The initial development of the bolometer was done by Samuel Langley in the year 1878. Later on, in 1880, there were few modifications to the instrument in order to detect thermal radiation which holds the ability to thermally detect a wide range of spectrum including Fraunhofer lines. Then, Langley’s bolometer was used by Nikola Tesla for the application of power transmission in the year 1892. With this, the initial demonstration using a bolometer got succeeded and then it was used in various applications across multiple domains. This article now explains bolometer working, circuits, and its applications.
What is Bolometer?
A bolometer is a measuring device that is mainly implemented for the detection and calculation of heat and radiation for the range of radiofrequency or microwave energy. The device functions by using a temperature-resistant component where its resistance varies accordingly with temperature. The resistive components can be thermistors or barretters. Bolometer even holds the ability to measure temperature changes in the order of 0.00010C.
In the initial stages of the device development, it has a Wheatstone bridge along with a galvanometer that creates a deflection relational to the radiation intensity for a minimal range of deflections. Whereas the next developments in the device are included with four platinum gratings.
Bolometer Circuit
The circuit appears like a bridge where one of its arms is included with a temperature-sensitive type resistor. This resistor is positioned in the extent of MW energy where the power has to be calculated. The resistor absorbs the calculated power for the reason that there is heat generation in it. The generated heat alters the resistance value of the element, and the bridge circuit calculates the resistance change. Below is the picture that shows the circuit of the bolometer.
The bolometer device operates using a bridge circuit working as oscillators and a differential amplifier that oscillates when the bride moves to an unbalanced condition. The resistive component in the device tends to absorb the power till the bridge comes to a balanced position. In order to make the bridge balanced, the DC bias has to be adjusted. As discussed in the above section that when the temperature changes, resistance gets varies and this causes the bridge to be unbalanced. This imbalance happens in the opposite direction due to the cold resistance.
And also, the imbalance condition minimizes the oscillator output level thus making the circuit balanced. An electronic voltmeter is used for measuring power that gets minimized and displays the power surge by an oscillator that is absorbed by the resistive component from the MW field.
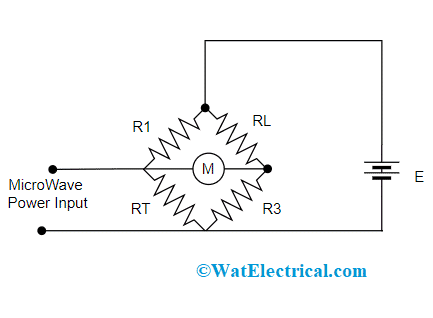
Bolometer Circuit
The resistive components that are used in the bridge are of two kinds which are
Thermistor – This is constructed of semiconductor substance and has temperature coefficient as negative which means that resistance decreases with increment in temperature.
Barretter – This is a type of metallic wire that has a temperature coefficient as positive which means that resistance decreases with a decrease in temperature.
Bolometer Working
The below bolometer diagram explains the working of the device.
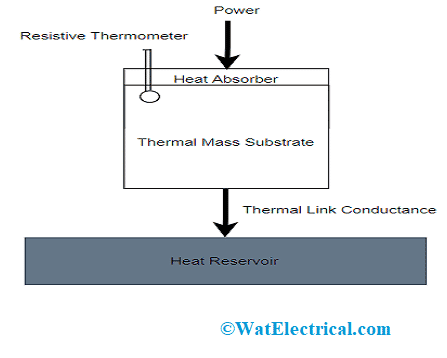
Bolometer Diagram
In general, a bolometer device comprises an absorptive component like a thin metal layered material that is connected with a thermal reservoir using a thermal connection. The output is that any kind of radiation that affects the absorptive substance increases its temperature level more than the reservoir. It can be said that the more absorptive power is, the higher is the temperature level. The intrinsic thermal time constant that sets the detector speed is equivalent to the ratio of absorptive substance heat capacity and the level of thermal conductance that exists between the reservoir and absorptive substance. The change in temperature value can be known directly from the resistive thermometer.
Metallic-type bolometers generally operate without any cooling effect. The current day bolometers make use of either semiconductor or superconductor substances other than using the metallic absorptive substances and these devices function at cryogenic temperature levels thus enabling higher range sensitivity levels.
This is the bolometer working principle.
Types
This section explains the types of bolometer and those are:
Microbolometer – These are exclusively constructed as detectors within the cameras. They are included with sections of heat sensors constructed by vanadium oxide. These sections are constructed on specific silicon grids. When these sensors are exposed to IR rays, then there will be a change in the resistance value of vanadium oxide. The resistance variations can be calculated and are shown in a graphical way.
Hot-Electron Bolometer – This type of bolometer functions mainly at very high cold temperatures which are near to absolute zero. At these temperature levels, the electrons present in the absorbent substances become very feeble. Thus, when the heat gets in contact with the substance, then the electrons are propelled from thermal equilibrium thus triggers for the creation of hot electrons.
As the molecular bonding of the metal substance is very strong with thermal elements, it even operates as a heat reservoir. When the absorbing component’s resistance is based on the electron’s temperature, then the resistance is utilized for measuring the temperature variations. Whereas, in few scenarios, the resistance is not based on the temperature of electrons. Because of this either voltage/current dependent resistive thermometers will be utilized as they provide precise readings due to minimal operating temperature levels.
Advantages
The advantages of bolometer include the following.
- Bolometers do not need any kind of cooling effect they can even operate are room temperatures
- Along with ionizing and photon particle measurements, these devices can even measure non-ionizing particles
- The sensitivity range is more, and they provide precise readings of energy resolution
- The response is quick, and bolometers even hold the capability to take clear images of moving substances
- The power consumption is minimal
- These are economical thus making the construction of devices so inexpensive
Applications
The applications of bolometer include the following.
- Microbolometers are used in thermal cameras
- Used in particle detectors for measuring radiation levels
- Security service departments like the military and police also utilize various equipment for knowing hidden weapons and bolometers are used in those devices
- Few of the fingerprint scanners utilize bolometers for the detection of changes in the light reflection which are used for the detection of fingerprints
- Used in air surveillance industry to know hidden locations
- Used in forest industries to analyze and observe forest fires that assist in before planning of evacuations and extinguishers
- Bolometers are even used in ESA and NASA agencies for studying external space in the far-infrared spectrum
- Microwaves can also be measured by bolometers where those are generated by a pulsing power
Please refer to the link for more information Resistance Temperature Detector MCQs, Pyrometer MCQs.
This shows that bolometers are crucial components in many applications across many industries and they are even crucial in daily lives. With the enhancements in technology, newer designs will be in reach. So, this article has provided a detailed explanation of bolometer working, circuit, types, and applications. Know, how a superconductor can be a bolometer?