One of the major problems that people are still facing these days is an irregularity in power distribution. So, to get rid of this problem, technology has provided us many approaches and various devices. The most general technologies that are used for this purpose is generator, inverter and UPS. Even these devices are extensively used in many household and commercial applications to standardize power deregulations, each device has its own capacity, advantages, and disadvantages.
So, this article explains clearly the generator, inverter, and UPS capabilities and also provides key differences between Generator, Inverter & UPS. Before directly going into comparison, let us have a quick view and features of the generator, inverter, and UPS.
What is a Generator?
A generator is the most general device found in many houses and companies. But one would like to know the exact generator definition of this, so here we explain that. A generator is an electrical machine that is used for the conversion of mechanical energy to electrical power. Though this is not the direct generation of electrical energy, in general, its functions upon the electromagnetic induction principle. The device generates electric power only when operated at specific speed levels using prime movers like diesel, natural gas, petrol, and also other renewable energy sources like that of water, wind, and solar-powered turbines.

Generator
Features
- Generators have the extensive capability to deliver a high range of power outputs. Both minimal and maximum power ranges can be easily delivered by selecting a perfect electric generator that corresponds with a power output
- Various kinds of powered up options are available both in the renewable and non-renewable sources
- Can be easily available in the desired model and design such as the devices having wheels or handles supported
- Few generator types also have the efficiency to decrease noise and distortions where this feature enhances the proximity level and lessens noise problems
What is an Inverter?
The inverter definition is stated as that it is the device that performs the operation of converting the current form from DC to AC (direct to alternating). To make use of these devices in household activities, they are probably combined with additional electronic devices that regulate load and battery charging systems. Depending on the battery-driven system, inverters operate as a power adapter to energize minimal power required devices using a general wiring approach. The amount of power supplied by electric grids has to be the same as that of mount delivered by inverters.

Inverter
But at the time of converting DC to AC form, the voltage gets increased. As per the principle of Ohm’s law, when voltage is increased, the current is decreased. This means that the conversion of DC to AC delivers less amount of power.
Based on this functionality, the inverters are basically categorized as:
- Stand Alone – Here, in addition to the conversion from DC to AC, these inverters also enhances the voltage amplitude levels and so generates frequency variation. In general, the output of this kind of inverters is a sine wave. Whereas in a few conditions, the output will be square wave because of some distortions.
- Grid-Tie – The name itself specifies that the delivered output is distributed to grid networks which means that these inverters supplies to huge units and from here the power is distributed to required appliances. As because of this, the inverters need complicated design and more components.
So, this is a general overview of inverters.
UPS (Uninterrupted Power Supply)
The UPS definition is stated that it is the electrical equipment that delivers backup power to the load at the times of power distortion in the main power system. In comparison to other kinds of alternative power supplies, UPS differs in the scenario that it quickly safeguards the sources from power disturbances. As UPS devices have minimal on-battery operating time, this time is sufficient to disconnect all the connected equipment.
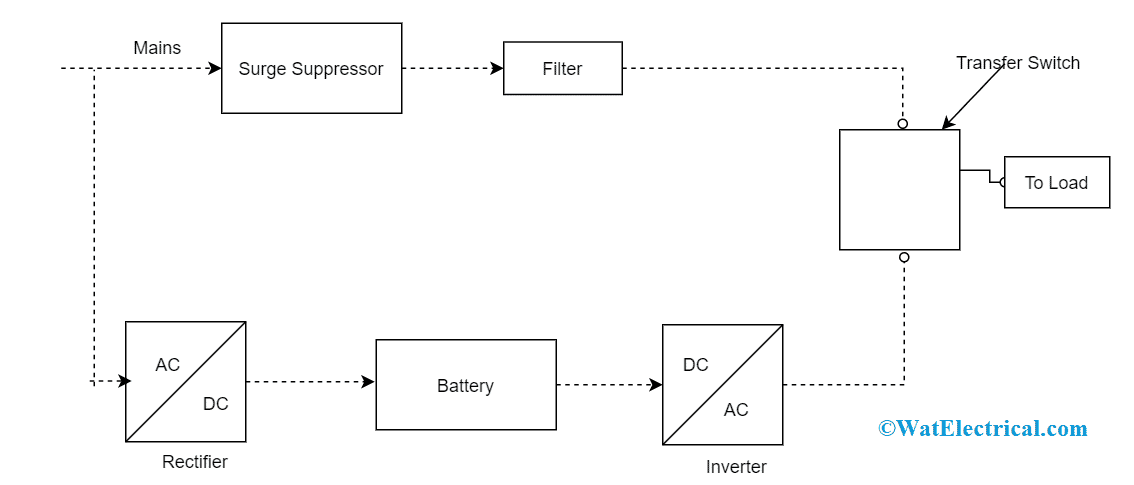
UPS Block Diagram
A UPS is also called a battery backup or flywheel backup because flywheels, batteries, and capacitors are the energy storage devices for UPS.
Characteristics of UPS
- Provides power supply for a minimal time
- Holds the ability to regulate complications associated with utility sources
- Also manages voltage spike and noise problems
- Controls frequency instability and harmonic distortions
Key Differences between Generator, Inverter and UPS
| Feature | Generator | Inverter | UPS |
| Form of output | AC | AC | AC |
| Basic functionality | Conversion from mechanical energy to that of electrical power | DC to AC conversion | Quickly safeguards the sources from power disturbances |
| Additional equipment | Generators need a chord to start up the device | Through sensor and switch, an inverter is turned ON when main supply gets OFF | Eliminates abrupt power disruptions |
| The capacity of power generation | Generators hold the ability to provide power nearly 10 – 12 homes | Inverters hold the ability to provide power nearly 5 – 6 applications in a home almost for 6 hours | UPS hold the ability to provide power for applications such as a laptop or minimal power required devices for 15 minutes |
| Switch over | Better than inverters | Takes more time | Quickly |
| Fluctuations | Frequency fluctuations during heavy loads | Has voltage fluctuations | Does not have any kind of fluctuations |
| Types | There are mainly inverter type, standby and portable generators | Line interruptive, offline, and online types | These are of stand-alone grid-tie types |
| Expensive | Based on power availability, generators vary in various ranges | Less cost | Heavy cost |
| Design and construction | Heavy size and construction is difficult | Minimal size and construction is simple than that of generators | Less size |
| Connection | Connected to main power supply systems | Inverters have a direct connection for the applications | Has direct connection with applications and battery |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance using the change of oil, lubricant oils, and distilled water | Minimal maintenance is sufficient | No need of maintenance |
| Noise generation | Creates heavy noise | No noise is generated | Not more noise is generated |
Applications of Generator, Inverter & UPS
Generator
- Mostly in power plants, vehicle generators, and hydroelectric power stations
- Provides power supply for cranes, drilling equipment’s and conveyor belts
Inverter
- Used to manage compressor speed in refrigerators
- Employed in induction heating purposes
- Used in solar generating networks
- To provide power for many kitchen tools (mixers, compressors, and refrigerators), lights, TV appliances and many others
UPS
- Used in data centers
- Hospitals
- Telecommunications and many others
Know more about Hydroelectric Power Plant MCQs, Synchronous Generator MCQs.
Know more about Function Generator.
So, this article clearly explains the concepts of the generator, inverter and UPS, their definitions, basic operating principles, and key differences of these devices. Apart from the mentioned information, each of these devices holds extensive information to know like functionality, benefits, and important features. Knowing crucial data regarding these electrical devices will show a streamlined approach of which device has to be used for which purpose. And the foremost question that arises is what are the advantages and disadvantages of generator, inverter, and UPS?