In this industrial era, the transformer stood as a crucial invention as it serves the requirements and necessities of multiple industries. The essence of the transformer lies completely in its energy conversion. Based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, Faraday expanded this concept to a transformer and even this device almost functions on the same principle. So, the primary kind of transformer that was invented in the induction coil. Whereas, the first alternating current transformers came into evolution in the year 1870 and there onwards the invention expands to release multiple kinds of transformers such as single-phase, double-phase, three-phase transformers, and many others. This article mainly focuses on the explanation of the three-phase transformer.
What is Three Phase Transformer?
Definition: It is a kind of three-legged tough core kind of transformer. Each of the legs holds its own primary and secondary winding connections. Here, most of the power is dissipated as a three-phase alternating current. In general, the power organized generators deliver electricity by the revolution of either three windings or coils with the support of the magnetic field. All the three windings are located at a position having 120 degrees in between each. Upon the coil’s revolution, power will be dissipated and transferred to the three lines. There has to be correct positioning of the windings so as to sync up with the receiving power and so to handle exact polarity levels and phasing. It is mostly employed for electric power broadcasts. These are either used to minimize or maximize the voltage levels required for power transmission. Three-phase transformer diagram is shown as:
three-phase- transformer
Three Phase Transformer Construction
The construction of three-phase transformers can be done either by core or shell. Generally, it is constructed by the utilization of magnetic core for primary and also for the secondary winding. And in core type of transformer, three single-phase transformers are connected which are of core type. And also, in shell type of transformer, three single-phase transformers are connected which are of shell type.
In a core type of three-phase transformer, the core part is constructed with three legs and two yoke parts which creates a magnetic path in between these. For every limb part, both the windings are wounded in a concentric path. Mostly, cylindrical coils are utilized as windings and each of the windings of single-phase is wounded on each leg. In the equilibrium situation, the magnetic flux in every single phase of the leg reaches to zero. So, in the general scenarios, there will be no requirement of the return leg. Whereas in the unstable scenario, there will be movement of extended current and because of this, three single-phase transformers are best to be implemented.
Working
The working of three-phase transformers can be explained as the scenario that the mutual induction between the primary and secondary windings are connected through the magnetic flux. In general, a transformer is constructed of two inductive coils and the two windings. These inductive coils are separated in an electrical way whereas connected in a magnetic way. When an A.C power source is passed through the primary winding, there happens the creation of magnetic flux across the winding. In order to establish a connection with a secondary winding, the core part shows a magnetic way for the flux. The amount of flux that gets associated with the secondary winding is termed as main flux or useful flux, while the amount of flux that is not associated is termed as leakage flux. As there will be an alternative kind of flux generation, EMF will be produced at the secondary winding based on Faraday’s law. And this induced emf is defined as mutually developed emf.
When the secondary winding is the closed loop, then there will be the flow of mutually induced current across it and so their happens the transfer of energy from one to another. This explains the flow of energy transformation from one circuit to another.
