In the year 1883, the inventor from America namely Charles Fritts developed a functional photoelectric cell. In the same year, Paul an engineer from Germany utilized the photocell in his observation called Nipkow’s disk. This is the instrument that takes images by measuring the object’s bright and dark locations and convert those into impulses in electrical form.
The pre-invention of the modern-day photocell was developed by Hans and Elster by giving few modifications to CRT (Cathode Ray Tube). So, this was the invention and a brief history of the photocell. This article explains photocell working, types, circuits, and applications.
What is a Photocell?
Photocell is also called an electron tube, photoelectric cell, electric eye, and phototube. This is an electronic instrument that is very vulnerable to incident radiation mainly light that is utilized for the generation or regulating the output levels of electric current.
It is also called a resistor which alters its resistance value based on the amount of light that is induced on it. This device functions on the principle of semiconductor photoconductivity which means that photons’ energy that hits the semiconductor allows electron movement and thus reducing the resistance level.
Photocell Construction
The essential parts required for the construction of photocell are:
- An Incident light
- Glass tube
The device is constructed using an emptied glass tube having two electrodes which are a collector (A) and an Emitter (C). The shape of the emitter looks like a semi-hollow cylinder, and it is always placed at negative potential.
Whereas the collector electrode will be like a metallic rod, and this is installed at the axis of the emitter section and always placed at positive potential. The emptied glass tube is installed on the non-metallic base section and the base section has pins to support external connection.
Working Principle
The photocell working might be based on the amount of resistance and the impact of photoelectricity. This is utilized for conversion from light to electrical energy. This happens when the connection of the battery is in the way that emitter and collector terminals are connected to the negative and positive terminals of the battery. The level of frequency radiation is more when compared with the emitter’s threshold frequency level and then the emission of a photon takes place.
The photoelectrons are in the same path of the collector’s direction and the collector edge is considered to be positive in correspondence to the emitter edge. So, the current flow takes place internal to the circuit. When the level of radiation intensity is increased, then the amount of photoelectric current also increases.
Photocell Sensor
A photocell has also been termed a sensor that can be utilized for the purpose of sensing light. The crucial characteristics of photocell sensors are uncomplicated usage, requires minimal power for operation, minimal size, and economical too. As because of these features, photoelectric cell sensors are implemented in various kinds of applications across multiple domains. These are mainly described as Cadmium- Sulphide photocells and constructed by light-dependent resistors and photoresistors.

Photocell Sensor
Also, the main usage of this sensor is in light applications like light or at dark.
Circuit
The cell which is used in the photocell circuit is called a transistor switched circuit. The essential elements necessary for the construction of a photocell circuit are:
- Battery of 9V
- Resistors of 22K and 47 Ohms
- Jumper connecting wires
- Breadboard
- Transistor
- LED
The circuit of the photocell operates in two scenarios which are dark and light.
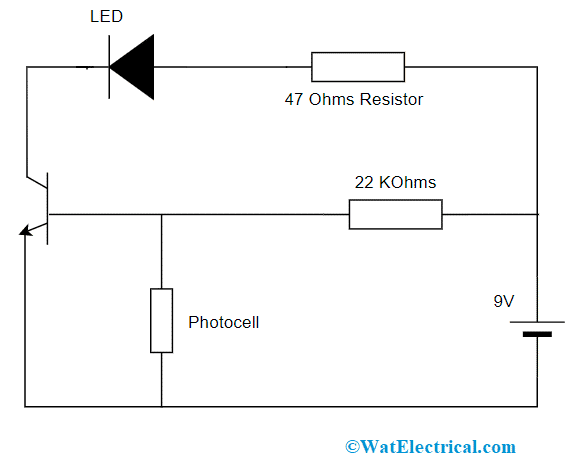
Photocell Circuit Diagram
In the darker scenario, the photocell resistance is minimal and current flow takes place in the 22KOhms resistor and in photocell and the performance of the transistor is such as the insulator. So, the path that consists of a resistor, LED1, and transistor will be in an OFF state.
In the lighter scenario, the photocell resistance is maximum and the current flow direction gets modified. So, at the transistor base, there will be minimum resistance. When the transistor’s base terminal receives power, then it operates such as conductor and the path that consists of a resistor, LED1 and transistor will be in OFF state and LED starts to blink.
