In the subject of chemistry, a condenser is considered as a laboratory tool that is utilized for the condensation of vapors along with other activities such as extraction, distillation, and reflux. There are various kinds of condensers that are developed for a variety of purposes and processes. Today, there are various condensers such as Graham, Liebig, West, Spiral, Coil, and others. This article explains one of the most popular types of the condenser and is Surface Condenser definition, its working principle, types, design, and applications.
What is Surface Condenser?
The surface condenser is considered as an instrument that is mostly used for steam to water conversion making no physical between coolant and steam. The alternative terminology for this device is tube and shell heat exchanger. These are the heat exchangers where conversion happens from gas to liquid type below the level of atmospheric pressure.
Design and Surface Condenser Working
In the surface condenser design, it has a cylindrical-shaped condenser that has a huge cylindrical vessel. Inside the cylinder, water tubes are mounted in a horizontal way which allows for continuous water flow into the tubes. The water flow direction in the upper section and lower section of the tubes are in opposite paths.
The device has both inlets and outlets for water flow and in the cylindrical vessel there exist two water storage tanks located at the two edges of the vessel and these two are separated by a baffle. From the steam inlet section, the steam flows into the cylinder. Also, a valve is present at the condenser bottom where the extraction of the condensate takes place. Both the perforated tubes are in a perpendicular direction to the tubes that carry water. This is how a surface condenser is constructed.
In the surface condenser working principle, its fundamental functionality is heat transfer from a higher temperature value to a low value which means that steam releases its heat to the water tube to cool down the temperature levels. And in the procedure of transferring heat, the steam is transformed into water.
The hot steam arrives in contact with water tubes by moving from steam inlet and the water after entering into tubes has a revolving flow. Once the contact of water tubes and steam takes place, heat transfer is initiated. Then, the steam is removed from heat and transformed into a liquid which is now called condensate. Now, the removal of condensate takes place from the vessel using a value that is present at the cylinder’s bottom level.
Efficiency
The surface condenser efficiency is defined as the ratio between actual vacuum and maximum attainable vacuum.
This is represented as
Vacuum Efficiency in % = [(Actual volume)/(Atmospheric pressure – Absolute pressure)] * 100
Surface condenser efficiency = [(Difference in the temperatures of cooling water inlet and outlet)/(Temperature of vacuum – Temperature of condenser inlet)] * 100
(T2 – T1)/(T3 – T1) * 100
Where T1 corresponds to the temperature of condenser inlet cooling water
Where T2 corresponds to a temperature of condenser outlet cooling water
Where T3 corresponds to vacuum temperature or absolute pressure present in the condenser
Surface Condenser Types
Generally, there are mainly two kinds of surface condensers which are
- Water-cooled type
- Air-cooled type
When there is a minimal necessity of water, an air-cooled type of condenser is utilized which is more pricy and it does not hold the ability to achieve as a minimum a steam turbine dissipate temperature than that of water-cooled type of surface condenser.
Whereas the further classification of surface condensers are of five types:
Downflow type – Here, hot steam moves from the condenser top section, and it flows in a downward direction in regard to the entire system. The steam flow is in the -ve path because of the vacuum developed by the air pump and gravitational flow. Here is the surface condenser diagram of the downflow type.
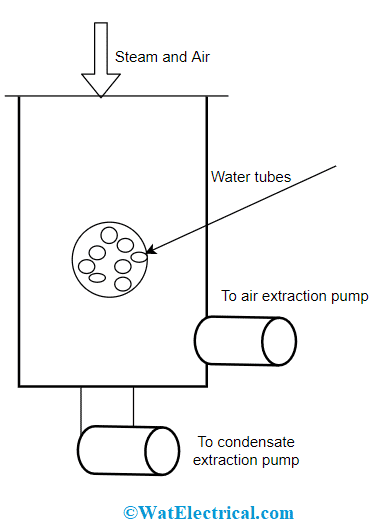
Downflow Type
As water flow is in an upright direction to the steam flow, in between these water tubes are present and the baffle exists in the condenser where it does not permit steam to enter into air filters. Immediately, when the exhausting steam is in contact with water-cooled tubes, heat conversion takes place where steam drops off its heat and the condensate settles at the bottom. From there, the condensate is extricated using a valve.
Evaporative Type – The name is called evaporative as the cool water gets dispersed in this condenser type. Here, when the hot steam streams into the tubes, cooling water is spewed on the steam. The spraying of cooling water on the steam happens from a cooling tank using a pump.
When the cool water is in contact with the hot tubes, the steam present in the tubes gets converted into liquid. For the air tubes, there are fins that are used to enhance the surface area dimensions and to reduce the cooling time.
Central Flow – This is the upgraded version for the downflow type of surface condenser. The main variation that exists in between both is the location of the air pump which is located at the system center in the central flow condenser and the steam moves into the system from the top section.
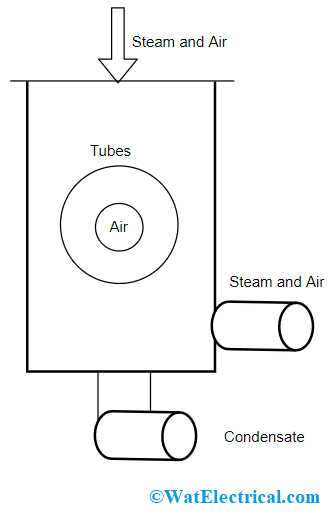
Central Flow Surface Condenser
The flow of exhaust steam gets altered and compelled to move in the direction of the system using an air pump. Because of this, the system is called central flow. Here, the moving path of cooling water and steam are in the upright direction to the tube’s surface. When the steam and cooling tubes get in contact, heat transfer takes place which results in the development of condensate.
Regenerative – This type of surface condenser is appropriate for higher levels of temperatures. Here, regenerative condensate is utilized, and the condensate temperature can be enhanced by allowing it to pass through exhaust steam. As because condensate is at high temperatures, it can be used again which enhances the efficiency of the condenser.
Surface Condenser v/s Jet Condenser
This section lists out the difference between surface condenser and jet condenser
| Surface Condenser | Jet Condenser |
| This is also called a water-cooled tube/shell heat exchanger | This is also called a direct contact condenser
|
| Here, condensate can be utilized again | Condensate gets wasted |
| Need a huge quantity of circulating water | Operates with less amount of circulating water |
| The surface condenser needs high maintenance | The jet condenser can operate with less maintenance |
| Mostly appropriate for huge capacity plants | Not appropriate for huge capacity plants |
| In this condenser, cooling water and steam will not get combined | In this condenser, cooling water and steam gets combined |
| Minimal power is sufficient for the air pump | More power is needed for the air pump |
| The condensing system is expensive and complicated too | The condensing system is inexpensive and simple as well |
| To pump out wastage, less power is enough | To pump out wastage, a high amount of power is needed |
Advantages
The advantages of the surface condenser are:
- Appropriate for huge capacity plants because of their huge size and increased efficiency
- The condensate which is obtained holds a high level of purity range which can also be utilized as boiler feedwater
- Here, the amount of vacuum created is more which helps in the removal of uncondensed air and reduces the internal pressure in the condenser
- The requirement of power needed is less to propel the air pump
Applications
A few of the surface condenser applications are explained as below:
- It can be used for the operations of vacuum refrigeration and evaporation
- Used in desalination systems
- Implemented for replacing barometric condensers in steam-propelled ejector systems
- Used in OTEC systems
- Can be employed for geothermal energy recovery
This is all about the concept of the surface condenser. This article has clearly explained the surface condenser working principle, types, its efficiency, diagram, and applications. Also, know what are the disadvantages of a surface condenser?