It is a type of motor used for precise movements and positioning of objects mainly in milling machines. It is a brushless type synchronous motor and it is operated stepwise. This step-wise rotation is considered as the step angle. One step angle is the rotation of the shaft per one step. The step angle can be of different degrees depending upon the construction of the rotor and stator teeth. The brushless motor rotates the shaft 360 degrees per one revolution whereas the step motor rotates depending upon the step angle given. For instance, the step-angle of the motor is 7.5 degrees and if it should be rotated to 225 degrees it takes 30 steps. Similarly, a stepper motor takes 12, 24, 72 and so on steps to rotate the rotor. It is highly precise such that it can accurately position the objects to the desired location.
Stepper Motor Construction
The core is made of a collection of steel laminations arranged together. It consists of stator and rotor, the stator is the stationary part and the rotor is the rotating part. The rotor and stator poles in stepper type motor are not equal. The core of this type of motor is shown in the figure below.

Core of Motor
The rotor poles are less than that of the stator. If the stator has 6 poles, then the rotor has 4 poles. The whole rotating part is housed inside the core. The stator is wound with the windings classified as A, B, and C. The coils will be energized based on the requirement. The shaft attached to the rotor is able to rotate when the coils are energized. The stepper motor diagram is shown in the figure below.

Construction
Stepper Motor Working Principle
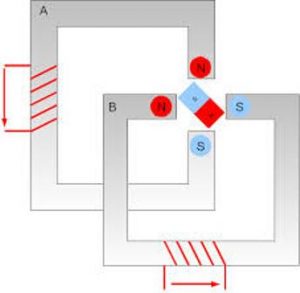
It also works on the principle of electromagnetic induction by Faraday I,e an emf is induced due to the carrying conductors in the magnetic field. As the motor is equipped with 6 separate stator teeth, these can be energized by using three separate dc sources namely A, B, and C. These coils are energized simultaneously to rotate the rotor. When the coil A is energized, the coil gets magnetized and pulls the rotor in the clockwise direction. When the coil B is energized, the coil A is de-energized and the rotor is rotated slightly.
The rotor rotation seems to be rotated at an angle of 30 degrees. This rotation is called the step size. And when the coil C is energized, the coil B is de-energized and such that the rotor rotates at an angle of 30 degrees. This continues simultaneously as and when the coils are energized. This angular rotation of the rotor is called the step angle. The 30-degree rotation of the stepper motor is shown in the figure below.
Working
However, the step size can be further decreased to 15 degrees by energizing the coils A and B together. When the coils A and B are energized together, the rotor rotates an angle of 15 degrees. After rotation, the coil A is de-energized and coil C and coil A are energized together and the rotor rotates further 15 degrees. This way the rotation continues as and when alternate two coils are energized together. This 15-degree step rotation is called half-stepping. The following figure explains the simultaneous energization of the two coils together.
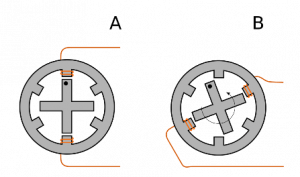
Working
Types of Stepper Motors
- Variable type and
- Hybrid type
Advantages
- Low cost
- Constant loading torque
- Parts offer a longer life
- Accurate
- Motion control is precise
- Operates with an open-loop system
- High readability
- Overload loss is less
- No stalling problem
- Steps can be digitally counted by controllers
- Do not require any sensors (To know the position of the shaft, we can count the number of pulses)
Disadvantages
- Less efficiency
- Torque decreases
- Stepper motors have less accuracy compared to servo motors
- No feedback is used becomes a disadvantage when the operation is inaccurate
Applications
- These are used mostly in miller machines, digital cameras, printing machines, medical scanners plotters, 3d printers, computer printers, and compact disc drives.
Thus, this is all about an overview of the stepper motor, construction, working principle, advantages, disadvantages and it’s applications. Here is a question for you, what are the types of stepper motor?