The development of the anemometer happened in the year 15th century. In the year 1450, Leon Alberti was the person who developed the initial mechanical kind of anemometer. Later on, in the next centuries, many others along with Robert Hooke invented their own styles where few of them were wrongly acclaimed as inventors. Whereas during the period 1846, John Romney enhanced the initial version of it using mechanical wheels and hemispherical cups. Then, a three-cup anemometer was developed by John Patterson in the year 1956 and then the next version of this was upgraded by Brevoort. In this way, the history of anemometer took place. Now, this article explains what is anemometer is working principle, types, purpose, advantages, and uses.
What is the Purpose of an Anemometer?
The word anemometer is originated from the term anemos where is a Greek word. This is the device that is mainly used to measure wind properties like its speed, level of intensity, flow direction, and amplitude. This method is regularly used by meteorologists in order to know about wind conditions. This device is even used in the geographical domain to analyze the airflow direction. Initially, this tool was developed to estimate wind measurement. These are now available in both analog and digital formats which are employed for measuring the velocity of the gas, the velocity of both unconfined and confined directions like the ambient wind. In addition, the device is also used to calculate wind pressure and pressure level of any stream of gas.
Construction
Using few fundamental components, an anemometer can be constructed. Based on various situations, atmospheric conditions, ecosystems, and calculations, there are many types of anemometers. The device also utilizes laser and ultrasonic approaches to get precise wind measurements.
Here, the construction of the device is done using disposable cups which is also termed as Robinson anemometer. These cups are used to pick up the wind flow which allows it to revolve. In order to determine the total number of spins in the specified time period, the below experiment will explain clearly and determines the speed of the wind.
The required apparatus are:
- Paper cups of small size – 5 units
- A plastic bottle
- Thin wooden made dowels – 3 units
- Scissors – 1 unit
- Punching device
- Duct tape
- Stopwatch – 1 unit
Process
- Using the punching device, make a hole on the side of four paper cups
- The final paper cup will be considered an anemometer center. In the last cup, punch four holes where these are exactly center from the rim of the cup
- Through these holes, slide two of the wooden dowels
- Now, place the ends of the dowel into the holes of other cups and connect them through tape.
- And to the center position of the last cup, attach the final wooden dowel and place one dowel into the plastic bottle
Final Observations
Through this experiment, it might not be able to find the speed of the wind, whereas the speed flow of the wind can be known. By measuring the number of revolutions per minute, the wind speed can be recorded. Highly capable anemometers that are implemented in weather forecasting allow you to calculate the wind speed in km/hr. Through this process, one can record wind conditions by observing its revolutions for some days and then measure the average speed of the wind per week. It is also possible to record wind speed at various timings in the day such as in the morning, midday, evening, and at night times.
Anemometer Working
As there are various kinds of anemometers, here we explain the anemometer working principle in a hot wire kind anemometer the airflow will allow a heated object to get cool is the basic principle of the device. A thin wire which is electrically heated is positioned inside the airflow. When the rate of airflow gets increased, the wire will get cooled. In a constant temperature type of anemometer, the power level is increased so as to manage constant temperature levels in the wire. The airspeed measurement is known by how much amount of input power is supplied to the hot wire and for the indication of airspeed, a meter in the circuit is calibrated.
Types of Anemometer
There exist multiple kinds of anemometers where each one is different from the other and they operate in various ways. This section explains few types of anemometers with few details.
Cup Type
This is the oldest type of anemometer which is also called a rotational anemometer. This device is included with four hemispherical cups that are placed on the horizontal arms and these arms are located on top of the vertical shaft. The airflow preceding the cups in ant of the horizontal path turns the shaft and this rotational speed rate was almost proportional to the speed of the wind. So, the total number of turns in a specified time period delivers a value that is proportional to the average level of wind speed. In this type, it is simple to observe because the cups are placed in a symmetric position on the edge of the arms.
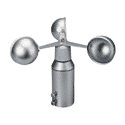
Cup Anemometer
In theory, the anemometer’s rotational speed has to be proportional to the speed of the wind due to the reason that the force developed in a body is proportional to the fluid speed that flows preceding it. Though, in the practical approach, there are other aspects those show impact on the rotational speed such as turbulence generated by the equipment, increasing the drag level in opposite to the torque which is developed by supporting arms and cups, and also friction generated by the mounting point.
This is mostly used in schools, meteorological departments and used by scholars.
Hot Wire Type
In a hot wire kind anemometer, the airflow will allow a heated object to get cool is the basic principle of the device. A thin wire which is electrically heated is positioned inside the airflow. When the rate of airflow gets increased, the wire will get cooled. In a constant temperature type of anemometer, the power level is increased so as to manage constant temperature levels in the wire. The airspeed measurement is known by how much amount of input power is supplied to the hot wire and for the indication of airspeed, a meter in the circuit is calibrated.
Even though these devices are subtle to handle, they have an increased level of frequency response and good spatial resolution when compared with other kinds of calculative approaches. So, these hot wire anemometers are mainly implemented for the thorough analysis of turbulent flows or used in any flow movement where the rapid velocity variations are more observed.
Ultrasonic Type
The ultrasonic anemometers are initially invented during the period 1950s in order to calculate the velocity of the wind. Depending on the time of flight for sonic pulses which was between the transducers, the wind velocity is measured. The calculations can be considered from various transducer pairs and these can be merged to generate velocity measurement in the order of 1-2-3. The spatial resolution is known by the distance between transducers where it is generally 10 – 20 cms.
