With the evolution of the electric grid concept, engineers understood that new equipment is required for the protection of high-level voltage power devices. Devices like electrolytic arresters came into evolution during the period 20th century which is appropriate for high power requirements. Comparatively, the short-lived technology came into existence in the next 20 years. The contemporary word arrester was initially used in the period the mid-1800s where its use was only for minimal gap devices to safeguard telegraph lines. From then, various kinds of arresters were introduced and one of those is “Surge Arrester”. This article explains surge arrester working, its purpose, types, and a few applications.
What is Surge Arrester?
A surge arrester is a tool that is used to provide protection for electrical devices from high voltage transients which are produced either by internal/external activities. This is also termed a surge protection device which comes under the classification of a protection device in distribution systems and power transmission domains. This device should hold a minimal impulse ratio so that when there is any surge case on the arrester it can be directly bypassed to ground other than passing on through the equipment. The surge arrester symbol is shown as below:
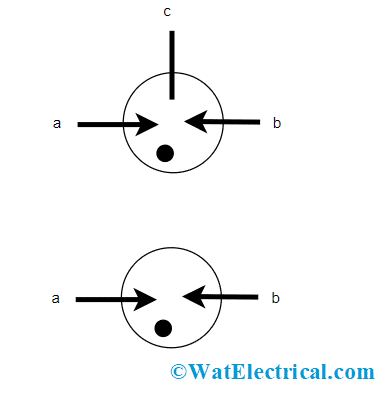
Symbol
The main purpose of the surge arrester is to provide protection for high-level voltages by discharging/releasing surge currents.
For example: In a distribution line, it can observe multiple voltage surges and the crucial source for this is lightning. There are almost 100’s of lightning strikes on the surface of the earth per second and lightning is one of the unpredictable activities. Here, the purpose of the surge arrester is to bypass high voltage levels by protecting the distribution line.
In addition, there are many other sources of surges consisting of temporary over voltages and switching surges. Switching surge is a type that is happened by variations in the functional conditions inside the system. It is the energy trapping and the corresponding energy release.
Working of Surge Arrester
Let us consider the working principle of surge arrester for a metal oxide varistor type which includes continuous MOV blocks. These blocks function in the way of a voltage-regulated switch that performs like an insulator that has line voltage. When the voltage level increases, the MOV arrester enhances its voltage above its reference level and then moves into a conduction state. As the metal oxide varistor is of extremely non-linear, when the voltage level decreases below the reference level, then the conduction comes to an end.
Characteristics
A few of the characteristics of surge arrester are explained below:
- Many of the surge arresters exist in non-linear nature.
- Surge arresters possess an increased level of operating voltage which can be in the range of frequency of 50-60 Hz
- It has rated short circuit current.
- Minimal value of discharge current which can be of 5k Amps, 10k Amps, and 20k Amps.
- When the arresters are installed above the voltage level of 52 kV, then they might be installed along with discharge operation counters.
- These devices are connected in between the life conductors and the earthing system.
- Metal oxide arresters do not need many gaps and they show good handling qualities for surge switching, showing minimal current level under balanced conditions and minimal lead lengths. These also have enhanced performance and more powerful system accessibility when compared with silicon carbide arresters.
Surge Arrester Classification and Types
Depending on the rating of voltage levels, protecting capabilities, and stability in pressure support, the grouping of surge arresters utilized for the power system can be as below:
Distribution Arresters – These offer minimal surge protection and also less energy discharging ability and are mainly employed in medium voltage types of networks.
Station Arresters – These provide better protection showing minimal discharging voltage levels, more energy absorption, and high-pressure relief. Crucial applications of station arresters are in strong surges and huge substations.
Intermediate Arresters – Have a medium level of protecting capabilities and also medium energy discharging capacity. The applications of these are in small substations, dry kind of transformers.
