Generally, a metallic conductor’s electrical resistance increases when temperature increases. These conductors are used by resistance thermometers to measure the temperature. A resistance thermometer is a precise temperature sensor used to determine temperature by the difference within a conductor’s resistance. This thermometer is best for measuring temperature with high precision due to good linear characteristics above a wide range of temperatures and stronger. This article provides brief information on a resistance thermometer, its working & its applications.
What is Resistance Thermometer?
The resistance thermometer is a sensor that uses an electrical conductor’s resistance to measure the temperature. The conductor’s resistance will change with time so this conductor property is used mainly for temperature measurement. So the resistance thermometer provides a positive change within resistance through temperature. These are capable of measuring the temperature precisely and also measure extremely low temperatures. These thermometers are not applicable for high-temperature measurement.
The materials used for resistance thermometer with operating temperature include; Platinum (260 to 110 Degrees Centigrade), Nickel(20 to 200 Degrees Centigrade), Copper(70 to 120 Degrees Centigrade), and Tungsten(200 to 1000 Degrees Centigrade).
Working Principle
A resistance thermometer simply works on the positive temperature coefficient principle. This principle states that a metal’s electric resistance is directly proportional to temperature. So when temperature increases then metal’s electrical resistance can also be increased. Thus, the electrical wire of any known material’s temperature can be measured simply if we measure its resistance.
Construction
The construction of a resistance thermometer is shown below which is arranged within the protective tube to protect injure. The resistive element which is made with copper steel or stainless steel can be formed simply by arranging the platinum wire above the ceramic bobbin. This resistance element is placed inside the tube which is made up of stainless steel or copper steel. The resistance element can be connected with the external lead using lead wire where this wire is covered by the insulated tube to defend it against a short circuit. The ceramic material can be used for high-temperature material as an insulator whereas fibre/glass is used for low-temperature.
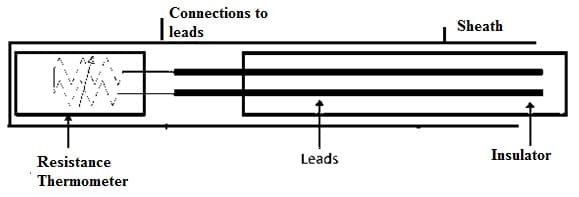
Resistance Thermometer Construction
Working
The working of resistance thermometer is, whenever the tip of this thermometer is located close to the heat source then heat can be distributed uniformly across the resistive element. The changes within the resistance change the element’s temperature and the final resistance can be measured. The variation within temperature can be measured using the following equation.
R0(1 + α1T + α2T^2+ α3T^3+……+αnT^n+…).
From the above equation, ‘R0’ is the resistance at T = 0 temperatures whereas α1, α2, α3……..αn are constants.
There are two approximations; linear and quadratic by which the temperature of the resistance thermometer can be measured by temperature variation.
Linear Approximation
The linear approximation is the method of estimating the resistance-temperature correlation with a linear equation.
![]()
where ‘Rθ’ is the approximation resistance @ θºC.
Rθ0 is the approximation resistance @ θ0ºC.
Δθ – θ – θ0 change within temperature ºC.
αθ0 is the resistance temperature coefficient @ θ0ºC.
Quadratic Approximation
This type of approximation provides a precise approximation for the resistance temperature correlation. The approximation can be expressed simply in the quadratic equation form.
![]()
‘α1’ is a linear fractional change within the resistance.
‘α2’ is a quadratic function change within the resistance.
The resistance thermometer is extremely less sensitive & the metal used to make the resistive element is not expensive.
Types of Resistance Thermometer
These are classified into different types based on sensing element, based on configuration which is discussed below. Resistance thermometers based on sensing element material are; platinum resistance thermometers and nickel resistance thermometers.
Platinum Resistance Thermometer
The platinum resistance thermometer is the most frequently used thermometer within industrial applications because it has outstanding corrosion resistance, long-term stability & a wide variety of temperatures from -200 to to1200°C. The working principle of this thermometer is that the platinum resistance changes through the temperature change because it uses platinum material for deciding the temperature. Platinum (Pt) is an unreactive metal that can be drawn easily into fine wires, so it is used mainly as a sensing element within a thermometer. The most commonly used platinum resistance thermometers are Pt100, Pt500 & Pt1000.

