A relay is a four-terminal electrical switch, used to control any electrical circuit with an independent low-power signal and also to control various electrical circuits with a single signal. The terminals of the relay mainly include; common, coil, NO (normally open) & NC (normally closed). Generally, in long-distance telegraph circuits, relays were employed as signal repeaters. After that, these were used widely in telephone exchanges and early computers for achieving logical operations. Relays are generally available in different types like reed, protective, thermal, electromagnetism, reed, Buchholz relay, Solid-state, and many more. This article provides brief information on one of the types of relays – protection relay (protective relay), working & its uses.
What is a Protection Relay?
A relay that is used to detect the faults of the circuit breaker and start the circuit breaker operation to disconnect the system’s faulty element is known as a protective relay or protection relay. These kinds of relays are compact and self-contained devices and they simply observe the abnormal conditions happening in the circuits by simply measuring the electrical quantities frequently which are different in normal and fault conditions. The electrical quantities in fault conditions like voltage, current, frequency & phase angle may change. The protective or protection relay diagram is shown below.
Working Principle
Protection relays mainly work on the two basic principles such as; electromagnetic attraction and induction. Electromagnetic attraction relay works on two AC and DC supplies which attract the relay coil in the direction of electromagnet poles. These kinds of relays work immediately and it does not get delayed. Electromagnetic induction relay mainly works on AC supply by using the induction motor for generating the torque. Thus, these are used regularly as directional relays for protecting the power system and are also used in high-speed switching operation applications.
This relay works by protecting any device or system whenever a fault is observed. Whenever the fault is noticed within a device, then the location of the fault can be found after that it gives the tripping signal to the CB (circuit breaker).
Protection Relay Types
Protective relays are available in different types which are used based on requirement.
Electromechanical Relays
An electromechanical relay is a type of relay that works with a produced magnetic field through an electromagnetic coil when a control signal is applied to it. These types of protective relays are known as the earliest relays however they are still used in a lot of areas. These are electromechanical because they include moving contacts within the output circuit that are functioned by applying simply an electrical signal.
This kind of relay simply modifies the voltages and currents to magnetic, and electric forces as well as torques that drive beside spring strains in the relay. In the relay, the taps and spring strain on the electromagnetic coils are the major processes by which an operator sets in a relay.

Electromechanical Relay
Overcurrent Relays
The relay which works only whenever the current value is higher as compared to the setting time of the relay is known as the over-current relay. This type of protective relay protects the power system’s equipment from the faulty current. Over-current relay has a pick-up value & this kind of relay triggers whenever the quantity & measurement of current go above the pickup value.
These types of protective relays are classified into two types; time-delay & instantaneous which are provided frequently in a single container. These relays are triggered by a similar current; however, their separate pickup values are changed separately by adjusting the tap settings in the input.
These protective relays are not costly and thus utilized in low-voltage circuits & high-voltage system-based applications. The main drawback of this type of relay is, it can also choose the fluctuations in current as well as the faults in the near regions.

Overcurrent Protective Relay
Directional Relays
Directional relays work by detecting the current flow within a particular direction for which only they are installed. This relay detects a variation between the actuating & reference current. This kind of protective relay can be used in combination with over over-current relay to improve the selectivity and capacity of the relay system. Directional relay responds to the phase difference angle simply in between both the reference & actuating current which is called the polarizing quantity.

Directional Protective Relay
Pilot Relays
A pilot relay is a type of protection relay that is applicable on some multi-terminal lines where reclosing & high-speed tripping is not necessary, although the circuit configuration makes it not possible for a distance relay to offer even the modest speed that may be necessary.
This is a kind of electrical switch, used for controlling electrical devices’ operation. This relay normally uses a small amount of current for controlling a large current by allowing exact control above the connected device operation.

Pilot Type Relay
This relay is used for determining the fault inside or outer of the protected line. When the fault is inside to the protected line, all the CBs at the line terminals at the highest speed are tripped. Likewise, if any fault is outside the protected line, the tripping of CB is avoided or blocked. These relays are available for power, wire power line carriers, and microwave pilots.
Differential Relays
The relay that operates based on the two or above electrical quantities phase difference is called a differential protection relay. This relay simply works on the comparison principle between the phase angle & the equivalent electrical quantities magnitude.
For instance, if we consider the main comparison for the input & output current of the transmission line, then the input current’s magnitude for the transmission line is above the output current’s magnitude, and the extra current will flow throughout it due to the fault. So the main difference within the current can control the differential relay.

