial transmission) or the combination of multiple bits called “byte” and is called (parallel transmission).
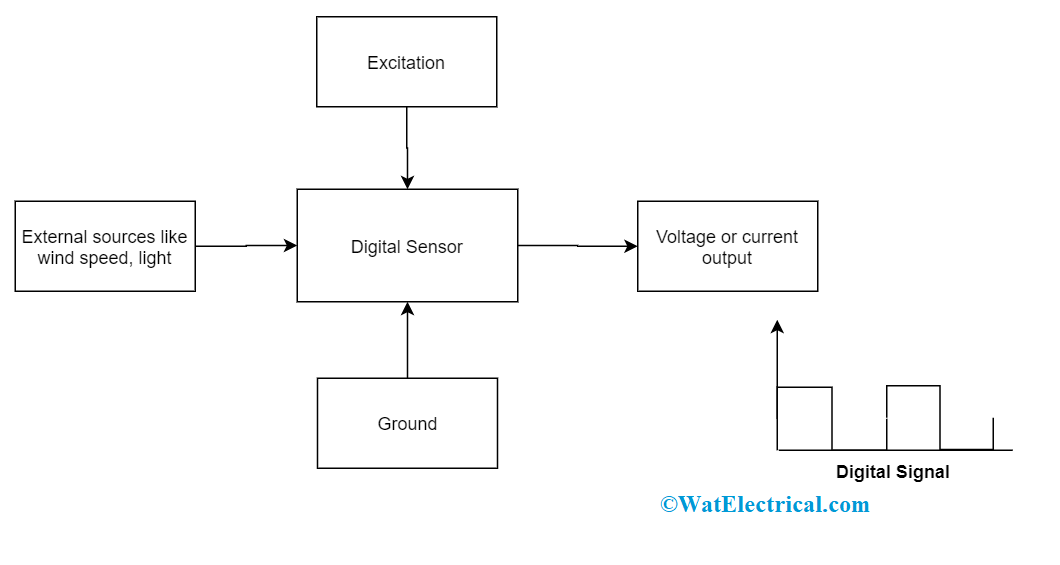
Basic Digital Sensor
The below example explains the output produced by a light sensor in digital form:
In the diagram, the rotating shaft speed is known with the help of a digital LED light sensor. Here, the place of the disk is positioned to the revolving shaft which has transparent slots internal to the disk design. As both the shaft and disc rotational speed are the same, every slot in the disk passes through the sensor thus generating output pulses in the form of logic ‘1’ and logic ‘0’ (the digital signal).
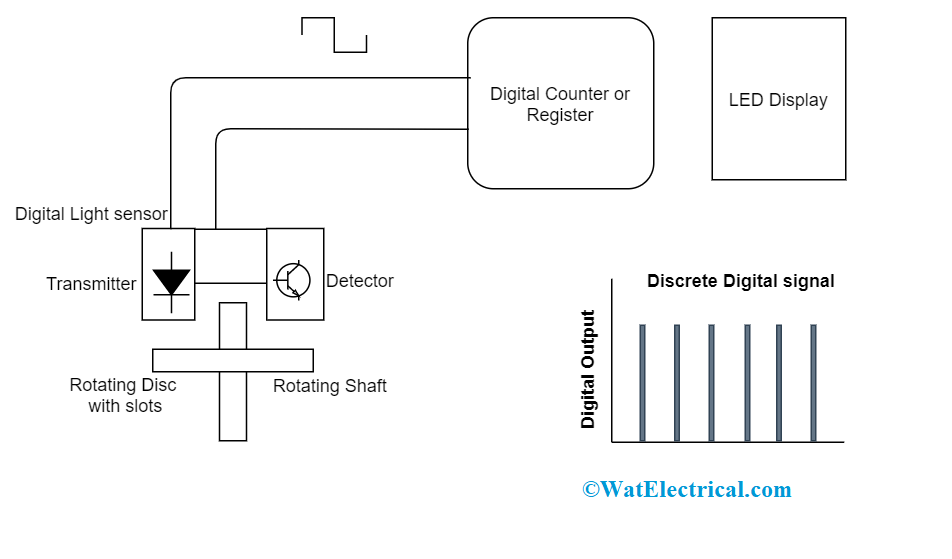
Digital Sensor Output
The generated pulses are then transmitted to the register in the counter and then to the output which displays the number of shaft revolutions. The number of output pulses for every rotation can be increased by augmenting the number of disk slots. The benefit of this increment is that higher accurateness and resolution can be obtained and minimal revolutions can also be observed easily. So, this kind of sensor construction is mainly utilized for controlling positions of the slots in the disk where this acts as a reference position.
