The resistor was invented in 1827 by a mathematician namely “Georg Simon Ohm” at the University of Erlangen. After that, he published several research papers on the transmission of heat within molded circuits & also invented the “ohm law”. After this law invention, there are many types of resistors were developed. At present, we are using different types of resistors in so many electrical and electronic applications. This article provides brief information on different types of resistors – working and their applications.
What is a Resistor?
The resistor can be defined as; a two-terminal passive electrical component used to create resistance within the current flow. In almost all electronic and electrical circuits, these components are used. The resistance is simply measured in ohms and it is represented with the symbol ‘Ω’. The resistance normally occurs whenever 1A of current flows throughout a resistor with a 1V drop across its two terminals. The flow of current is simply proportional to the voltage across the two ends of terminals. So this ratio is simply signified by Ohm’s law (R = V/I).
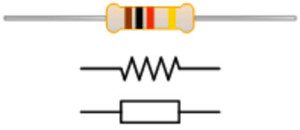
Resistor with symbol
Different types of resistors are mainly used for various purposes like restricting electric current, division of voltage, generation of heat, matching & loading circuits, setting time constants & gain control.
Please refer to this link to know more about a Resistor.
Different Types of Resistors
Generally, resistors are available in different types made from materials like manganin, nickel-chromium alloy, constantan & gold chromium. Each resistor has its own properties based on its construction & manufacture which are used in different applications. Generally, resistors are available in various sizes, shapes & materials. Generally, resistors are classified into two types linear resistors & non-linear resistors.
Linear Resistors
The resistors whose resistance value changes with the applied temperature & voltage are known as linear resistors. Linear resistors are classified into two types fixed resistors and variable resistors.
Fixed Resistors
The resistors which have fixed resistance value is known as fixed resistors. These are the most commonly used resistors that are used in different electronic circuits to set the right conditions. Fixed resistors are available in small sizes and are very cheap, so they occupy very less space. These resistors are consistent & also available in various ohmic & power ratings.
Fixed resistors are used in power supplies for decreasing the incoming voltage, used in different circuits to restrict the current flow & also used in heaters that need to dissolve heat energy. These resistors are available in different types like the following.
- Carbon Composition Resistors
- Wire Wound Resistors
- Thin Film Resistors
- Thick Film Resistors
Carbon Composition Resistors
Carbon composition resistors come under the types of fixed resistors which are made from fine carbon elements by mixing with a binder. These resistors are used to protect the circuits, limiting the flow of current, high-power lighting or strobe lighting, welding & high-voltage power supplies. These types of resistors are available from 1 ohm – 25 mega ohms range and also power rating ranges from ¼ watt – 5 Watts. Please refer to this link to know more about Carbon Composition Resistor.

Carbon Composition Resistors
Wire Wound Resistors
These resistors are made with an insulating core otherwise a rod is simply wrapped with a resistive wire like manganin, Tungsten, nickel or Nichrome, or nickel-chromium alloy whereas the insulating core is made with Bakelite, porcelain, ceramic clay material, or press bond paper.
The ohmic value of these resistors ranges from 1 ohm to 200k ohms & they operate very safely up to 350°C. Additionally, the high power wire wound resistor’s power rating ranges from 500 Watts whereas the resistance value of these resistors ranges from 0.1 ohm – 100k Ohms.
Wirewound resistors are normally used in industrial & high-power-based applications like fuses & circuit breakers.

Wire Wound Resistors
Thin Film Resistors
Thin film resistors are simply made with a resistive material and a high-grid ceramic rod. This resistor has a thin resistive layer arranged on top of a ceramic base. The thickness of this layer is approximately 0.1 microns. Thin Film resistors are applicable where high accuracy, and high stability otherwise less noise is required like monitoring, test & measurement, medical equipment, etc. These resistors are classified into two types carbon film and metal film resistors.

Thin Film Type
Carbon Film Resistor
Carbon Film resistor includes a core or an insulating material rod made with a substrate which is also called high-grade ceramic material. This insulating material rod contains a film overlaid or a thin resistive carbon layer around it. These types of resistors are extensively used within electronic circuits due to their wide operating range, stability & negligible noise as contrasted with solid carbon resistors.

Carbon Film Type
Metal Film Resistors
These resistors are similar as compared to carbon film resistors within construction except for the material used like metal. These resistors are available in very small sizes, low cost & reliable within the operation. The temperature coefficient of these resistors is very low like ±2 ppm/°C, so applicable where a low noise range & stability is significant in a circuit. These are also utilized in filter circuits, low-noise analog signal circuits & bridge circuits.