Differential Protection Relay
Distance Relays
This protection relay is most frequently used for protecting transmission lines and it also measures the impedance from the installation side to the location of fault & works in response to changes within the ratio of current & voltage measured. This type of protective relay is used to differentiate between typical operating conditions and a fault. This relay also differentiates faults in a specific region and also in a different part of the system.
For a specific range of pickup values of impedance, the operation of this relay is not enough. This kind of distance relay picks up when the measured impedance is low or equal to the chosen value of pickup impedance.

Distance Type
The voltage and current parameters in this type of relay are balanced from each other. This relay responds to the ratio of these parameters which is the transmission line impedance from the location of the relay to the interest point. This impedance can be used for determining distance throughout a transmission line, so it is called a distance relay. These kinds of protective relays are accessible in different kinds such as; mho, reactance, and impedance relays.
Protection Relay Circuit
A protection relay is a switchgear device used for detecting the fault & starts the CB operation to separate the faulty element from the rest of the system. These relays are self-contained & compact devices that are used for detecting strange conditions within the circuits by measuring different electrical quantities constantly like current, voltage, phase angle & frequency. These are dissimilar under standard & fault conditions. In fault conditions, electrical quantities may change. So, during the changes within minimum one or above quantities, then faults signal their type, presence & location to the relays.
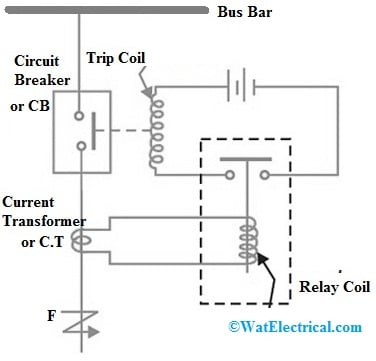
Protective Relay Circuit Diagram
The circuit diagram of the protective relay is shown below. The following circuit shows the 1-phase of a three-phase system for ease. This circuit can be built with a bus bar, relay coil, current transformer, circuit breaker, and trip coil. The connections of this relay circuit are divided into three parts which are discussed below.
The primary part of this circuit is the current transformer’s primary winding which is connected simply in series through the line to be guarded.
The next part of this circuit is the current transformer’s secondary winding, the CB (circuit breaker) & the relay operating coil.
The last part of the circuit is the tripping circuit which may be either DC/AC. This part includes a supply source, the circuit breaker’s trip coil & the stationary contacts of the protective relay.
Working
The protection relay circuit works; whenever a short circuit in the circuit takes place at the ‘F’ point over the transmission line, then the flow of current will enhance within the transmission line to a huge value. This results in a heavy flow of current throughout the relay coil to make the protective relay function by simply closing the relay contacts.
In turn, the circuit breaker’s trip circuit will be closed to make the CB open & separate the defective segment from the system. In this manner, the protective relay confirms the security of the equipment of the circuit from harm. The protective relay’s main function is to cause the on-time front service removal of any element within the power system once it begins to function in a strange way otherwise interferes with the efficient process of the system.
Protection Relay Functions
The functions of protection relays are discussed below.
- The protection relay’s main functions are; the detection of fault presence, fault location, fault type, etc.
- This relay helps in closing the trip circuit and operates the CB to separate the faulty system.
- It improves the system’s reliability, performance, stability & service continuity.
- The faults cannot be avoided totally but can be reduced.
- It avoids subsequent errors by separating the unusual operating element to keep away from interference or damage in the efficient operation of the system.
- It detects the faults like short circuits.
- It detects irregular operating conditions like unbalances, overloads, frequency or low voltage.
Functional Characteristics
The functional characteristics of the protection relay are discussed below like reliability, sensitivity, selectivity, and speed are discussed below.
Reliability
A protective relay must be reliable & also work whenever it is necessary. Each electrical circuit and its components which are involved within the relay operation are very important & they must be considered as a possible failure source. Some failures can be decreased by consistent design supported by regular maintenance. Some design features & manufacture will make these relays reliable inherently are; high contact pressures, good contact material, well-braced joints, robust construction & dust free enclosures,
Selectivity
This relay should be capable in choosing the system element which is defective & must separate it from the strong one.
Speed
A protection relay should be fast otherwise they may cause harm to the system & the equipment. This relay’s operating time ranges from 30 – 100 ms based on the level of fault. In addition, these relays should not be very fast otherwise it results in not preferred operation throughout transient faults like lightning surges.
Sensitivity
The protective relay’s sensitivity refers to the least value of activating quantity at which the protective relay starts operating in relation to the minimum value of fault current in the protected zone.