Types
This section explains on types of photocell.
Photoresistor – These are light-dependent resistors where the level of resistivity towards electric current reduces corresponding to the amount of light exposure on it. This photoresistor is mainly implemented in-camera meters those work for camera and alarms and their applications.
Photomultiplier – These are the detectors that have a high level of sensitivity. The slightest wave of light is multiplied by more than 100 million times. This is also called a photoconductor.
This is a semiconductor with high resistivity. When the light that reflects on the device holds an increased frequency level, then the photons that are absorbed by the semiconductor provide sufficient energy for electrons to move to the conduction band. The output of the free electron and hole allows for conduction of electricity thus reducing the resistance value.
Golay Cell – These cells are used for the detection of infrared radiation. It has a tube with having a blackened metal plate where one of its ends is filled up with xenon gas. When infrared rays fall on the plate, it heats the xenon gas and distorts the variable diaphragm on the other end and the movement is utilized for the determination of energy source as output.
Photovoltaic cell – This type of photocell transforms solar to electric power energy. The photons that hit the electrons in the cell into higher energy develop a current in usable form.
Charge-Coupled Devices – These devices are mainly implemented in the scientific domain as a highly consistent and precise photosensor. The charges emitted by the sensors are utilized for analyzing multiple things ranging from huge galaxies to simple molecules.
Uses of Photocell
The photocell uses can be observed in many applications and today here are the few uses of photoelectric cells.
Sound Reproduction
This is used in sound reproduction in a movie. In a film, the sound is recorded in the film of actions using the manner of a slim translucent strip, and this strip is termed as the soundtrack. The transparency of this soundtrack is based on the change in frequency level of the sound that is recorded.
When the film is projected, the projector light of the soundtrack hits the photocell. As because of the change in soundtrack levels, there will be a change in the intensity of the sound and so the photo-electric current varies. Then the electric current gets amplified and supplied to speakers.
Burglar Alarm
The photocell is also employed in burglar alarms. The main purpose of this instrument is to safeguard from thieves. This device is mainly employed for detecting intruders and finding precious and expensive things from thieves.
A burglar alarm is included with a photocell and infrared light source. The light coming from the infrared source falls on the photocell which makes a constant photoelectric effect. When there is any deviation in the direction of infrared light because of the thief, then their will cut-off in the light that falls on the photocell and so no flow of photoelectric effect takes place. This activates the relay circuit and so the siren starts to shout.
Exposure Meter
In exposure meters also, photocells are used. This is the instrument implemented together with the camera in order to know the precise time of exposure of the film to have good pictures. For a picture to be perfect, when the light intensity is high, film exposure has to be minimal and vice-versa.
This exposure meter is constructed using a photocell, series-connected battery, and a sensitive milliammeter. The amount of photoelectric current developed in the cell has direct proportion with the amount of light intensity.
When the milliammeter deflection is less, the photoelectric current will also be minimum which indicates minimal light intensity so that exposure is maximum. In the same way, when the milliammeter deflection is more, the photoelectric current will also be more which indicates high light intensity so that exposure is minimal.
Applications of Photocell
- Photocells are used in television and also in photography devices
- Also employed for calculating the light intensity level and monitoring the fine shape of spectral lines
- Used in micro photometers, lux meters
- In various solar cells
- Photocells are also utilized for counting the number of vehicles on the road
- Photocells are even employed as sensors as well as switches
- Used in robotics domain such as guiding robots to conceal from view in the dark location or else to go along a beacon
- Implemented even in automatic lights for the activation of streetlights and this is especially dependent on daytime or dark time
- The photocells are even utilized in control systems, where the light’s beam interruption allows for opening a circuit thus makes a relay to get activated and this provides power for the operation of the door opening.
- Also used in the domains of spectroscopy and photometry
Know more about Radiation Hazards MCQs.
And this is all about the concept of the photocell. This article has provided the detailed concept of photocell working, its types, photocell sensor, uses, circuit, and applications. In addition, by conducting a photocell experiment, one can know more about how photocell works in real applications?