Three Phase Transformer Connections
The connections of a three-phase transformer will vary based on the way that the primary and secondary are connected. Based on the type of connection, the voltage and current levels will get varied. And the possible way of connections with these two windings are of:
- Star- Delta
- Delta-Delta
- Delta-Star
- Star-Star
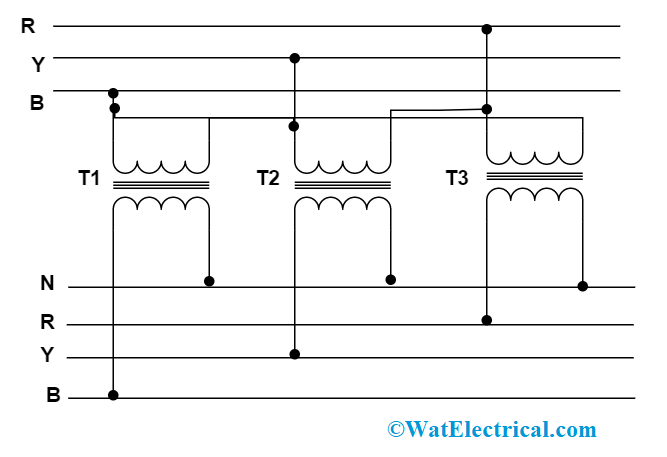
Star-Delta
This connection type is essentially utilized to minimize the voltage levels and employed mainly at broadcast end substations. Here, the primary winding is connected as star and secondary winding as the delta. The central point which is on the primary winding side is mostly grounded. The line voltage for primary and secondary windings is √3 times of the transformation ratio. In this type of connection, stable three-phase voltage is obtained either at the LV or secondary and in the case of instability, the flow of current will be at HV or primary side. The circuit connection is as below:
star-delta-connection
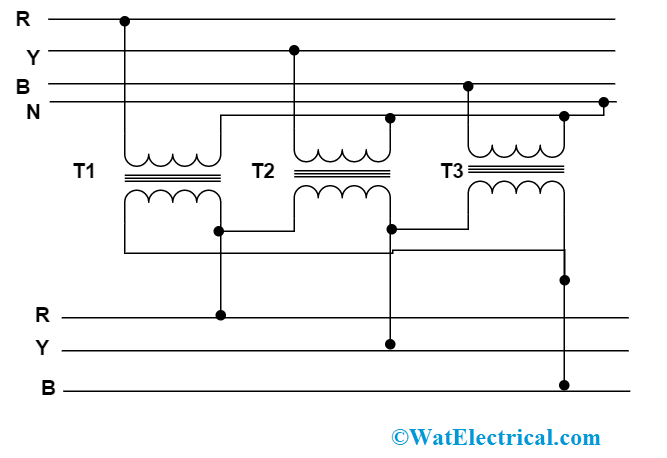
Delta-Delta
Here, the power supply is connected in delta way along with the primary and secondary windings and the secondary side requires maximum current with a single voltage. It is mostly implemented for three-phased motor applications. There exists 00 phase difference between both the winding voltages. Here, the three-phase voltages maintain good stability even in unbalanced load conditions thus delivers balanced loading. Here any of the failed transformers will not show an impact on the other. The circuit connection is as below:
delta-delta-connection
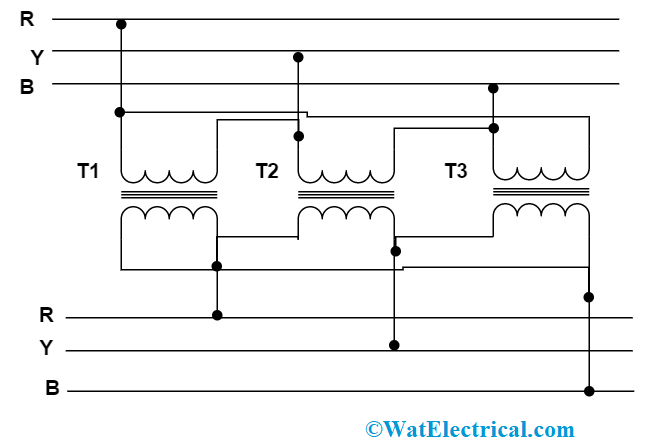
Delta-Star
This connection type is essentially utilized to maximize the voltage levels and implemented mainly at high-tension broadcasting systems. Here, the primary winding is connected as delta and secondary winding as a star where this allows for 3 four-phase wire methodology at the secondary winding. The voltage levels between the primary and secondary windings are in the ratio of 1:√3. In this connection, dual voltage levels can also be obtained. One can achieve minimal single-phase voltage levels when the wiring is made in between ground and phase. While maximum single-phase voltage levels are achieved when the wiring is made in between two phases. There exists 30 degrees phase difference between both the winding voltages. The circuit is connected as below:
delta-star-connection-in-three-phase-transformer
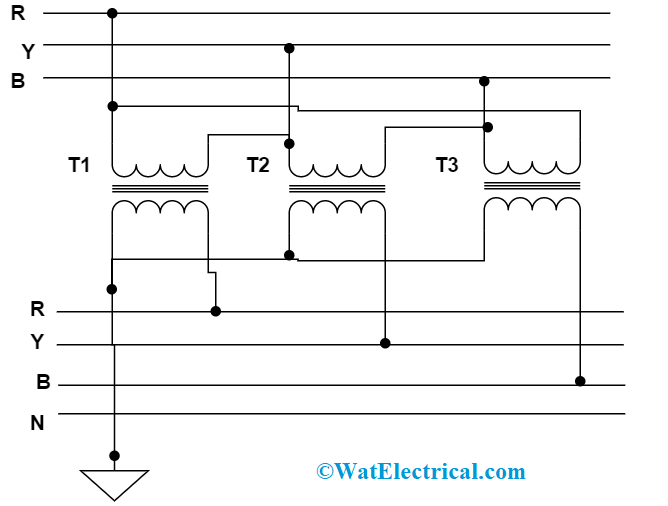
Star-Star