Also, the other types of surge arresters are:
MOSA
This metal oxide surge arrester consists of metal oxide with non-linear resistive disc components having good thermal energy enduring abilities. Every disc component includes the crushed form of zinc oxide substance blended with other kinds of metal oxides. This operates in the way of a high-speed switch that has an open condition at steady-state voltage levels and a closed condition at high levels of voltages.
These also possess minimal losses when the device functions under steady-state circumstances. MOSA is further classified into three types which are of:
- Gapless MOSA
- Series gapped MOSA
- Shunt gapped MOSA
Silicon Carbide Surge Arresters
The SiC kind of surge arresters consists of a non-linear substance which is a resistor constructed of inorganic kind of binders and silicon carbide material.
Few of the applications those use surge arresters need that the valve substance should possess minimal resistance at the time of steady-state in order to accomplice with corresponding power and surge characteristics producing high power losses. In order to overcome this complexity, SiC surge arresters consist of spark gaps that are in series with the valve substances.
Because of series gaps, the valve substance is kept separated while steady-state and this minimizes losses and valve substance is introduced when there is a surge from the series gaps. There exists no outflow of current in between the line substance and earth which makes the valve manage voltage restricting role and energy dissipation only at the time of the surge.
Distribution Arresters
These arresters are rated between the range of 1 to 36k Volts. These distribution types of surge arresters are further categorized as
- Light duty
- Normal duty
- Heavy duty
The distribution surge arresters are utilized in transformers in the way of cubicle-mounted, oil, and elbow arresters. The applications of normal duty and heavy-duty arresters are in minima lighting and high lightning.
Along with these, the other crucial kinds of surge arresters are
- Intermediate
- Secondary
- Station class arresters
Breakdown Modes in Surge Arresters
The arrester failure in any kind of surge arrester results in an entire short circuit of the system. The crucial reason for exhibiting failure modes in surge arresters is a dielectric breakdown which corresponds that the device is not able to tolerate applied voltage levels.
The other surge arrester failure modes are:
Contact with moisture – This is the other common reason that makes a surge arrester failure. The moisture ingress implies that that the device is not well constructed, has no proper manufacturing, and is due to other factors, that result in its negotiation on the sealing section.
Temporary Overvoltage – During normal functional conditions, the arrester operates at its maximum voltage level where the MOV component’s temperature level increases somewhat above the ambient temperature. At one of the points, the increased heat level comes in equilibrium with the arrester, and then it starts dissipating into the air. This is the surge arrester general thermal stability operating point.
The below picture represents the thermal response at multiple levels of voltage.
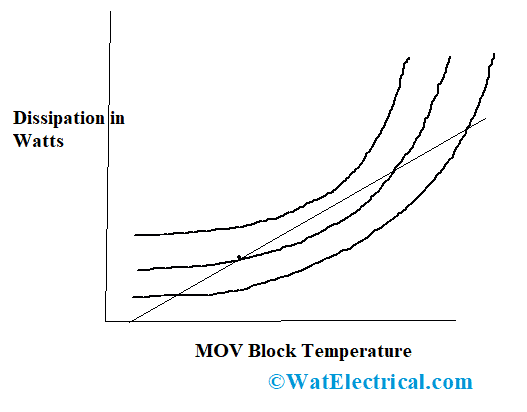
Thermal Response of Arrester
Also, the other factors for failure of the arrester are deterioration of MOV blocks, MOV blocks aging, and thermal runaway from surge duty.
Applications
A few of the applications of surge arrester are:
- Employed for surge protection equipment.
- Surge arresters are employed in electrical installations for safeguarding the systems.
- Implemented in lightening applications and also in distribution boards.
- Also utilized in data applications.
- Used for purposes to ensure increased durability.
Please refer to this link to know more about Types of Losses in a Transformer.
So, this is the overall concept of the surge arrester. As because the device’s main purpose is in protecting the electrical systems from high voltages, it has huge applications across the various domains. And this article has provided a detailed description of surge arrester working, types, failure modes, features, and applications. Also, know how the selection of surge arrester is made?