In the field of physics, particularly in electromagnetism, the concept of magnetic flux across the surface is defined as the surface integral of the general factor of the magnetic field which is represented with ФB. In order to measure the magnetic flux, there has to be a device, and it is the flux meter. Even though the development of flux meters started many years back, the usage of these devices started a few decades back.
Now, with the advancement, flux meters are employed in many applications. This article mainly describes on flux meter working principle, construction, its theory, and other related concepts.
What is Flux Meter?
A flux meter is an instrument that is mainly used for the calculation of flux in the permanent magnet. This device is termed as the improved version of a ballistic galvanometer that holds specific benefits like it has less level of controlling torque and intense electromagnetic damping level. The device consists of evaluating coils and electronics, where assess the voltage changes in the coils to know the magnetic flux measurement. This is the fundamental flux meter theory.
Flux meter is also considered as a permanent magnet device that consists of a moving coil of less inertia and minimal controlling torque. The damping level can be increased through a heavy aluminum former where the period gets extended by this. This does not depend 74on the time considered to modify the search coil linkage which is connected to the moving coil which is of either short or long.
In regard, the device is also helpful in iron testing because the time considered for the flux either to collapse or alter might be of many seconds. The level of deflection is noted down from the starting position of the pointer on the quadrant scale once the pointer gets to the highest deflection. Then, the pointer gets back to the ‘0’ position. A general kind meter reads a deflection of 10 μWb-t.
Working Principle
The flux meter working principle is explained as below:
When magnetic flux flows across the searching coil, it tends to induce a voltage in the search coil. Based on Faraday’s induction law, the induced voltage is considered as differential to the magnetic flux which crossed all across the search coil. Providing this induced voltage into the integrating flux meter will initiate the integration procedure so that the differential is removed. This results in the device displaying the total magnetic flux across the component.
In order to measure the total amount of magnetic flux, the device needs a dynamic component because it is needed for flux to cut down the search coil to generate voltage. By standardizing the flux meter internal to the number of search coil turns and area, then it is more likely to display the flux density which is measured in Tesla/Gauss along with the magnetic flux measured in Webers.
Construction of Flux Meter
The device comprises a coil that is freely placed between the two magnetic poles using a single tabled silk thread and a spring. This is the basic construction of the device. It also consists of loose helices where the current moves into the coil and there is no controlling spring in the device. As because of this, there has to be some current in the coil.
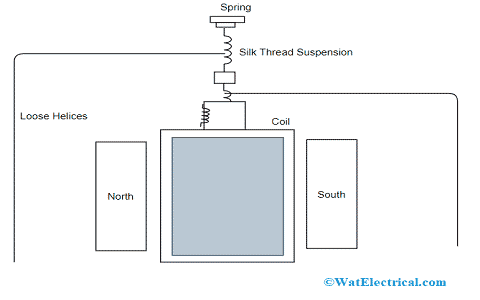
Construction
The current which enters into the coil through helices minimizes the amount of regulating torque to the most minimum value. Due to this, regulating the torque of a measuring device to be the least is needed. So, using the current, the regulating torque gets lessened to the least value.
Working
This section explains how magnetic flux is measured which is connected to a permanent magnet through a flux meter. Here, the device is connected together with a coil termed a search coil. Together with search coils, the flux meter terminals are also connected. Here, the flux linkage can be modified either by getting it disconnected from the magnetic field or by reversing the magnetic field direction. To achieve this, the magnet is located inside of the magnetic field and then makes few flux variations.
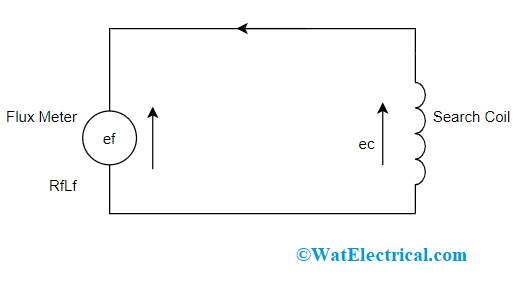
Flux Meter Working
To know, whether the variations are identified by the flux meter or not, the direction of flux in the search coil should be changed. When the changes are detected, there will be the generation of EMF in the coil. The EMF induction directs to develop current in the coil. The generated current flows through the flux meter and search coil. This defects the pointer in the flux meter where this deflection has a direct relation to flux linkage. In the same way, when flux variation gets reduced, pointer deflection reaches a minimum, and current also gets minimized. The reduction in flux linkage results in the stoppage of coil moment and shows ‘0’ deflection. This is represented as
V(t) = -dФ/dt
The total amount of flux in the coil is given by
Ф = ʃB.dA
Ф = BA
Ф = NBA
As the coils are field sensitive, they hold the ability to measure only direction and voltage is shown as
V(t) = -dФ/dt = -dNBA/dt
As the coil’s area and the

Construction
The total number of turns in the coil is constant, only change of flux density with respect to time remains. To remove the derivative, it is done as below:
ʃtstarttend V(t) = ʃtstarttend -dNBA/dt
B = (1/NA) ʃtstarttend Vc(t)
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of flux meter are:
- The device is very portable
- Field map can be done through this device
- The calibration of the device can be done directly in W/m so that direct reading can be considered without converting into other units
- The operation of the device is so simple
- This is an ideal device for measuring magnetic flux
The disadvantages of flux meter are:
- When compared with other devices, this device has less sensitivity
- Flux meters do not have great efficiency and also heavy
- The design of the test coil is complicated
Applications of Flux Meter
The applications of a flux meter include the following.
- They are employed for evaluating the field
- Employed in creating the hysteresis loop graphs which means hysteresis loop tracers
- Implemented in voltage integration circuits
- Ferromagnetic indicators
- Field evaluators
- The testing system in production
- Voltage incorporation
- Magnetic elements quality regulation
- Used for measuring DC as well
- Magnetic shielding efficient miscalculations
- Development of the magnetic system
Know more about Tesla Coil.
Know more about Electromagnetic Field Theory MCQs, Pyrometer MCQs, Electric Flux MCQs.
This is all about the concept of the Flux Meter. The article has provided a clear explanation of the flux meter working principle, construction, operation, advantages, drawbacks, and applications. Know how to use flux meter relative to static coil, and moving coil configuration?