Here, both the windings are connected in star manner and there exits 300 phase difference in between the windings. One can gain accurate results in this connection only when the load is in a balanced condition. Whereas in the unstable condition, the change in neutral point leads to dissimilar phase voltage levels. The drawback in this is that the way of connection creates noise in the communication lines and thus because telephone lines can’t be operated in parallel. So, star-star is not widely implemented in the applications. The circuit is connected as below:
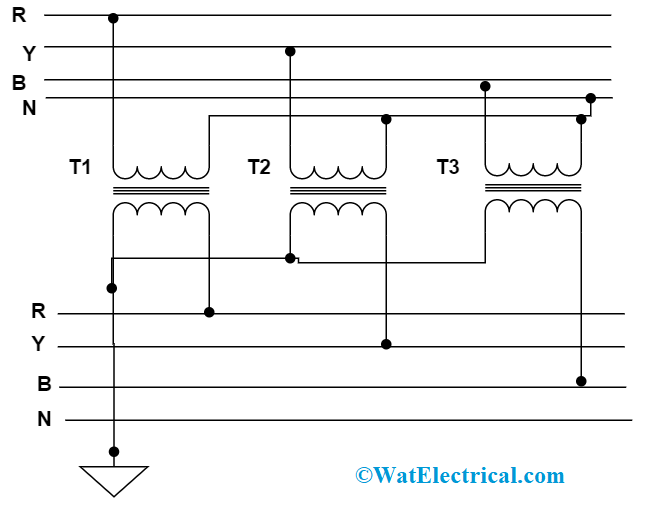
star-star-connection-in-three-phase-transformer
Advantages/Disadvantages of Three Phase Transformer
Few of the advantages of this type of transformer are as follows:
- Construction is simple and easy to handle
- Delivers maximum efficiency
- To deliver the same KVA ratings, there will be a minimum necessity of the core material than that of three single-phase transformers
- It is so economical so that every range of business can be implemented
The disadvantages are
- Sharing of core material results that failure of single-phase lead to all other phases failure too
- Metallic parts get easily heated which might lead to the damage of the entire device and when tried to cool down, there will happen a reduction in the capacity
- Cost inquired for the repair of the device is high
FAQs
1). What are the foremost kinds of transformers?
They are step-up and step-down transformers
2). What are the top-most applications of a three-phase transformer?
They are mostly used in electric grids, distribution, and power transformers.
3). What is the difference between single and three phases?
A single wire is necessary to connect the whole circuit in a single phase whereas in three phases it needs three wires and there will be variation in output voltage levels.
4). What does RYB in a three-phase define?
RYB corresponds to Red, Yellow, and Blue where each phase has an angular variation of 1200.
5). What happens when there is a breakdown in the neutral wire?
There will be leakage of electricity and causes electrical shocks.
Finally, this is all about the concept of a three-phase transformer. Apart from this, there exist multiple kinds of transformers depending on the industry necessity, kind of supply, utilization requirement, and voltage levels. So, it all depends on one’s own thoughts to choose the corresponding kind and gain success through its advantages. Know what are the other kinds of three-phase transformer?