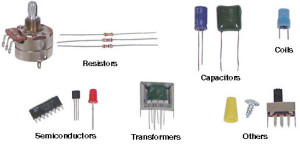
Electrical Components
There are numerous important basic electrical components commonly found in the circuits of almost all peripherals. These devices are the essential building blocks of electronic and electrical circuits. These electric components can be found in great numbers on motherboards, video cards, hard disk, logic boards and everywhere else in personal computers. The electrical circuit components can be combined with each other and with dozens of other devices.
Electrical circuits on different parts of equipment share similarities. Many circuits have resistors, inductors, capacitors, transformers, fuses and switches. Understanding the concepts of these components will help you while troubleshooting a circuit. Therefore, this article gives information about different types of electrical components and electrical component symbols which are used in electrical and electronic projects.
Types of Electrical Components with Symbols :
1) Resistor
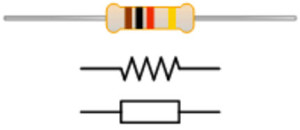
Resistor with symbol
A resistor is an electrical component that regulates or restricts the flow of an electrical current in a circuit. This can also be used to provide a specific voltage to a transistor. When current flows through the resistor, the electrical energy is absorbed by the resistor and dissipated in the form of heat. Resistors may have fixed or variable resistances and they can be found in photo resistors, thermistors, trimmers, varistors, humistors and potentiometers. The current through a resistor is directly proportional to the voltage across the resistor’s terminals. The relationship is represented by Ohm’s law
(V=IR=>I=V/R)
Where,
- V is the potential difference of the conductor
- I is the current through the conductor, and
- R is the resistance of the conductor.
2) Capacitor
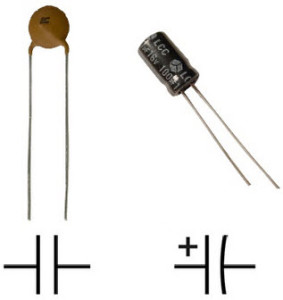
Capacitor with symbol
A capacitor is a two terminal linear passive component made from two conductive plates with an insulator between them. The function of a capacitor is that it stores electrical energy when an electric charge is forced on to its electrical conductors (plates) from a power source. A capacitor still maintains this charge even after getting disconnected from the power source. A capacitor is used with a resistor in a timing circuit and also can be used as a filter to block the DC signals, but allows AC signals.
The stored charge is Q=CV
Where,
- V is the applied voltage, and
- C is the capacitive reactance
Therefore, the current through a capacitor is I= C dv/dt
When a DC current is applied across a capacitor, a positive and negative charge builds on a set of plates. The charge stays until the capacitor is discharged. When an AC current is applied across a capacitor, a positive and negative charge builds on a set of plates during the part of the cycle when the voltage is positive. When the voltage goes negative in the second half of the cycle, the capacitor releases what it had charged before, and then charges the opposite way.
3) Inductor

Inductor with symbol
An inductor is a two-terminal passive electrical component, and it also called as a coil or reactor. The function of an inductor is that it stores electrical energy in the form of magnetic energy. Generally it consists of a conductor, usually wound into a coil. It works on the basic principle of Faraday’s law of inductance. When a current flows into the coil from the left to the right side, the coil generates a magnetic field in the clockwise direction. The inductance of the inductor is represented by L= (µ.K.N2.S)/I.
Where,
- L-inductance
- K-Nagaoka coefficient
- µ-Magnetic permeability
- N- the Number of turns of the coils
- S- the Cross section area of the coil
- I- the Length of the coil in axial direction
4) Transformer
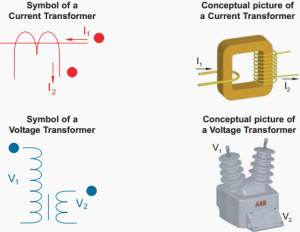
Transformer with symbol
A transformer is an electrical device, wherein two coils of wire are linked by an iron core. Transformers provide much needed capability of changing the voltage and current levels easily. They are used to step-up (increase) or step-down (decrease) AC voltages. The working principle of a transformer is Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, that is, mutual inductance between two circuits, which is linked by a common magnetic flux. Transformer transforms electrical energy from one circuit to another circuit with the help of mutual induction between the two windings without electrical connection between them, and also transforms power from one circuit to another circuit without changing the frequency but with a different voltage level.
