The conservator tank is one of the most important parts of the operation of the transformer. Its main role is not only to circulate and maintain the oil level in the transformer but also plays an important role in the protection of the transformer against earth faults, heating and maintains the insulation of the windings. It is placed on the top of the transformer tank and has its own capacity based on the rating of the transformer. Generally, it is placed between the main tank of the transformer and the breather which maintains the healthiness of the transformer oil. It main objective being is to maintain the transformer oil in the main tank within the standard limits.
What is a Conservator Tank?
A conservator is a device that regulates or conserves the oil levels in the transformer. It makes sure that the transformer oil circulates properly within the main tank. Oil has an important function in the working of the transformer. A transformer that works on Faraday’s Law of electromagnetic induction steps up or down the input voltage. The change in the magnitude of the voltage is dependent on the number of windings. For a large 3 phase transformer, it steps up the voltage from 11 kV to 450 kV, which is very high potential.
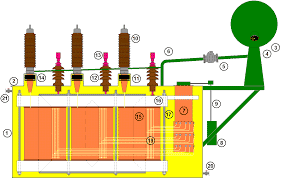
Conservator Tank
One of the disadvantages of the distribution transformer or power transformer is it dissipates a huge amount of heat in its windings. These losses are due to copper losses in the windings. If this heat is not dissipated immediately, then the transformer windings will burn to lead to the failure of the machine. And one more important requirement of the transformer is insulation. If the windings are not insulated properly, then it would cause short circuits of the windings which again leads to failure of the machine.
Hence cooling and insulations are two important operations of the transformers. This is achieved by the transformer oil. The transformer oil circulates within the main tank and provides cooling to the windings. For efficient operation, correct levels of oil must be maintained through the operation, which is done by a conservator.
Purpose of Conservator Tank
The main purpose of the conservator tank is to maintain the transformer oil in the main tank. Oil which is required for cooling and insulation of the transformer windings circulates around the transformer windings. The transformer windings are placed in a tank that is full of transformer oil. When the transformer operates, the transformer dissipates the heat losses in the windings. This heat is absorbed by the transformer oil.
This how transformer oil cools the transformer windings. In this process, the oil gets heated up and the hot oil must be cooled immediately. The cooling of the oil is done by different methods like natural cooling, forced cooling, etc. When the transformer oil heats up, its level increases and the hot oil is transferred to the conservatory. The oil level maintenance is achieved by a conservator.
The Function of the Conservator Tank of a Transformer
The main function of the conservator tank is the regulate and maintain the oil levels in the transformer. The conservatory is attached to the main tank of the transformer in which oil circulates and cools the transformer windings. When the oil becomes hot, its level increases and it reaches to the conservator. In between the conservatory and main tank a Bucholz relay is placed. The oil has to reach the conservator after passing through the Bucholz relay. The main purpose of the Bucholz relay is to provide protection against internal faults.
It is a relay that operates before the fault takes place. It anticipates the presence of the fault based on the oil condition. And trips immediately if it senses the fault. The conservator maintains and regulates the oil level in the transformer. To check the quality of oil, a breather is connected to the transformer. A breather is a device by which we can comment on the healthiness of the transformer oil. Generally, the transformer oil loses its insulation and cooling property due to the formation of moisture in the oil.
The moisture content degrades the insulation levels of the transformer oil. Once the transformer oil is degraded, it has to be replaced immediately. The degradation of transformer oil is identified by the breather. The breather consists of silica gel, whose color changes if the transformer oil is degraded. So based on the color of silica gel, the healthiness of transformer oil is detected. The breather is connected to the outlet valve of the conservator tank.
Construction
The construction of a conservator tank is normally made up of iron having one inlet and more than one outlet. As shown in the figure, the inlet of the transformer is connected to the main tank. Where the oil enters into the conservator tank. A magnetic oil level gauge is connected to the conservator tank to check the level of the oil. One of the outlets is connected to a breather, which checks the healthiness of the transformer oil. In between the conservator tank and the main tank, the Bucholz relay is placed which protects the transformer from internal faults.
We have a connecting valve, which connects the conservator tank and the main tank. Other important parts of a conservator are vent, which regulates the airflow. One float is connected to a magnetic oil level gauge, which senses the oil level in the conservator tank. It sends the oil level to the magnetic oil level gauge, which keeps on checking the oil level in the conservator tank with the help of float. The float works based on the position of the air cell.
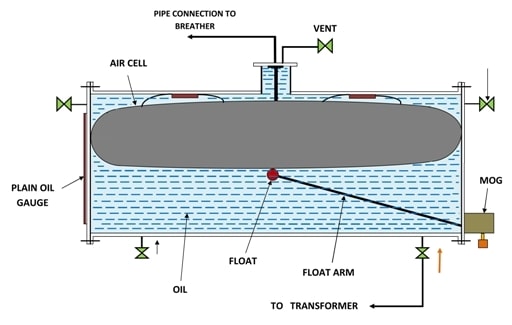
Construction of conservator tank
The oil in the conservator or main tank is called transformer oil or also called as mineral oil. As the property of transformer oil is to cool and insulate the transformer windings, the transformer oil is selected such that it has got high dielectric strength. Because of the high dielectric strength, the oil is able to provide insulation to the windings. The insulation of the oil is checked by a breather.
Working of Conservator Tank
The main function of the conservator tank is to maintain or conserve the oil level in the main tank of the transformer. This is achieved by allowing the transformer oil to expand and enter the conservator tank when it is heated up. The conservatory gives the transformer oil space to expand so that the heat in the transformer tank can easily be dissipated. As the major role of the transformer oil is to cool the transformer, by dissipating the heat. While dissipating the heat, the transformer oil absorbs the heat of the transformer and expands. The hot oil travel to the upper layer of the main tank and then to the conservatory.
It is made sure that the conservator should be always half-filled with the transformer oil. Then only it is possible to check the oil level in the main tank. The oil level in the conservator is checked by the use of a magnetic oil level gauge which is connected to the conservator. The other outlet of the conservator is connected to the breather. When the oil insulation degrades, it can be identified by the color of silica gel which is present in the transformer oil.
Types of Conservator
There are mainly two types of conservator tanks
Atom seal Type Conservator
In this type, the air cell in the conservator tank is made of Nitrile rubber (NBR). The breather is connected above the air cell. When the air inside the air cell inflates, the breather pushes to try to push the air from the outside atmosphere. Similarly, when the air cell deflates, the air is pushed outside the atmosphere, via a breather. The magnetic oil level gauge monitors the oil level in the conservator tank. The presence of an air cell allows the transformer conservator tank to be half-filled. The pressure inside the air cell is maintained at about 1.0 PSI.
Diaphragm Conservator
In this type, to provide a barrier between transformer oil and atmospheric air a diaphragm is provided. The diaphragm is provided between the two halves of the conservator tank. Here, the magnetic oil level gauge is provided as before which regulates the oil level.
Hence we have seen the operation and working of conservators, and types of conservator tanks. Based on the rating of the transformer tank, the size of the conservatory is decided. It is be seen that what are the advanced materials used for air cells in the conservator tank? Based on this the operation of the transformer is improved.