The development of reluctance motor took place in the year 1838 so as to boost a locomotive. Here, the mechanical switches used for windings energization only hold the capability to provide energization for the motor at minimal speed levels. And in addition, electronic devices such as transistors, IGBTs are needed for driving the motors.
But in 1920, the development of variable reluctance motor took place in the U.K and this development was used in many applications. And now, this article completely focuses on explaining reluctance motor definition, its working, construction, types, and uses.
What is Reluctance Motor?
This is an advanced kind of motor that consists of both rotors and stators similar to many electrical motors. Few kinds of reluctance motors function with precise RPM levels by synchronizing rotor speed with the stator’s RMF value which makes the device a synchronous reluctance motor. Reluctance motors of single-phase are generally similar to single cage kind of induction motor.
Construction
The construction of the reluctance motor has mainly two components which are the rotor and stator. The stator consists of a covered construction with stampings. These stampings are placed on its periphery which carries the winding, and it is termed as stator winding, and it has only a single winding. The excitation to this winding is supplied by single-phase A.C current.
As the stator has laminations, this keeps the iron losses at a very minimal level and the stampings are made of silicon steel that lessens the hysteresis loss. The rotor has a specific shape and because of its shape, the air gap that exists between the rotor and stator is not the same. The rotor is not supplied with any kind of D.C supply and it is free to turn around.
The resistance level of the magnetic circuit is based on the air gap and when the air gap increases, the reluctance level enhances. And because of the variable air gap that exists between rotor and stator, when the rotation of the rotor takes place, then reluctance between stator and rotor also gets varied. These components are constructed in the manner that the change in the inductance value of windings is sinusoidal related to the rotor’s position.
Working of Reluctance Motor
The stator present in the motor comprises of single winding termed as main winding but it is not possible to generate a revolving magnetic field. So, for the generation of a magnetic field, the device should consist of a minimum of two windings separated by some phase angle difference. So, there is an auxiliary winding that has a capacitor that is in series connection with it.
Because of the phase angle variation, there develop phase differences between the currents generated and their fluxes. The generated fluxes from two windings react and develop a revolving magnetic field. This scenario is termed a split-phase approach. The speed level of this field is called synchronous speed which can be determined by the number of poles present in the stator winding.
The rotor section includes short-circuited either aluminum or copper-made bars and this functions in the same way how a squirrel cage motor works in the induction motor. When a piece of iron is located in the vicinity of the magnetic field, then it gets aligned in a direction where the reluctance position is less and then it gets locked sealed. In the same way, in the case of the reluctance motor, the rotor gets aligned in a direction where the reluctance position is less. But, because of rotor inertia, there is no possibility rotor to be in a standstill position.
Due to this rotor begins to rotate close to the synchronous speed and at this position, the magnetic field of the stator draws the rotor into the synchronism which means pulls towards a minimal reluctance position and makes it get sealed. This type of torque implied on the rotor is termed as reluctance torque. This finally states that the reluctance motor operates as a synchronous motor.
With this, the reluctance motor torque equation is given by:
T = -Im2Lsin2ϴsin2ωt
The average torque is:
Tav = ¼ Im2Lsin2 δ
And the torque-speed characteristics is shown in the below picture
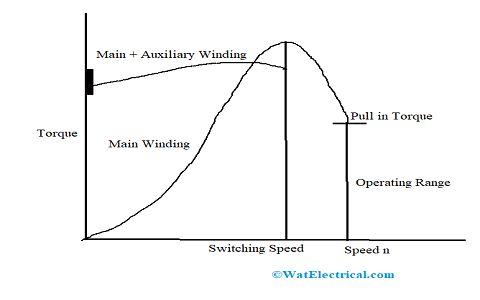
Reluctance Motor Torque Speed Characteristics
Types of Reluctance Motor
There are mainly two types of reluctance motor which are switched type and synchronous type. The below section explains clearly each of these reluctance motors.
Synchronous Type Reluctance Motor
These types of motors are constructed to function at precise synchronous levels of speed. This can be achieved by the implementation of the three-phase stator winding along with the rotor that has rotor poles and internal flux barriers. The rotor employs a modified type of squirrel cage all across the poles which stands as a benefit to make the reluctance motor to self-start. When it is self-started, then it moves near to the synchronous speeds through the help of induction.
Switched Type Reluctance Motor
These come under the classification of the stepper motor, but the variation lies in the setup of inverted winding. Here, the field windings exist in the stator section and not in the rotor. The rotor is made of a ferromagnetic substance of permanent poles ad rungs which are operated by the stator poles. This scenario of construction in the switched type reluctance motor simplifies the constructional design but complicates the setup in the electrical way where the electronic regulating system needs to switch the rotor poles to ON and OFF positions and creates a rotation.
For the calculation of the angle in between the stator windings and rotor poles, an electronic positioned sensor is used in the motor. It also uses a timing scenario that allows for the synchronization of stator poles with the rotational frequency level. These motors are mainly utilized in microelectronics and in semiconductor domains.
Specifications
In all kinds of reluctance motors, there are few common parameters that allow for a clear understanding of reluctance motors and their performance. A few of those are explained below:
Type of Phase – These motors are operated either by a single or polyphase. In general, the commonly used poly phased reluctance motors are in three-phase motor designs and mainly implemented for a high level of torque applications because of the non-existence of auxiliary windings and supplied more power to the device.
Power Factor – The power factor of the reluctance motor is termed as lagging PF and this parameter specifies the amount of output power and torque supplied by the device at a stable state. The power factor ranges in the order of fractional to hundreds of horsepower.
Advantages of Reluctance Motor
The advantages are:
- Simplified construction – As the device consists of no commutator sections, brushes, copper/aluminum present in the motor
- Provides a high level of efficiency and enhanced reliability
- The more self-starting torque level
- These are economical when compared with other types of brushless DC kind motors
- Reluctance motors are easily adjustable for high-level ambient temperatures
Applications
The applications of reluctance motor are:
- Employed in electric type automobiles
- In the construction of washing machines
- Analog meters are electric in nature
- Used in clocks, controlling, and signaling devices.
Know more about Capacitor Start Capacitor Run Motor MCQs.
Know about more Variable Reluctance Stepper Motor , Excitation.
This is all about the detailed concept of reluctance motors. The article has provided a detailed explanation of reluctance motor construction, working, types, advantages, and applications. Also, know what are the disadvantages of reluctance motor?