Platinum Resistance Type
Nickel Resistance Thermometer
The thermometer that uses Nickel as a sensing element is known as a Nickel resistance thermometer. These thermometers are less expensive because their construction is simple as compared to the platinum type. The nickel material in this thermometer is more subject to corrosion over time & loses its accuracy at high temperatures. The temperature range of this thermometer is from -80 to +260 ° C).

Nickel Resistance Type
Copper Resistance Thermometer
The thermometer that uses Copper as a sensing element is known as a Copper resistance thermometer. Copper material has a very linear resistance–temperature relationship, but it oxidizes at moderate temperatures & cannot be utilized above 150 °C (302 °F). These types of thermometers are inexpensive and they have a small difference in temperature characteristics. But because of their small resistivity, their size cannot be decreased.

Copper Resistance Thermometer
Resistance Thermometer Circuit Diagram
The circuit diagram of the platinum resistance thermometer is shown below. The changes within resistance can be caused by change in temperature which is detected by the following Wheatstone bridge. So, the temperature-sensing element within this circuit is platinum. The Rs sensing element is made with a material that has a high-temperature coefficient whereas R1, R2 & R5 are made with resistances that are stable practically in normal temperature changes.
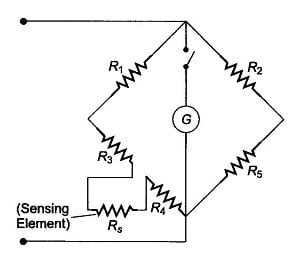
Resistance Thermometer Circuit Diagram
Whenever there is no flow of current throughout the galvanometer (G), then normal Wheatstone’s bridge principle states the ratio of resistance is
R1/R2 = Rs/R5
The sensing element in normal practice is away from the indicator where its leads have an R3, R4 resistance. Therefore,
R1/R2 = R3 + Rs + R4 /R5
Now ‘Rs’ resistance changes and the balance cannot be maintained. So the galvanometer will show a deflection that can be calibrated to provide an appropriate temperature scale.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of resistance thermometers include the following.
- Resistance thermometers are very easy to install & also replace.
- Its operating temperature is wide and ranges from 200 to 1000 Degrees Centigrade.
- It has better sensitivity.
- This thermometer has good accuracy.
- They have nearly linear characteristics.
- These are suitable for remote indication.
- These are very accurate in temperature measurement.
- Its performance stability is the long period.
- These are available in small sizes.
- Differential temperature measurement is possible.
- The response time of resistive element is from 2sec to 10sec.
- Above one resistance element is clubbed to a similar indicating or recording instrument.
- No need for temperature compensation.
- The resistive element diameter is about 6 to 12 mm & length is 12 to 75 mm.
- The error limits for a resistive element are ± 0.25% for the scale reading.
What are the Limitations of the Resistance Thermometer?
The limitations of resistance thermometers include the following.
- These are expensive.
- They need a bridge circuit including an external power supply.
- There is a self-heating possibility.
- They need large-size bulbs for high-temperature measurement.
- It takes more time for bridge balancing.
Where are resistance thermometers used?
The applications of resistance thermometers include the following.
- The resistance thermometer is used to measure environmental temperatures.
- These are used frequently for measuring very high temperatures.
- These are used wherever continuous temperature control & measurement is necessary.
- These devices measure temperature in remote areas.
- These are used to measure temperature within drying ovens, heating ovens, pressure vessels, etc.
- It is used to measure radiant heat, used in food processing plants and petrochemical industries.
- These are used in AC and refrigerating applications.
- These are used for exhaust gas temperature measurement.
- Resistance thermometers are used for temperature measurement of boilers, cold storage plants, power generators, etc.
What is the range of the resistance thermometer?
The measurement range of platinum resistance thermometers is from-200 to +660°C or-328 -+1220°F, copper type is 0 to +180°C or 32 to +356°F, Nickel type is from -50 to +300°C or -58°F to +572°F and Platinum-cobalt type is from -272 to +27°C or -457.6 to +80.6°F.
Is infrared a thermometer?
Yes, this thermometer uses the IR radiation concept to decide an object’s surface temperature without any physical contact.
To know your understanding try few of the questions on RTD Sensor MCQs.
Thus, this is an overview of resistance thermometer, their working, types, advantages, disadvantages, and their applications. Resistance thermometer is an indispensable tool that has reliability, versatility & accuracy which have made them important in various manufacturing to healthcare industries. Understanding this thermometer’s principles & applications will empower researchers, engineers, and technicians to make informed choices and ensure the efficient working of processes & systems. Here is a question for you, what is the thermometer?