Metal Film Type
Thick Film Resistors
Thick film resistors are similar to thin film resistors except for the resistive material layer used. These resistors are made by simply applying a paste or resistive film, a glass mixture & conductive materials to a substrate. These resistors have high resistance values of up to 10 tera-ohms which are printed on a flat substrate or cylindrical either covered completely or in a variety of designs. These resistors provide high voltage capability, and high-temperature performance & are non-inductive inherently. So these are used in aerospace, medical, oil & gas based applications. These resistors are available in three types metal oxide, cermet film & fusible resistors.

Thick Film Type
Metal Oxide Resistors
Metal oxide resistor is made by simply oxidizing a Tin Chloride thick film on a substrate (heated glass rod). These types of resistors are accessible in a broad range of resistance through high-temperature stability. Additionally, the operating noise level is extremely low & they can be utilized at high voltages. These resistors are applicable where the dissipation of power requirements are > 1 W & high stability is necessary.

Metal Oxide Type
Cermet Oxide Resistors
Cermet oxide resistors are also known as network resistors. In these types of resistors, the internal region includes ceramic insulation materials. After that, a metal alloy film or carbon layer is wrapped simply around the resistor & after that, it fixes within a Cermet (ceramic metal). These are simply designed in a rectangular or square shape where the pins or leads are available under the resistors which are used for simple installation within PCBs.
Cermet oxide resistors provide a stable operation within high temperatures as their temperature values do not vary with changes in temperature. Cermets are normally used to make small surface-mount chip-based resistors, multi-resistor networks within a single package for PCBs & high-frequency-based resistors.

Cermet Oxide Resistor
Fusible Resistors
As compared to wire wound-type resistors, these resistors are similar. This resistor is fused whenever the power rating of a circuit is enhanced than the particular value which means it opens or breaks the circuit. These resistors are capable of performing double tasks they are used to limit the flow of current & also used as a fuse. So these are extensively used in Amplifiers, TV & other costly electronic circuits. So the ohmic value of these resistors is below 10 Ohms.
Fusible Type
Variable Resistors
If the ohmic resistance value of a resistor is adjusted either electronically or mechanically then it is known as a variable resistor. This resistor usually works by simply sliding a wiper over a resistive element. Once a variable resistor is utilized as a potential divider with three terminals then it is called a potentiometer. Whenever two terminals are used from this resistor, then it is called a rheostat.
When variable resistors are controlled electronically rather than by mechanical action then these are known as digital potentiometers. These resistors are simply used in different electronic devices used in our homes like speakers, radios, microphones, TVs, smart home control devices, oscillators, etc. These resistors are available in three types potentiometers, rheostats, and trimmers. Please refer to this link to know more about variable resistors.

Variable Resistors
Potentiometers
Potentiometers are three-terminal components mainly used for voltage level control within the circuit. In this resistor, the resistance in between two outside terminals is stable whereas the remaining terminal is simply connected with a wiper or moving contact which is not stable. The resistance value of this resistor can be changed by turning the wiper that is allied to the control shaft. The resistance value of these resistors is up to 10 Mega Ohms.
Potentiometers are used as voltage divider circuits, and TV & radio receivers for controlling volume, linearity & tone control. These are also applicable to medical equipment. Machines for wood processing machines & injection mold machines.

Potentiometers
Rheostats
These resistors include two or three terminals which are used for limiting current through hand or physical operation. These are also called variable wire wounds or tapped resistors. The construction of these resistors is the same as potentiometers, but used like a variable resistance but not as a potential divider.
Previously, rheostats were utilized as power control devices with the load in series like a light bulb. Currently, these are not used frequently for power control as this is an inefficient technique. So these were replaced with more efficient switching electronics for controlling power.

Rheostats
Trimmers
A resistor that has an extra screw with a variable resistor or Potentiometer for better operation & efficiency is known as Trimmers. The resistance value of this resistor is simply changed by simply changing the screw position to turn with a mini screwdriver. The materials used to make these resistors are carbon film, carbon composition, wire & cermet materials. The resistance value of these resistors ranges from 50 Ohms to 5 mega ohms. The power rating of these resistors ranges from 1/3 Watts – ¾ Watts.
Trimmers are used in adjusting the light brightness, controlling volume in audio equipment & used where electrical resistance needs to be adjusted within a circuit.