A transformer that has more turns on the secondary coil than the primary coil is called as a step-up transformer and a step-down transformer has more turns in the primary coil than the secondary coil (step-down transformer). Transformers are one of the main reasons we use AC current in our homes and not DC: DC voltages cannot be changed using transformers. Transformers come in sizes ranging from small ones equivalent to an inch across, to large ones that weigh hundreds of pounds or more, depending on the voltage and current they must handle.
5) Battery
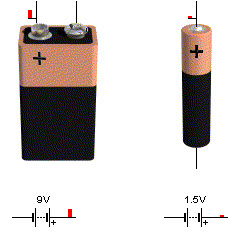
Battery with symbol
A battery is used to convert chemical energy into electrical energy through electrochemical discharge reactions. Batteries are composed of one or more cells each containing an anode (-), cathode (+) and the electrolyte. The anode and the cathode are kept up to an electrical circuit. Cells are classified into two types’ primary cells and secondary cells, wherein the primary cells are not rechargeable while the secondary cells are rechargeable.
6) Fuse
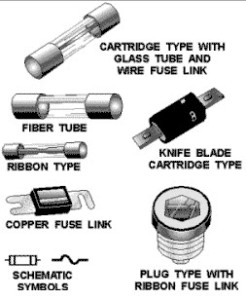
Fuse with symbol
A fuse is a piece of wire of a material, which is used to protect the components from damage due to extreme current flowing through them. When an excessive current flows through the circuit, the wires get heated up and melt. As a result, the current stops flowing. When the fuse melts, the fuse element absorbs some energy. This energy is given by I2t, where ‘I’ is the peak value of the current interrupted, and‘t’ is the time taken to clear the fault. When the fuse blows, it gives an indication that there is some kind of malfunctioning in the circuit.
Each type of fuse is designed for a precise amount of current. A standard fuse consists of main components such as metal-fuse element, a set of contacts, support body and connection. A fuse element is made of copper, zinc, silver, alloys or aluminum to provide predictable characteristics. This may be surrounded by material or air, which is proposed to speed the quenching of the arc non-conducting liquids or silica mat used.
7) Diode/LED
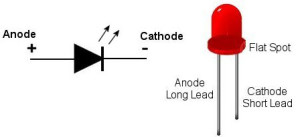
Diode with symbol
A diode is a device, usually made from semiconductor material that allows current to flow in one direction; it blocks the volume of any current that tries to go against the flow in a wire. Diodes are often used in many circuits that convert AC to DC. An alternative of the diode is LED or light emitting diode, which is designed to emit light of a particular frequency when a current is applied to it. LEDs are used on everything from hard disks, keyboards to TV remote controls, and are very useful as battery-operated electronics and status indicators in computers.
8) Transistors:
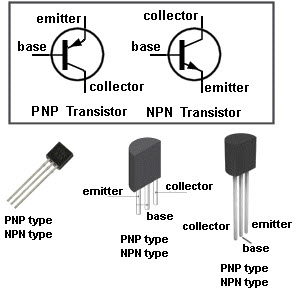
Transistors
Transistor is a three terminal electronic device made of semiconductor material which regulates voltage or current flow and acts as a switch for electronic signals. There are two types of transistors PNP and NPN, most circuits tend to use NPN transistor. Transistors are designed in different shapes and they have three terminals namely, base, emitter and collector. Where, base is responsible for activating the transistor, emitter is the negative lead and collector is the positive lead.
9) Integrated Circuit:
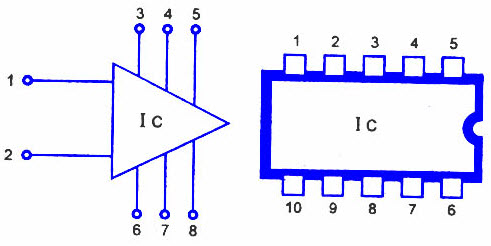
Integrated Circuit
An integrated circuit is also referred as IC and sometimes it is also called a microchip, is a semiconductor where millions of resistors, capacitors, and transistors are fabricated. It can function as oscillator, amplifier, timer and microprocessor. An IC is classified as either linear or nonlinear depending on its application. Linear or analog integrated circuits have continuously variable output and that depends on the level of input signal. These linear integrated circuits are used as audio frequency and radio frequency amplifiers. Digital integrated circuits operate at only a few defined states, rather than over a continuous range of signal amplitudes. These ICs are used in modems, computers, frequency counters and computer networks. The basic building blocks of digital ICs are logic gates, which work with binary data.