So, in comparison to analog signals, discrete signals are with extensive accurateness and they can be calculated even at increased clock speeds. The exactness of the digital pulse is linear to the bits that are utilized for quantity measurement.
For instance, a processor of 8 bits, will generate an accuracy of nearly 0.390 percent, whereas with a 16-bit processor and accuracy of almost 0.0015 percent can be achieved. So, this accurateness can be asserted as digital quantities and these are many times quicker than that of analog signals.
Types of Digital Sensors
Digital sensors are also classified as many types and few of those to be described as follows:
- Digital accelerometers
- Digital temperature sensor
Digital Accelerometer
Digital accelerometers generally make use of PWM (pulse width modulation) to generate output pulses. It corresponds that the output is a square wave of corresponding frequency and the time for which the voltage is high is linear to the amount of time taken for acceleration.
When a BASIC stamp or any kind of microcontroller is used as digital inputs, then the digital accelerometer is the preferred one to generate output.
Features of Digital Accelerometers
- The data rates can be selected by users
- Operates using FIFO/FILO memory buffers
- One can achieve digital high-pass filter outputs
- Minimal power consumption
- Solderability can be done without using lead
- Exceptional temperature performance
- Extensive shock survivability
- Factory programmable offset and compassion
Applications
- Implemented in mobile phones and other internet equipment’s
- Used in-game controllers and computer components
- Used in the health care industry
- Also implemented in personal navigation equipment
Digital Temperature Sensors
These are silicon dependent temperature sensors where the output is the accurate digital representation of the measured temperatures. These devices are designed to read the temperature ranges from 00C to that of 700C and with this, an output of nearly ±0.50C accurateness can be achieved. Whereas, packaged components are designed for extensive ranges which means for -550C to 1750C, the accuracy is ±10C and for -1300C to 1500C, the accuracy is ±1.50C.
The flexibility of Digital Temperature Sensors
In general, registers are programmed with the temperature levels of high, low, and medium. The calculated value is related to that of these temperature limits and either increased or decreased values apart from these limits prompts corresponding pins on the package. So, through the serial bus, the calculated temperature value is transmitted to the system controller which is even utilized for configuration.
On the other hand, these digital temperature sensors operate basically as thermostats.
Example:
DS18B20 is a kind of single wired digital temperature sensor. Each of these sensors is wit a 64-bit serial number engraved into it which permits for an extensive number of sensors to be utilized on a single data bus. The features of this sensor are as follows:
- This singled wired sensor needs only one port for communication purposes.
- The feature called multidrop ability streamlines distributed temperature sensing functionalities.
- No additional components are required
- It can be powered up through data lines
- The operating power supply ranges from 3.0V to 5.5V
- It can measure temperatures ranging between -550C to +1250C providing an accuracy of -100C to +850
- The resolution of a thermometer is customizable selecting from 9 -12 bits.
- Through alarm search command detects and addresses the devices where the temperature range is external to that of programmed limits.
With the one can measure the temperature ranges of air, water, and even the ground temperature.
Use of digital sensors
- Measuring signals are simply converted to digital signal internal to the sensor
- Digital sensors have no complication for humidity and corrosion
- These can be calibrated separately from the system
FAQs
1). What is the difference between analog and digital sensors?
The main difference is in their outputs. In analog, it is a continuous signal and in digital it is non-continuous in the form of 1’s and 0’s.
2). Why digital sensors are preferred than analog?
Switching from analog to digital sensors allow broadcasters to provide increased image definition, due to the reason a digital signal might be condensed far more than that of the analog signal.
3). What is a digital camera sensor?
A digital image sensor comes under the classification of solid-state devices where a part of the camera’s hardware which illustrates light and converts the visible light into a picture.
4). Are sensors digital or analog?
Sensors are of two types digital and analog and both have their own benefits and drawbacks.
5). What devices use analog signals?
Mostly microphones, flex sensors, photocells, force-sensitive resistors use analog signals.
6). Is ultrasonic sensor analog or digital?
Basically, ultrasonic signals are implemented with analog to digital converter. Therefore, the analog signal is converted to that of digital.
7). Is a light sensor analog or digital?
This is an analog sensor where it can detect minimal light variations too.
So, this all about the concept of digital sensors. Furthermore, people implement digital sensors in various practical applications in both industrial and commercial domains. With the advancement in the scope of technology, and also these sensors overcome the drawbacks of analog sensors the progression of digital sensors also enhances. Know more about the real-life examples of digital sensors and how their operation is based on?