Trimmer Resistor
Non-Linear Resistors
In nonlinear resistors, the flow of current throughout it does not vary according to Ohm’s Law although, changes with applied voltage or temperature change. Additionally, if the current flowing throughout a resistor varies with changes in the temperature of the body, then these types of resistors are known as Thermistors. If current flows throughout a resistor changes with the voltages applied, then called a voltage-dependent resistor or varistor. Nonlinear resistors are classified into three types thermistors, varistors, and photoconductive cell or photoresistors or LDR.
Thermistor
The resistor whose resistance mainly depends on temperature is known as a thermistor because the resistance of the thermistor changes with temperature. When the heat increases then the resistance will be decreased. So this resistor is mainly used for control and measurement purposes. Thermistors are available in two types NTC & PTC.
The NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) is one kind of thermistor where the resistance of this decreases once the temperature increases. These types of thermostats protect the devices from over-voltage situations. The PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) is another type of thermistor where the resistance of this resistor increases when the temperature increases. So these are used in protecting the devices from over current conditions.

Thermistor
Varistors
A varistor is also known as VDR or voltage-dependent resistor. The resistance of whose resistor changes with the applied voltage. When the applied voltage increases, then the resistance of the varistor will be decreased. Similarly, if the applied voltage reduces, then resistance will be increased. Varistors are applicable approximately in all small electronic designs to heavy electrical circuits. These resistors provide high-voltage surge protection for both AC & DC circuits.

Varistors
Photo Resistor
The resistance values of whose resistor changes with light are known as photoresistors. Whenever the light increases then the resistance will be decreased. This resistor is also mainly used for control & measurement purposes. A photoresistor is also known as light dependent resistor or LDR.

Photo Resistor
Surface Mount
Surface mount resistors are also called chip resistors because the resistive material of these resistors is integrated into a ceramic chip. These types of resistors are extremely small compared to regular resistors, so they occupy very less space. These resistors are very effective & dissipate less amount of heat. These resistors are extensively used along with another surface mount-based electronic components. Now, most industrial or consumer electronics are manufactured with surface mount technology.

