Well, let us start the topic of hot wire anemometer by knowing its history first, then we can move into the detailed concepts. Initially, the enhancement of an anemometer started in the 15th century. The first anemometer was invented by Alberti in the year 1450 and it is of mechanical type. Then, many versions came into existence developed by many scientists. In the year 1846, Romney enhanced the anemometer design by implementing mechanical rotational wheels and semi-circular cups. In the later years, the design and construction of anemometers got changed and with this basic principle, a hot wire anemometer got developed. So, now let’s get into the concepts like its history, working principle, equation, uses, and benefits.
Hot Wire Anemometer Definition
This is the instrument used for the calculation of fluid direction and velocity. This measurement is done by calculating the heat loss in the wire that is located in the liquid stream. These devices make use of a thin wire which is usually some micrometers electrically heated up to some level of temperature almost higher the ambient temperature range. The air that flows through it cools up the wire. As the metal’s resistance is based on the temperature, a relation is developed in between the wire’s resistance and the speed of the liquid flow. In many of the scenarios, they will not be utilized for the calculation of direction of a wind, only when they are integrated with a wind vane. The usage of hot wire anemometer allows rapid flow velocity that has to be measured from the electric voltage dimensions.
The crucial element of this type of anemometer is its thin wire sensor when it is pressured up heat flow takes from the wire to flow across the wire.
Principle
The basic principle of hot wire anemometer is that when an electrically heated up is kept in the flowing gaseous stream, then the heat gets transferred from wire to gas and this reduces the wire temperature levels. Because of this, the wire’s resistance value also gets changed. This variation in wire resistance allows us to calculate the flow rate of the liquid.
Working Principle Of Anemometer
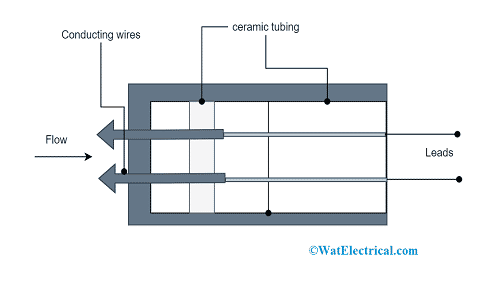
Construction of Hot Wire Anemometer
For the construction of a hot wire anemometer, mainly two parts are necessary which are the wheat stone bridge and conducting wire.
Here, conducting wire is placed inside of the ceramic material. The wires those come out from the ceramic material are connected to the Wheatstone bridge. Connecting wire to the bridge measures changes in the value of the resistance.
Working
The working of hot wire anemometer can be known using two types
- Constant current method
- Constant temperature method
Constant Current Method
In this method, the hot wire anemometer is kept in the fluid flow where here speed of the liquid flow can be calculated. From the wire, a constant magnitude level of current is passed. Also, the wheat stone bridge is maintained at a steady voltage level. When the wire is placed in the liquid flow, then heat transfer takes place to liquid from the wire. As because the heat has a direct relation to the wire’s resistance, when heat value reduces, the wire’s resistance also gets decreased. Also, the wheat stone bridge calculates the change in resistance value that is equivalent to the liquid’s speed flow.
Constant Temperature Method
In this method, the wire gets heated up by the electric current, the hot wire anemometer is kept in the fluid flow where here speed of the liquid flow can be calculated. When the wire is placed in the liquid flow, then heat transfer takes place to liquid from the wire. Here, the change in wire’s temperature value also modifies the resistance value. It is operated on the principle that the temperature level of the wire persists to be constant. The whole current that is required to bring the wire into the starting condition is similar to the gas speed flow.
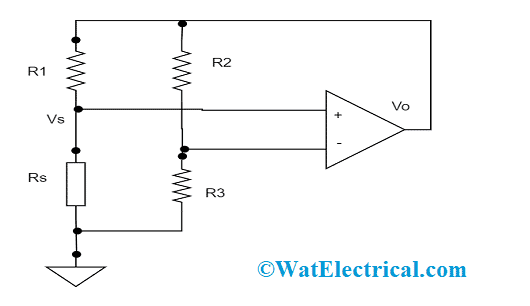
Schematic Diagram Of Hot Wire Anemometer
In both these operating modes, it is essential to calculate and alter the time constant range of the anemometer. As this is completely based on the thermodynamic situations that exist at the wire, the alteration is somewhat complicated to operate in the supersonic movements. While in the subsonic method, test signals are probably implemented and include either square or sine wave being fed as input for the circuit thus developing an unstable wire heating. On the other hand, this kind of heating is not similar to the unstable heat transmission changeover in the flow, and in specific for an extensive range of frequency properties, this electrical analysis seems to be uncertain.
Hot Wire Anemometer Equation
In this device, there will be a direct transfer of heat from the wire to liquid when kept in the liquid flow. To know the temperature level of the wire about resistance, a wheat stone bridge is used. To calculate the heating current, the temperature stays as persistent so that the bridge stays in equilibrium condition. The resistor is in series connection with heating wire. The current flow along the wire is known by measuring the voltage drop that flows across the resistor. And the voltage drop is measured by a potentiometer. The loss of heat across the electrically heated wire is known by the equation
a(vρ + b)1/2 Joules/sec
here ‘v’ corresponds to heat flow velocity and ‘ρ’ is the fluid density. Whereas ‘a’ and ‘b’ are constant values and the value of these constants is based on the physical characteristics and size of the wire and fluid too.
In the equilibrium case, the heat generated equals heat loss, then
I2R = a(vρ + b)1/2
V = [I2R/(a2-b)]/ρ
Here ‘I’ corresponds to current and ‘R’ corresponds to the resistance of the wire. Both the temperature and the resistance values of the device are maintained as constant to calculate the fluid flow rate through the calculation of I.
Advantages
Few of the advantages of hot wire anemometer are as follows:
- These devices can be operated simply because no additional sensor equipment is required
- The device is small and also provides high range of sensitivity
- Can deliver enhanced fluid flow rates
- With few changes, errors those arise because of temperature changes can be easily eliminated
- These devices are exactly applicable to measure the high range of frequencies
- It has minimal air velocities
- It includes data hold functionality
Disadvantages of Hot Wire Anemometer
The disadvantages of this device are:
- It requires more power to operate
- It has non-uniform scalability
- These devices are highly sluggish and need more time in heating up the wire
- For the ascending and descending values, the deflection is not similar and it varies
- The reading of the instrument is based on the values of atmospheric temperature
- As because the thin wire is used, it has only constrained physical strength
Applications
The major applications of hot wire anemometer are in the calculation of temperature variability levels and also to know the co-relation that exists between temperature and velocity in turbulent flow with heat transmission. Then, this device can also be implemented to know the mean relative concentration that is in the combination of two gaseous substances of dissimilar known thermal properties.
Also, hot wire anemometers allow for the calculation of concentration fluctuation level along with the velocity range.
Used to know turbulence measurements for the engines.
Know more about Wheatstone Bridge MCQs.
On the whole, hot wire anemometers are considered as the heat transducers used for the measurement of quick flow velocities. As because of these advantages, and applications and its operating principle, it is even employed as a research tool in the fluid mechanism. These devices have been in implementation for many decades in the analysis of conventional, turbulent, and laminar boundary layer fluid flows. With all of these, it is even more crucial to look at hotwire anemometer circuit diagram and what is its detailed operation?