These devices have the ability to measure very good temporal resolutions in the order of 20 Hz where this characteristic allows them to be implemented for turbulence calculations. The absence of movable parts in the device allows this anemometer to have an extended life period even in external weather situations when the anemometers are badly disturbed by dust and pollution.

Ultrasonic Type
Acoustic Resonance Type
Acoustic resonance type anemometers are the modified version of sonic anemometers. The general kind of sonic anemometers depends on the flight calculation, whereas the acoustic resonance type employs ultrasonic waves having a miniature purpose-built section for knowing the measurement.
In the cavity section, there are ultrasonic transducers where these transducers develop separate sanding waveforms at the ultrasonic frequency levels. When there is the passage of wind through the cavity section, there will be a modification in the feature of waves which generates a phase shift. So, by calculating the phase shift from each transducer, and then after data processing, the sensor then accurately provides the horizontal measurement of wind direction and speed.
As acoustic technology facilitates measurement even in small sections, so the sensors are also minimal in size than other kinds of ultrasonic sensors. The minimal size of these anemometers lets them to be more strong and shows a simple heating process and hence they are impervious to icing. These all features make acoustic resonance anemometers have enhanced data availability and they are suitable for controlling wind turbines and useful in the battlefield meteorology domain.
Laser Doppler Type
These laser doppler anemometers operate using a light beam received from the laser and the beam is then classified into two beams where one of the beams is spread out of the device. The wind velocity is known by measuring the amount of light that was reflected off by the moving air elements when the beam enters into the anemometer. When the light particles have good movement, they generate Doppler shift which is used for calculating the speed of the wind in laser light, and also this measures the light particles’ speed.
Laser Doppler Type
In addition, there are also pressure anemometers which are again categorized into tube and plate types.
Plate Type
The plate anemometers are the most latest version of anemometers. These devices comprise a flat type of plate that is suspended from the top position so that when there is wind flow across the plate, it deflects it. The latest versions in the flat type of anemometer include a flat plate which is either of circle or square in shape and the plate is placed normally to the wind using a wind vane.
The wind pressure on the face of a flat plate is balanced using a spring and the compression level in the spring defines the actual pressure level that the wind exerts on the plate. This pressure level is considered either by a proper gauge or a recorder. The plate anemometers do not act in response to minimal wind levels, and these are not quick in showing response for variable winds. These are used for triggering high-level wind alarms on bridges.
Tube Type
The generally used tube type anemometers are pressure tube anemometers. This device consists of glass shaped U tube where it has a liquid manometer inside that. The tube is bent on one side in a horizontal path that faces the wind direction, and the other end is in a parallel direction to the flow of wind. When there is wind flow into the tube, it creates an increase in the pressure level at one end of the manometer. Whereas the wind flow on the vertical side tube creates minimal variation in the pressure level at the manometer’s other end.
So, the variation of pressure levels at both ends of the tube results in knowing the wind speed level. To get exact measurements, it needs that the wind speed be straightforwardly flown into the open edge of the tube.
Windmill Type
This anemometer is employed for the measurement of both the speed and direction of the wind. The device consists of a propeller that is connected at its front side and there is a large tail connected at its back edge. There is no need for any additional device for measuring wind speed, but the rotational speed of the propeller signifies the wind speed.
This is all about the concept of types of anemometers.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The main and crucial advantages of an anemometer are:
- Anemometers provide increased precision
- The device can operate even with minimal power level
- Using an anemometer, various parameters can be known such as speed level, wind velocity, direction, and pressure level of wind
- The anemometers are available in various shapes and sizes so that they can be used in many domains for many applications
- Using low power, the device has the ability to provide accurate measurements
- This is referred to as a common station device as it provides all the data concerned to wind
The disadvantages of an anemometer are:
- The device many experience distortion levels which adds additional noise levels in the wind
- Because of strong winds, there may be a chance of the device getting destroyed. So proper maintenance and protection is needed
Applications of Anemometer
A few of the applications of various types of anemometer are as follows:
An anemometer is mainly useful to measure the entire velocity magnitude, either the component of the velocity in a particular direction or the magnitude velocity in a flat plane.
- Used in drones, helicopters, and in RC planes
- Before the leap, skydivers use this to forecast weather conditions
- Used in the measurement of airspeed for aerodynamics
- These devices are useful in ship navigations, weather buoys, and wind turbine domains
- Useful for pilots and also for shooters who practice for long ranges
- The anemometers have their applications in all the weather stations ranging from frigid arctic levels to humid equatorial ranges.
- Also used in the fields of agriculture, heating, frozen storage, and ventilation.
Please refer to this link to know more about Anemometer MCQs, Parallel Resonance MCQs.
This is the detailed concept of anemometers. Many of the hand-held appliances are resistant to water and few other kinds are useful for accessing different wind speed dimensional units. The digital kind and recent version of anemometers are also available with wind meters where are connected to a smartphone through Bluetooth. Currently, these devices are applicable in many domains mainly in measuring wind speed, which signifies a variation within the features of weather for meteorologists such as tornadoes, windstorms & cyclones. In addition to the above-stated information, also know how an anemometer gets impacted by icing?