In the initial period of 1856, discharge tubes came into existence, but discharge lamps existed in the market in the 1930s. Initially, a French scientist Jean Picard noticed that barren space in the mercury barometer shined as the mercury wiggled when he was carrying it. Many researchers along with Francis Hauksbee attempted to know the actual phenomenon behind it. Francis initially showed a discharge lamp in the year 1705. He demonstrated that either emptied or partially emptied glass globe where he placed a few drops of mercury, as charged by the static current might generate luminous light. This scenario was later known that it is the principle of the discharge lamp. So, this article is on a discussion about what is a discharge lamp, its working principle, types, example, and many other related concepts.
What is the Discharge Lamp?
Discharge lamps come under the classification of artificial light sources that produce light by transmitting an electrical discharge via ionized gaseous substances. Usually, those lamps make use of either xenon, argon, krypton, neon, or a combination of these gases. Most of the lamps were filled up with other elements such as sodium, mercury, or other halide materials. To the basic functionality when the gas gets combusted and free electrons when gets speeded up by the electric field present in the tube, they have a collision with the gas and the metal substances.
High-Intensity Discharge Lamp
Few of the electrons present in the atomic orbitals are energized by these collisional forces and they get transferred to higher energy phases. When this energized atom drops down to a lesser energy phase, it releases either distinctive energy or photon which results in UV, infrared or visible light. These discharge lamps provide enhanced life period and performance but are a little convoluted to design and construct. Moreover, these lamps need electronics to offer exact current flow across the gas substance.
Discharge Lamp Working Principle
In general, gases are poor conductors at increased pressure levels mainly and atmospheric pressure values. But with the specific range of voltage levels, mainly ignition voltage in between the two electrodes will generate a discharge across the gas and this is accompanied by electromagnetic radiation. This electromagnetic radiation is based on the gas, vapor present in the metal, and the pressure that is in the lamp. In general, sodium, mercury vapors, and argon gas are used for the development of discharge lamps.
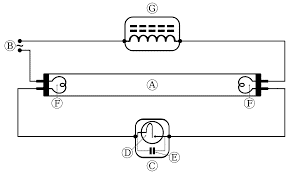
Discharge Lamp Example
When the isolation process has initiated in the gas, it holds the tendency to enhance constantly resulting in the drop-down of the circuit’s resistance value which means that the discharge lamp holds negative resistance attributes. So, as to regulate the current to the protected range, either a ballast o choke is developed. The choke operates two functionalities of offering the ignition voltage levels and restricting the current values correspondingly. As because of the usage of choke, the power factor seems to be minimal and it comes to the range of 0.3 – 0.4. So, to enhance the power factor values of the discharge lamp, a condenser is used here. The resulted light spectrum is therefore irregular which means it has either two or extra colored lines. The resultant light color is based on the vapor and behavior of gas that is used.
So, this is the discharge lampworking.
Different Types
Discharge lamp types are mainly classified as three types and those are:
Low-pressure Discharge Lamps
These discharge lamps operate at minimal atmospheric pressure levels. Mostly, fluorescent lamps which will be at domestic and office spaces function at an atmospheric pressure level of 0.3% and they generate nearly 100 lm W-1. Whereas minimal pressure range of sodium lamps which are the most powerful discharge lamps deliver nearly 200 lm W-1, but these have reduced color rendering characteristics.
These low-pressure discharge lamps radiate monochromatic yellow color light, where this is suitable for only road light and other specific purposes. These lamps also have extended life period.
High-pressure Discharge Lamps
These discharge lamps operate under higher pressure values when compared with that of low-pressure discharge lamps. This means that pressure values might be either less or high than that of atmospheric pressure levels.
For instance, an enhanced pressure level sodium lamp operates at a range of 100-200 torr which means 15-30 percent of the atmospheric pressure level. Some of the types of high-pressure discharge lamps are:
- Metal halide
- High-pressure sodium
- High-pressure mercury-vapor
High-intensity Discharge Lamps
Generally, these are highly efficient lamps and they hold a tendency to provide extended service life for any type of these lamps. They will save almost 80 percent of lighting power when they are substituted in the incandescent lamps.
These lamps make use of electric arcs to deliver an intense range of light. Similar to fluorescent lamps, these also need ballasts. When initially turned on, these lamps require almost 10 minutes of time to generate light due to the reason that the ballast requires time to create the electric arc. For the reason of intense light, these lamps have are highly effective, and are mostly used in huge indoor spaces and outdoor lighting purposes. As these discharge lamps need somewhat more time to create, they are appropriate for the application where they can remain for long hours. The luminous effectiveness of the HID lamp is almost 3 times more than that of a halogen light, and this lamp life period is nearly 2000 h, which is only 300–700 h for a halogen light.
So, HID lamps deliver considerably higher road lighting by using a similar amount of electric energy, and, in many situations, they should end the life period of the vehicle. The high-intensity discharge lamps also deliver a white color light than halogen lamps because their color spectrum is near to the solar spectrum range.
Discharge Lamp Example
A xenon flash lamp generates a flashlight either in the range of 10-3 or 10-6 and they are mainly employed for film and theatrical lights. Specifically, strong lamp versions called strobe lights can deliver a long period of flashes thus permitting the stroboscopic analysis of the motion. This is the example of a discharge lamp.
Advantages of Discharge Lamp
- These lamps provide an extended range of spectrum visibility
- The enhanced life period of operation
- These lamps are cost-effective
Disadvantages
A few of the disadvantages of the discharge lamp are:
- They deliver minimal power factor
- These devices need either transformers or in few situations’ starters are required because starting is somewhat difficult
- To achieve completse brilliancy, these devices take extended time
- These discharge lamps are implemented only in a single direction
- Flickering in these lamps produces a stroboscopic effect
- To balance the output current, ballasts are necessary
Applications of Discharge Lamp
- The most prominent usage of these discharge lamps are neon signs
- Discharge lamps are extensively effective in providing a high range of luminosity
- Implemented in many domestic and commercial applications
- Used in sodium lights those deliver orange spark which we observe on streetlights
- These discharge lamps are used in the applications to create reduced pressure and steady levels of luminosity
So, this is the all-over explanation about discharge lamps. This lamp includes an inside electrical discharge which is developed between two of the electrodes. And the developed intensity level might vary across each kind of discharge lamp and this ranges from a minimal level of high-intensity levels. There exists correspondingly multiple application of discharge lamps. It is more worthy also to know about what is the discharge lamp symbol?