10) Relays:
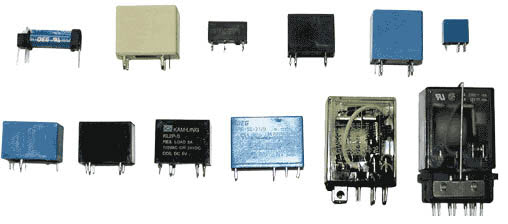
Relays
Relays are electromechanical switches, which are used to control the circuits by using one signal or low power signal. The first relays were used as amplifiers in long distance telegraph circuits. Basically, a relay consists of an armature, an electromagnet, a spring and a series of electrical contacts. There is no electrical connection between inside the relay between the two circuits and these circuits are connected each other through magnetic connection. Relays are used to perform logical operations in computers and telephone exchanges.
11) Switches:

Switches
A switch is an electrical component which is used to break an electrical circuit, interrupting the current and to deliver the current from one conductor to another conductor. It is works with ON and OFF mechanism. Switches are classified into four types such as single pole single throw (SPST), single pole double throw (DPST), double pole single throw (DPST) and double pole double throw (DPDT).
12) Motors:

Motors
A motor is a device, which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It includes stator, rotor, bearings, conduit box, eyebolt, and enclosure. Electric motors are all around us, from common appliances to our most complicated computers. These motors are clean and relatively competent for the tasks they perform when compared to hydraulic alternatives or pneumatic. These are classified into different types such as, stepper motor, brushed DC motor, brushless DC motor, permanent magnet synchronous motor, Ac inductance motor and switched reluctance motor.
13) Circuit Breakers:
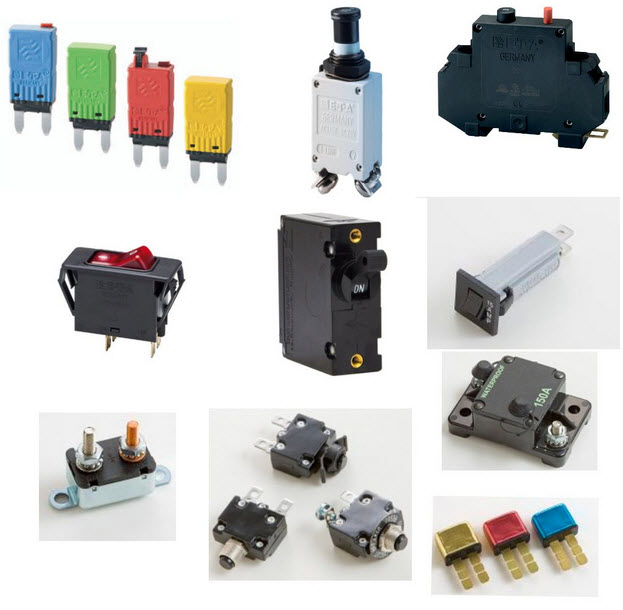

Circuit Breakers
A circuit breaker is a mechanical switching device which is operated automatically. A circuit breaker is used to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by short circuit overload. The basic function of the circuit breaker is to interrupt the current flow and detect a fault condition. It consists of two contacts such as moving and fixed contact. Moving contact is used to make and break the circuit using stored energies in the form of spring or compressed air. Fixed contact includes a spring which holds the moving contact after closing. Circuit breakers consist of two coils, closing and tripping coil. Where closing coil is used to close the circuit and tripping coil is used to trip the circuit.
Know more about Electrical Insulator MCQs.
Thus, these are some of the basic electrical components used in implementing various electrical projects and device or appliances. We hope that you might have got satisfied with this article and believe that you have got an idea about the electrical components. Apart from this, if you have any queries regarding testing these components in a practical circuit and their assembling procedures, you can comment below.
Photo Credits:
- Electrical components by electronicsandyou
- Resistor with symbol by clipartbest
- Capacitor with symbol by nmsu
- Transformer with symbol by electrical-engineering-portal
- Battery with symbol by yenka
- Fuse with symbol by rfcafe
- Diode with symbol by mainbyte
- Transistors by talkingelectronics
- Integrated Circuit blogspot
- Relays by area51esg
- Switches by electricswitches
- Circuit Breakers by electricswitches