It will not be an exaggeration to call transducers the backbone of instrumentation due to their widespread use. In other words, we can say that a transducer is a panacea for the instrumentation/electrical industry. The flexibility in input and output that a transducer offers not only connects us to the real world of physical movement also helps us controlling these. Many kinds of transducers can be classified in many ways. If classified on the operating principle, then an Inductive transducer is the one with very widespread use in industrial instrumentation. Many industrial equipment and gadgets will be unsafe to use without proxy switches(inductive transducers). Now, with increased automation, even many domestic gadgets use these transducers. Here we shall limit ourselves to Inductive Transducers.
What is an Inductive Transducer?
Definition: A transducer is a device that converts one kind of energy/quantity into another kind of energy/quantity mainly electrical. It has two main parts namely the sensor which is an input of the actuator which performs the output part. A sensor that is based on the principle of induction is known as an inductive transducer.
Let us further understand the principle of induction, whenever there is a rate of change current and a conductor sees it, it produces a voltage which opposes it. In a mathematical way we can say:
V= L.di/dt
Where ‘L’ is the inductance, ‘V’ is the voltage and ‘di/dt’ is the rate of change of current.
Further, ‘L’ depends on the number of turns in a coil, magnetic flux, and the area. The magnetic flux can be changed by changing the area or reluctance and thus producing a proportional output voltage. And if we use two conductors/coils we have a phenomenon of mutual induction as both coils affect the magnetic flux mutually.

Inductive Transducer
Types of Inductive Transducers
There are mainly three types of inductive transducers:
- Inductance type
- Mutual inductance type
- Eddy current type.
Inductive Transducer Working Principle
One by one we will look into the working principle of each.
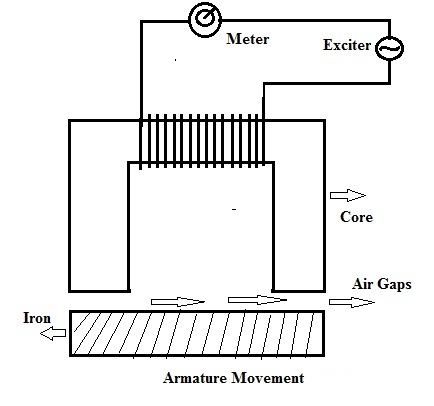
Inductive Transducer Working
Inductance Type
From the above figure, it is clear that as the armature/iron moves relative to the core it changes the reluctance of the magnetic path and hence the inductance of the coil. The meter in the path of the coil shows the variation in current proportional to the relative movement between core and coil. This change can further be used to generate an alarm/trip etc.
Mutual Inductance Type
This type is based on mutual induction and has two coils one for excitation and the other for output. We can see from the above figure that the relative movement between the core and the armature changes the air gape and hence the reluctance and the output in the secondary/output coil.
It may be added here that the output can be changed by adding one more coil and connecting it in such a way that the voltage generated in each coil is in opposition and thus create a differential voltage depending on the relative position of the armature. This type of transducer is called a differential mutual induction transducer.
Eddy Current Mutual Induction Transducer
This type of transducer works on the principle of eddy currents produced in magnetic material due to the magnetic field, these eddy currents have two effect. The eddy currents produced will affect the inductance of the coil responsible for producing it. The proximity of magnetic material (armature)will alter the magnitude of eddy currents
The eddy currents will generate heat which has to be compensated otherwise it will have a secondary effect of changing electrical parameters. To understand it better we can see a very common household example of induction heater where the proximity of the cooking vessel is known to the heater immediately.
Eddy Current Production
As magnetic flux linkages to a conductor change, voltages are induced in all possible paths which produce circulatory currents and these circulatory currents which are perpendicular to the magnetic flux path. These currents produce their magnetic field and heat loss as given hereunder:
Eddy current loss, Pe = KeBmax2f2t2V watts
Where Ke = constant
Bmax = maximum flux density in Tesla
‘f’ = frequency of magnetic reversal in Hz
‘t’ = thickness of laminations in mm
‘V’ = volume of core in m3
Advantages and Disadvantages of Inductive Transducers
The advantages include the following.
- Inductive transducers can withstand adverse environmental conditions like temperature, humidity, etc. It can perform in an industrial environment.
- This transducer has good accuracy and is considered to be stable in operation with a good life span.
- It can be subjected to a high switching rate as is required in industrial applications.
- Inductive transducers are available in wide ranges and can be used in several applications.
The disadvantages include the following.
- The shape/composition of the armature (metal to be sensed) plays a role in selecting the transducer. Some times it has to be almost tailor-made.
- The inductive transducer will work metallic (magnetic) material.
Application of Inductive Transducer
Inductive transducers find very wide applications in the industry some of the common applications are given here.
- The most common application of inductive transducer is as proximity switch/sensor which is used in vital equipment as safety devices like cranes, elevators, etc.
- These transducers are also used in process plants to perform programmed sequential functions and counters.
- In monitoring the medical condition of patients, the inductive transducer plays a very important role. As they find use in PB monitors, heart monitors, stethoscope, etc.
FAQs
1) What do you mean by transducer?
A transducer is a device that converts any physical quantity like motion, pressure, temperature into an electrical quantity like the current, voltage, etc.
2) What is the inductive pressure transducer?
A pressure transducer is one that converts pressure into electrical quantity which can be measured accurately.
3) How does the transducer measure pressure?
Various types of transducers can be used for pressure measurement. For low-pressure measurements generally, resistance type(load cell) type transducer is used otherwise we use the inductive type in which core moves inside the coil proportional to the pressure to be measured. This, in turn, increases the inductance of the coil thus changing the current drawn which can be calibrated in terms of pressure and measured.
4) What is an example of a Transducer?
A very common example of a transducer is a proxy switch which is mostly used as a safety device.
5) What is the purpose of a transducer?
The purpose of a transducer is to convert physical quantities into electrical quantity which offers flexibility in measurement and control.
Thus, this is all about an overview of an Inductive transducer that offers very wide applicability in Industry and one can choose one that is most useful from the various types and range available. Its use and circuitry are simple, which makes it user friendly especially for the industrial environment. Here is a question for you, what are the disadvantages of inductive transducer?