Surface Mount
The surface mount technology simply allows the electronic components to be arranged and soldered on the PCB easily through an automated process. These resistors offer the same functionality as the fixed axially leaded resistors with a low power dissipation capacity, lower stray capacitance & inductance, etc. These resistors are available in different sizes with popular values like E3 to E192. Some of them are small and very hard to handle physically.
Please refer to this link to know more about pull-up and pull-down resistors.
Resistors Color Code Calculation
Generally, resistors are very small, so it is very hard to print resistance values onto the tiny surface region of the resistor. As a result, instead of printing numbers directly onto the resistor, color codes are utilized.
Resistors are normally available with different color codes. So, the color code is simply provided with different color bands which specify the value of resistance, the tolerance & sometimes the failure rate/ reliability. The number of bands in the resistor varies from 3 bands to 6 bands. In a three-band resistor, first, two bands indicate the value of resistance whereas the remaining band serves as a multiplier.
The resistor color code chart is shown below. This chart simply determines the resistance as well as tolerance values of resistors. This color code table is used to specify the color bands once the color values are known so that we can find the values of the resistor very quickly.
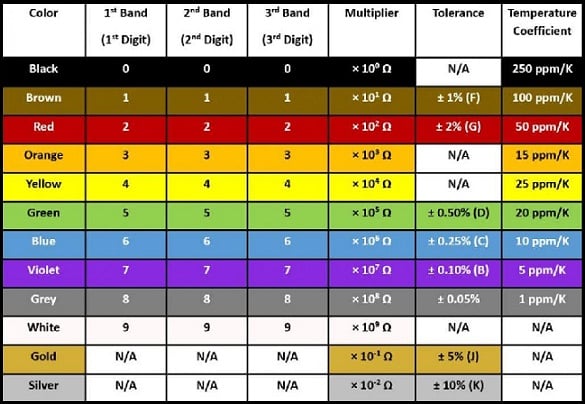
Resistor Color Code Chart
To remember these color codes, need to remember the acronym like BBROYGBVGW (B.B. Roy of Great Britain has a Very Good Wife). So, understanding the resistor color code is significant in order to obtain the right resistor value. The color-coded bands are being read from the left side to the right side.
Digit, Digit, Multiplier = First Colour Band, Second Colour Band x 10 Colour in Ohm’s
For instance, if a resistor includes these color codes like Yellow Color Violet Color, and Red Color then these color code values are 4, 7 & 2, so the resistance value will be 4 7 x 10^2 = 4700Ω (or) 4k7 Ohm.
For 3 Band Resistor Color Code
In three band color code resistor, the 1st two color bands denotes always the first two resistance value digits whereas the third band signifies the multiplier (XY × Z ± 20% ).
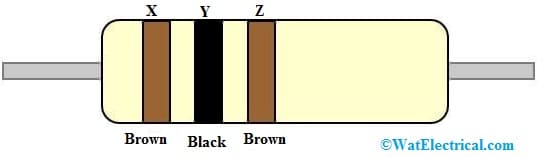
3 Color Band Resistor
In the above three band resistor, the first band color is brown, the second band color is black & third band color is brown. So, from the color code chart, the first brown color band value is ‘1’, the second black brown band color value is ‘0’ and the 3rd color band is brown, which means the multiplier is ‘1’. So the resistance value of the 3-band color code resistor value will become 10 × 10^1 ± 20% => 100 Ω ± 20%. The three-color band resistor doesn’t have a 4th tolerance band, so the tolerance value can be taken as 20% by default.
For 4 Band Resistor Color Code
The four-color band resistor is the most frequently used resistor. Like a three-color band resistor, the four-color band resistor also gives the resistance value from the first two digits. The third band signifies the multiplier and the 4th band signifies the tolerance value (XY × Z ± D%)
For this resistor color code, the first color like brown color value is ‘1’, the second band color value is red – 2, and the third color band value is green -5 which is the multiplier, so the value will become 12 × 10^5 = 1,200 kΩ. Finally, the tolerance band is gold that a value is ±5%. So this four-color band resistor resistance value will become like 12 × 10^5 ±5% => 1,200 kΩ ± 5%.
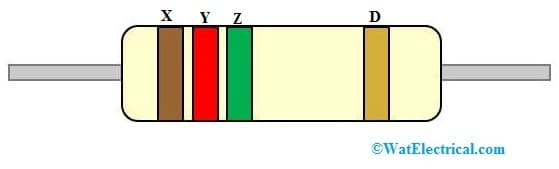
4 Color Band Resistor
For 5 Band Resistor Color Code
For five color band resistor, the first three color bands indicate the significant resistance digits, the fourth band is a multiplier and the last band is the tolerance (XYZ × D ± E%). In the above 5 color band resistor, the first band is yellow color – 4, the second band is violet color -7, the third band is blue-6 and the fourth color band is black which gives a multiplier value of 10^0. Using the formula, we get the resistance value of 476 × 10^0 = 476 Ω. Finally, the tolerance color band value is brown, so its tolerance value is ±1%. So this five-color band resistor resistance value will become like 476 × 10^0 ± 1% = 476 Ω ± 1%.
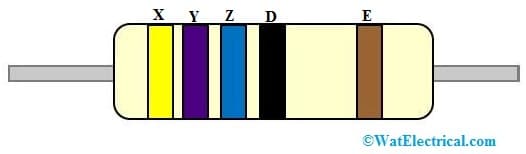
5 Color Band Resistor
For 6 Band Resistor Color Code
For six color band resistor, the first three color bands indicate the significant resistance digits, the fourth band is a multiplier, the fifth band is the tolerance and the final band indicates the temperature coefficient value (XYZ × D ± E%, F).
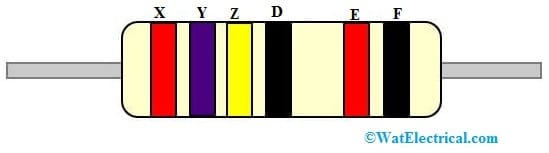
6 Color Band Resistor
For a six-color band resistor, the first three color bands are red – 2, violet- 7 & yellow – 4 respectively. The fourth color band is black which is a multiplier value of – 10^0. So the resistance value of this resistor will become 274 × 10^0 = 274Ω. The fifth color band indicates the tolerance value (±2%) and the sixth color band is a temperature coefficient value. For the black color, the temperature coefficient value is – 250 ppm/K. So this six-color band resistor resistance value will become like 274 × 100 ± 2%, 250 ppm/K => 274 Ω ± 2%, 250 ppm/K.
How many types of resistance are there?
There are two types of resistance are there fixed value resistance and variable value resistance.
What is the color codes for resistors?
The color codes are printed on resistors that represent the electrical resistance.
What is an example of resistance?
An example of resistance is an electron trying to make its own way through a wire.
What are the colors of resistors?
The resistor’s different colors are; black, brown, red, orange, yellow, green, blue, violet, grey & white.
What is the purpose of a resistor?
The purpose of a resistor is to restrict the flow of current within a circuit.
Please refer to this link to know more about Electrical Drive MCQs, Resistors MCQs
Thus, this is all about brief information on types of resistors with color code calculation. These are the two-terminal passive electrical components used to implement electrical resistance like a circuit element. These are the most essential electrical components which are used for many purposes like current flow reduction, signal level adjustment, bias active elements, divide voltages, etc. There are different types of resistors available where fixed resistors have fixed resistance values that simply change resistance slightly through time, temperature, or operating voltage. The variable resistors are mainly used for adjusting different circuit elements like a lamp dimmer or volume control. Here is a question for you, what is resistance?