In the previous articles, we have discussed different kinds of motors. This article discusses an overview of repulsion motor and how its principle helps in rotating a motor. This motor is a special type of 1-phase AC motor and working of this can be done by the repulsion of related poles. The stator in the motor supplies 1-phase AC supply & the rotor circuit will be shorted using carbon brush. The classification of these motors can be done under single-phase motors. Let us discuss an overview of repulsion motors which includes its definition, working principle, and its applications.
What is Repulsion Motor?
Definition: A repulsion motor can be defined as, an electric motor that works by using an AC (alternating current). In the past, these motors are used as a traction motor in electric trains like SR Class CP as well as SR Class SL however they have been outdated by recent types of electric motors. The classification of these motors can be done based on single-phase motors. In these motors, the windings of stator are directly allied to the power supply whereas the rotor is allied to a brush assembly & commutator related to a DC (direct current) motor.
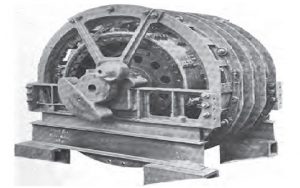
repulsion-motor
These motors are equivalent to an AC series motor excluding; brushes in the motor are not allied with power supply although they are short-circuited. As a result, the flow of current can be induced within the armature conductors through transformer action. The field structure of the motor has a cylindrical construction.
Repulsion Motor Working Principle
The working principle of repulsion motor is repulsion between two magnetic fields. For instance, consider a motor which has two poles along with a magnetic axis. The armature winding of this motor is connected to a commutator as well as brushes. The brushes are short-circuited with the help of a jumper with low-resistance.
Once an alternating current (AC) is applied to the stator winding, an e.m.f will be induced within the armature. The direction of AC will create two poles like south and north, where a north pole can be formed at the top of the magnetic axis and a south pole can be formed at the bottom of the magnetic axis.
The induced electromagnetic force direction can be given by Lenz’s law. As the induced electromagnetic force induces the flow of current within the armature conductors & the induced current direction will depend on the brushes position.
The Lenz’s law states that the induced current’s direction is induced within a conductor through changing a magnetic field so that the magnetic field which is formed through the induced current will oppose the primary varying magnetic field.
E.M.F = -N ΔΦ/ Δt
Construction
The construction of a repulsion motor is shown below. This motor can be built with a rotor, stator, brush and finally commutator. The stator of the motor is the generally cylindrical type with slots. The connection of the rotor can be done with the commutator and it is similar to the DC armature construction. The rotor windings are distributed type may be either lap winding otherwise wave winding. These motors include a commutator and the type of this may be vertical or axial. Carbon brushes in the motor are used for conducting current using the armature.
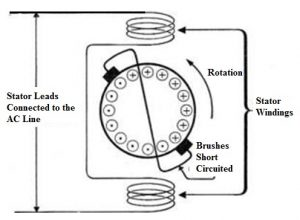
construction-of-repulsion-motor
The key difference between the AC series motor & repulsion motor is how the power supply is supplied in the direction of the armature. In AC series type motor, the armature gets voltage through the conduction of the power supply whereas, in repulsion motor, the armature can be supplied through induction of the stator windings.
Working
At the time of the early frequency of rotor, e.m.f is more. Therefore, the inner cage winding reactance will be high. So, a very small amount of current flow will be there in the cage winding. Once the rotor gets speed then the rotor frequency e.m.f will be reduced. So the rotor’s reactance will be decreased. At present, the squirrel cage winding gets a huge amount of the current.
The brushes in the rotor are short-circuited and they continuously ride on the commutator. The speed-torque characteristics of this motor are the speed regulation is good and the starting torque is high. So it can build up torque for unexpected heavy loads.
Types of Repulsion Motor
There are three kinds of motors available in the market which works under the principle of repulsion like the following.
- Compensated Repulsion Motor
- Repulsion Start Induction Motor
- Repulsion Induction Motor
1) Compensated Repulsion Motor
This motor includes an extra winding namely compensating winding. The set of two brushes are placed in between the normal short circuit brush set. Both the compensating winding as well as brush sets are connected in series to deactivate the effect of cross magnetizing of armature response. The windings that are connected in series will generate a magnetic field, which changes directly through armature current.
2). Repulsion Start Induction Motor
This type of motor work like a repulsion motor, although they run like an induction motor with stable speed characteristics. It includes a stator, a rotor, a commutator, and a centrifugal device. Here rotor is similar to the wire-wound dc armature. A centrifugal device is used to short circuit the bars of the commutator.
3). Repulsion Induction Motor
This kind of motor mainly works on the principle of both inductions as well as repulsion. It consists of a stator winding, two-rotor windings and a set of two brushes which is short-circuited. The two rotor windings are normal DC winding and one squirrel cage, connected to the commutator.
Advantages
The advantages of repulsion motor include the following.
- Starting torque is high
- Good speed regulation
- For sudden heavy loads, the torque can be developed.
- Starting current will be reduced
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of repulsion motor include the following.
- Sparks will occur at brushes
- The power factor is very less at less speed.
- The speed at no-load condition is extremely high & unsafe
- Brushes & commutator exhaust quickly due to heat generation & arcing at the assembly of the brush.
Applications
The applications of repulsion motor include the following.
- Applications of Farm Motors
- Film winding machines
- Hoists
- Machines in Textile
- Machines for floor maintenance
- Printing presses
- Air compressors
- Pumps & Fans
- Laundry equipment
- High-speed lifts
- Mixing machines
- Machine tools
- Air pump
- Mining tools
- Petrol pumps
- Drive compressors
Please refer to this link for Repulsion Motor MCQs.
Thus, this is all about the repulsion motor. Most of the commutator motors are restricted to about 1500 V as high voltages provide rise to a threat of arcing across it. These motors are used where high voltages are required because the circuit of the rotor is not connected electrically to the power supply. Here is a question for you, what is the role of repulsion motor in an air compressor?