A Transformer is a static electrical device because it doesn’t have moving parts. The main function of a transformer is to change the electrical power from one electric circuit to another by changing voltage & current but not changing frequency. Transformers are classified into two types based on their function as a step-up transformer and step-down transformer. This article discusses an overview of a step-down transformer and its working with applications.
What is a Step-down Transformer?
A Transformer that is used to convert the voltage from a high primary to a low secondary is known as a step-down transformer. In this transformer, the turns within the primary winding are high than the secondary winding. The typical step-down transformer diagram is shown below.
Step Down Transformer
Step Down Transformer Working Principle
Transformer works on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction principle. So, the Mutual induction in between the two windings of the transformer is accountable for transmission action within a step-down transformer.
Faraday’s law can be defined as, whenever the magnetic flux in a circuit changes, then an emf (electromotive force) induced within the circuit is directly proportional to the rate of change of the flux linkage”.
The induced electromotive force in between the two windings can be determined through the turns present within both the primary & secondary windings correspondingly. So, this ratio is known as Turns Ratio.
In these types of transformers, the step-down voltage capacity mainly depends on the two winding’s turn ratio. When the number of coils present in the secondary winding is low as compared to the number of coils present within a primary winding, then the flux linkage toward the secondary winding of the transformer can also be low as compared to the primary winding.
Thus, the induced electromotive force will be low in the secondary winding. So as compared to the primary winding, the voltage will be reduced at the secondary winding.
Construction of Step-Down Transformer
The construction of this transformer can be done by using core & windings which is very similar to a step-up transformer.
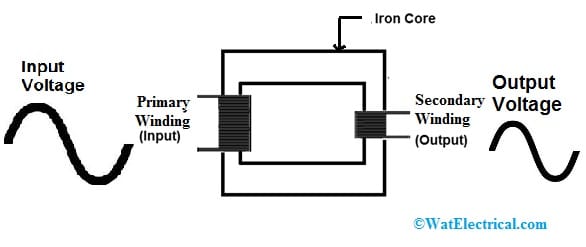
Construction of Step Down Transformer
Core
In this transformer, the core is made with soft iron which permits the magnetic flux to supply throughout it. Both the winding coils in the transformer are covered around the core. Here the core is available in two types depending on the wrapping. If windings in the transformer are covered outside the body, then that is called a closed core transformer. Similarly, if the windings of the transformer are covered within the iron core, known as shell core transformer.
As compared to shell type, closed core transformer suffers from leakage flux. So shell core is mostly used instead of a closed core.
Windings
In the transformers, windings are the current conductors which are made with a loop of wires. So the material used for the wire is aluminum or copper.
Generally, transformer windings are available in two types like primary and secondary. Primary windings get the voltage whereas the secondary windings provide the induced voltage towards the load. The electrical energy can be supplied from the primary winding to the secondary with no metallic contacts.
In this transformer, the number of turns present in the primary is high as compared to the number of turns within the secondary. But in primary windings, the wire density is not thicker as compared to the secondary windings.
Working of Step-down Transformer
A transformer works through the mutual induction principle. So, once there is a change within the electric current in one winding, then the current within the secondary winding can also be induced in its proximity.
We know that each transformer includes two windings or coils like primary & secondary. The primary coil is connected to the AC power source directly whereas the secondary coil is connected to the load. Once AC is given to the primary winding, then a magnetic flux can be generated throughout the transformer core, the magnetic field completes its lane.
When the secondary coil comes in contact through this magnetic flux, then an EMF can be induced on it. So, the generated EMF strength mainly depends on the no. of turns within secondary coil winding.
Formula
The formula which is used for designing a step-down transformer is given below.
Ns/Np = Vs/Vp
Where,
‘Ns’ is the no. of turns within the secondary winding.
‘Np’is the no. of turns within the primary winding.
‘Vs’ is the voltage within the secondary winding
‘Vp’ is the voltage within the primary winding
As compared to the primary winding, the number of turns within secondary winding should be low (Np>>Ns) to work the transformer as a step-down transformer. When the no. of turns within the secondary winding (Ns) is low, the induced emf & the output voltage will be low as compared to the voltage in the primary winding.
Types of Step-down Transformer
The classification of secondary transformers can be done into three types based on tapings within a secondary coil-like single-phase, center-tapped, and multi-tapped step-down transformer.
- Single-phase step-down transformers are used to reduce the input voltage and current ratings provide less voltage & current output such as 12V AC.
- Center tapped step down transformer includes one primary winding & a center split within the secondary winding, where it provides the output voltage through the center split like 12v-0-12v.
- Multi tapped step-down transformer includes several tapping within the secondary winding. These tappings are mainly used to obtain the desired output through secondary coils like 0 to 12v, 0 to 18v.
The following things must know before purchasing a transformer
- Voltage ratios should be from 11 kV to 33 kV.
- Capacity should be from 25 KVA TO 10 MVA).
- Frequency either 50Hz or 60Hz.
- Installation.
- Tappings like OFF Circuit Type or OLTC.
- Standards.
- Transformer Fitting.
- Accessories.
- Protection Level.
Advantages
The advantages of a step-down transformer include the following.
- Less cost.
- High Reliability.
- High Durability.
- Used to reduce the voltage, so transmission power making is cheaper and easier.
- Efficiency is above 99%.
- We can obtain the desired o/p voltage simply without power loss.
- It provides less voltage & high currents.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of a step-down transformer include the following.
- It needs more maintenance.
- Takes more time for fault rectification.
- Instability in feedstock costs.
Applications
The applications of step-down transformers include the following.
- Main adapters.
- Cell phone chargers.
- Stereos.
- CD players.
- Reduces the level of voltage within the transmission line.
- Welding machines.
- Televisions.
- Voltage stabilizers.
- Inverters.
Know more about Shell Type Transformer MCQs.
Know more about Efficiency of Transformer.
Thus, this is all about an overview of a step-down transformer and its working with applications. These transformers are normally used near our homes and almost all less voltage-based wall adapters. Here is a question for you, what is a step-up transformer?