All the contemporary power delivering systems like that of transformers function in the internal environment which is exemplified by the production of substantial heat. Also, it is more crucial to restrict the flow of power through the transformer for the functioning equipment. This corresponds that transformers need both insulators and coolant devices to limit their operation. Owing to this, transformer oil is the one important ingredient in the power devices which results in the protected and soft functionality of the devices. As a transformer does not have any movable components, it might not require oil, but for a few huge constructional devices, they need some thousands and liters of oil. So, today our discussion is on transformer oil, various kinds of properties that it possesses, and types.
What is Transformer Oil?
Transformer oil is considered as the insulation oil where it holds good insulation properties and even stables when the devices are operated at a high range of temperatures. This oil is used to protect the transformer core section and also the windings where the windings are completely submerged in the oil. The other crucial thing about this insulation oil is its capacity to not allow devices to undergo the oxidation process. It stands as a barrier in the between the cellulose and the oxygen that exists in the atmosphere thus eliminating direct interaction and so reduces oxidation.
This oil functionality is to shield and cool down the transformer core section. As because of this the oil should possess high levels of stability, dielectric strength, and thermal conductivity.
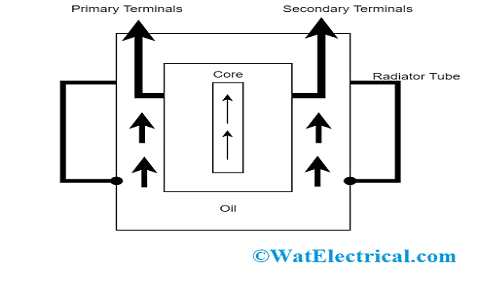
Transformer Oil in Transformer
Specifications
The general specifications of this oil are:
- Dielectric breakdown voltage in the range of 28kV or more
- Pour point is at -400C or less than this
- Flashpoint of 1400C
Different Types
There are mainly two types of transformer oil and those are:
- Paraffin dependent oil
- Naphtha dependent oil
Of these two, naphtha oil has more oxidizing properties, but the sludge of naphtha oil has increased solubility than paraffin oil. As because of this, naphtha dependent type of oil will not get precipitated at the transformer bottom. Therefore, it will not prohibit convention oil transmission, which means that it will not interrupt transformer cooling.
Even though paraffin dependent oil has poor oxidation properties than naphtha-based oil, the sludge is impenetrable and gets situated at the tank bottom. This sludge functions as a hindrance for the transformer to cool. The other drawback in paraffin-dependent oil is that the melted waxes internal of it might result in increased pour point. Even because of these downsides, people in India commonly recommend using this because of its extensive availability.
Transformer Oil Properties
In order to know the oil performance, it is more recommended to know about its properties. Few of the crucial properties to be considered in this oil are its
Electrical Properties
The electric properties of transformer oil are
Specific Resistance
It is the calculation of DC resistance that exists between two opposing ends in each oil block which is measured in cm3 and unit is ohm/cm calculated at a particular temperature value. When the temperature is increased, there will be a decrease in oil resistivity nature. The resistivity of the protecting oil needs to be maximum at room temperature and even it should possess better values at maximum temperature also. As because of this specific resistance or resistivity of this oil must be calculated in the range of 27oC and also at 90o Minimum range of specific resistance for this oil is at 90oC is 35 × 1012 ohm-cm and at 27oC the value is 1500 × 1012 ohm-cm.
Dissipation Element
This factor is also termed as either loss factor or tan delta value of the oil. When a shielding material is kept in between grounded and live components of the electrical apparatus, this creates a flow of leakage current. As because this shielding material has dielectric properties, the current flow through the insulation preferably precedes the voltage level by 900. This is the general case. But in fact, there exist no insulating materials with dielectric behavior.
Dielectric Strength
It is the breakdown voltage of the oil. The voltage is calculated by monitoring at what level of voltage will the sparking strings placed between the electrodes will get separated by a particular space. When this dielectric strength is minimal, it specifies that there exists humidity content. Less humid and fresh oil provides BDV results, better than that of the oil having humidity content and other kinds of conducting contaminations. The least possible breakdown voltage of transformer oil is at which the oil can securely be implemented in the transformer which is generally 30 kV.
Chemical Properties
The chemical properties of transformer oil are
Level of Acidity
It is a destructive property. When the oil becomes acidic in nature, then water gains more solubility nature. This property destroys the insulation nature of windings. The enhanced level of acidity also increases the oxidation procedure and also causes iron rusting. Detailed analysis of the acidity level of transformer oil might be utilized to calculate the acidic ingredients of pollutants. Mostly, acidity levels of this oil are represented in mg of KOH necessary to neutralize the level of acid in a gram of oil. This is even termed as a neutralization number.
Sludge and Water Amount
A high level of water content shows an impact on dielectric properties, core insulation, and transformer windings. Also, when the water content is more, oil becomes hot and hence solubility of water accelerates in a loaded transformer.
Physical Properties
The physical properties of transformer oil are
Flash and Pour Points
Flashpoint is the temperature level where the oil provides sufficient fumes to generate flammable composition with air. Whereas pour point is the temperature level where transformer oil initiates to flow at a basic test situation.
Viscous Nature
A good oil used in transformers should possess minimal viscosity because it provides reduced resistance to the oil flow so that it will impact the transformer’s cooling process.
Transformer Oil Testing
Transformer oil has to be tested to make sure that the performance and efficiency of the transformer are good. When the standards and principles stated by ASTM are followed, then it results in good oil. There are various factors in testing the oil and those are breakdown voltage, its properties, and many others.
The factors as mentioned by ASTM are
| Liquid Power factor | ASTM D924-08 |
| Interfacial tension | D971 of ASTM |
| Acidic number | D664 of ASTM |
| Specific resistance | D1169 of ASTM |
| Dielectric BDV | D877 of ASTM |
The test results will clarify whether the implemented oil is clean and free from impurities. Even though there are a wide number of testing scenarios available, the most common and general one is diagnostics. This is applicable in the primary stage testing of the oil. When the test results show any kind of red flags, this indicates that the frequency of the oil to be increased.
Sometimes, testing of oil also shows errors which are
- Oil overheat – Will generate the combination of methane and hydrogen or methane and ethylene at high temperatures.
- Cellulose overheat – Will generate carbon monoxide
- Arcing – Will generate the combination of methane and hydrogen in small amount or will produce hydrogen and acetylene
Importance of Testing
People might come across the question of why is transformer oil testing important?
The answer is
- It knows the important electrical properties of the transformer oil
- Finds out that a specific kind of oil is appropriate for future purposes
- Discover which process that regeneration or filtration is required of the oil
- Lower oil prices and extends the shelf life of the transformer oil
- Eliminates any kind of unfortunate breakdowns and thus increases protection
In general, many of the transformer oil will have a life period of a maximum of 30 years. So, the maintenance of oil will absolutely save many rupees.
Process In Oil Testing
Finally, this is a detailed and clear explanation of transformer oil, types, various properties of it, and why the testing is more crucial. So, having proper maintenance and care will protect oil for many years which indirectly enhances the performance, reliability, and efficiency of the devices. The other thing to be known about this topic is what is the function of transformer oil?