Protection Relay Codes
The protection relay ANSI codes within the design of the power system indicate what features a protecting device supports like a circuit breaker or relay. These protecting devices help protect components & electrical systems from damage whenever a fault occurs. These codes are helpful in recognizing microprocessor devices’ functions based on medium voltage. So the ANSI codes of protection relay are discussed below.
The current functions protection using ANSI codes are discussed below.
- The phase-over current is indicated by ANSI 50 or 51.
- Earth fault is indicated by ANSI 50N or 51N otherwise 50G or 51G.
The breaker failure is indicated by ANSI 50BF.
The negative sequence or unbalance is indicated by ANSI 46.
The thermal overload is indicated by ANSI 49 RMS.
The directional current protection using ANSI codes is discussed below.
- The directional phase over current is indicated with ANSI 67.
- The directional earth fault is indicated with ANSI 67N or 67N.
The directional power protection using ANSI codes is discussed below.
- The directional active over power is indicated with ANSI 32P.
- The directional reactive over power is indicated with ANSI 320 or 40.
The function of machine protection using ANSI codes is discussed below.
- The phase under current is indicated with ANSI 37.
- The locked rotor (or) severe starting time is indicated with ANSI 48 or 51LR/14.
- The start for each hour is indicated with ANSI 66.
- The voltage or restrained over current is indicated by ANSI 50V/51V.
- Buchholz or thermostat is indicated with ANSI 26/63.
- Temperature monitoring is indicated with ANSI 38/49T.
The protection function of voltage using ANSI codes is discussed below.
- The positive series under voltage is indicated with ANSI 27D.
- The remanent under voltage is indicated with ANSI 27R.
- Under voltage is indicated with ANSI 27.
- Overvoltage is indicated with ANSI 59.
- Neutral voltage displacement is indicated with ANSI 59N.
- A negative sequence overvoltage is indicated with ANSI 47.
The frequency protection function using ANSI codes is discussed below.
- Over frequency is indicated with ANSI 81H.
- Under frequency is indicated with ANSI 81L.
- The frequency rate change is indicated with ANSI 81R.
- The frequency rate change is indicated with ANSI 81R.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of protection relay include the following.
- The protective relay monitors frequency, current, voltage, and power continuously.
- This relay reduces the fire risk.
- This relay enhances the stability of the system by separating faulty sections.
- This relay simply clears the fault in no time & therefore it reduces the injury.
- This relay helps in detecting the failures of the system & separates faulty segments from the system.
- This relay provides electrical security by protecting the working person on the system.
- This relay enhances the stability of the system during the defective section isolation.
- This protective relay notices failures and faults within the system.
- These relays operate very fast and this relay is very fast to reset.
- This protective relay can be used in both power supplies.
- These types of relays work within milliseconds and their result is instantaneous.
- These relays are very simple, compact, robust and reliable.
The disadvantages of protection relays include the following.
- High maintenance, slow response time & its functionality is limited.
- These relays cannot execute communication tasks or complex logic.
- These types of relays have mechanical failures & contact erosion.
- It needs testing, unlike static relays.
- The operation of this relay can be simply affected because of the dust, components aging & pollution.
- Its operation speed is limited by the component’s mechanical inertia.
- This relay cannot evade faults in a power system, thus, this spends extra time monitoring the power system.
Applications
The applications of protection relay include the following.
- A protection relay is used to protect the device whenever a fault is noticed in a system. Once any fault is noticed, then the location of the fault can be found to provide the tripping signal for the CB.
- The distance protection relay is used to give protection for sub-transmission lines or Transmission.
- A differential protection relay is used to protect the transformers, motors, or generators.
- This type of relay is employed to serve electrical protection.
- This relay helps in detecting an error throughout its early stage and considerably decreases or removes harm to equipment.
- This relay is a switchgear device utilized for detecting faults and starts the operation of CB to detach the defective element in the system.
- These relays help protect medium-voltage, high-voltage, and protection currents to complex distances.
What is a protection relay used for?
A protective relay is used to trip a CB (circuit breaker) once a fault is noticed.
Is relay a protection device?
A relay is a protection device that gets inputs, evaluates them to set points & gives outputs. Here inputs can be voltage, current, temperature & resistance.
What is the application of under voltage relay?
The application of an under-voltage relay is to protect against voltage drops and for detecting short-circuit faults and many more.
Thus, this is an overview of the protective relay or protection relay, working, circuit, types, functions, codes, characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and its applications. Here is a question for you, What is the function of a relay?