Well, you might be well-versed with the word “Vibration”. Mostly we all know what vibration in mobile phones is where it vibrates our mobile when there is a notification or when we receive any call. This is the only scenario that gets into our thought about vibration, but there are many cases where vibration pays attention such as in the compressor rotation in refrigerators, to run the washing machine vibrator. Extending this concept, we need to be clear of what a vibration motor is, how does it deliver energy, where this concept will be implemented and many others. So, let’s have our session to be on Vibrator Motor
What is a Vibrator Motor?
Definition: Vibrator Motors are the mechanical devices used to develop vibrations. The generation of vibration has happened with the support of an electric motor having an inequitable mass on its driveshaft. It is a miniature sized DC motor that lets the user know the sound through vibrations. The foremost feature that has to be noted in this is its magnet coreless DC motor which is permanent where it means that it possesses magnetic properties (performs like a magnet only when the electric current is passed through the device).

vibration-motors
Mostly, vibration motors are designed as two types:
- Coin or flat-sized vibration motor
- Cylinder or bar sized vibration motor
Vibration Motor Working
The working principle of both the vibration motors is discussed below
Coin or Flat-Sized
A Coin or flat-sized motor works with the help of ring magnet, power supplied brushes connected to ring magnet, weight and a rotor with the commutation points connected at the front side and the coils connected on the backside. The commutation points and the brushes end are connected together. This construction will strengthen the rotor electrical coils. This will generate a magnetic field, and this is as much as necessary to interrelate with the ring magnet and causes rotation. A force is produced because of a magnetic field. This force allows the weight to get transferred. The continual movement of weight generates a changing force so that it is felt as a vibration. The commutation points are utilized in altering the polarity pairs; thus, the rotor rotates, and the coils are perpetually switching the polarity.
Cylinder or Bar Sized
Here, it has an improperly balanced vibrating motor. It means that the shaft is connected to an off-centered weight so that a centrifugal force is developed while its rotation. The improperly balanced force causes a high-level speed displacement in the motor and this creates vibration. The generated centrifugal force creates vibration in the motor and allows the motor to vibrate in the X and Z axis.
The frequency of the vibration can be calculated as
fvibration = (Motor RPM)/60
and Force is calculated as
Fvibration = m× r× w2
Where ‘m’ corresponds to mass the eccentric weight
‘r’ corresponds to offset distance of mass
‘w’ corresponds to motor’s speed = 2∏f
The internal design and construction of both the motors are the same and the components are as below:
Rotor
It is the non-stationary section of the rotational electric motor. The construction and construction between the wires and the magnetic field generate torque. In a few of the constructions, the rotor operates as a motor’s armature, where the input voltage is distributed.
Stator
It is the stationary section of the rotational electric motor. It operates like a magnetic field where its contact with armature develops motion. It even functions as an armature that receives force from the motor coils.
Commutator
It is a rotating electrical switch wherein specific kinds of motors or generators occasionally stores the current flow between the external circuit and the rotor. As it is a switch, it has extended life period, observing the number of circuits creates and collapses which happen in the normal procedure.
Windings
These are the coil turns. All the coils are connected in a way so that it develops a magnetic field when the electricity is passed through these.
Armature
It is the assemblage of two thin metal plates where copper wires are twisted all across the armature’s three poles. Its functionality is to transform magnetic energy to that of kinetic energy.
Brushes
In the shaft, these brushes develop current in between the coils and stator. When the brushes are worn out, motor life also will be ended. So, depending on this aspect, brushless motors which are termed as BLDC are implemented to enhance motor life.
Weight
The shaft is connected with a weighing element so that it generated vibration because of mass. Through this, the pressure and the magnitude can be easily modified and regulated.
Vibrator Motor Specifications/Datasheet
The specifications of vibrator motors depend on the size, weight, operating conditions and many others. Let’s look into the specifications of a few types of vibration motors. For a 10mm shaftless motor with a 3.4mm button type, the specifications are as below.
| Specification | Value | Measured in |
| Operating Voltage | 3 | V |
| Frame Diameter | 10 | mm |
| Body Length | 3.4 | mm |
| Voltage Range | 2.5 – 3.8 | V |
| Start Voltage | 2.3 | V |
| Weight | 1.2 | g |
| Rated Current | 75 | mA |
| Rated Speed | 12000 | rpm |
| Start Current | 85 | mA |
| Vibration Amplitude | 0.8 | G |
| Terminal Resistance | 75 | Ohm |
For a mini vibration motor, the specifications are as below.
| Specification | Value | Measured in |
| Operating Voltage | 2.2 – 3.6 DC | V |
| Rated Voltage | 3.0 DC | V |
| Rotation | Clockwise | – |
| Motor Position | Operates in all positions | – |
| Operating Conditions | 30 – 700C | Ordinary Humidity |
| Shaft end play | 0.05 – 0.2 (Maximum) | mm |
| Mass | 1.23 | Grams |
| Holding strength of vibration weight | 49N | – |
| Storage Conditions | 40 – 800C | Ordinary Humidity |
| Rated Load | Counterweight | – |
Vibrator Motor Arduino
The operation of a vibration motor through Arduino can be done on the Genuino UNO board. Before this discussion, it has to be noted that the DC vibration motors operating, and initial currents have to be limited because these are high in value than that of microcontroller’s pins.
There has to be a component in between the motor and the microcontroller, and it is the transistor. These transistors operate as ‘Switch’ to ON and OFF the motor. They can be easily regulated either by connecting to a minimal current source or a high current source. Transistors help to drive the motor safely at the rated voltages.
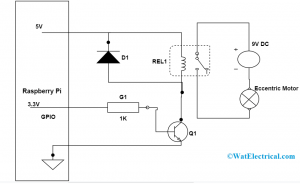
vibrator-motor-Arduino
The construction of the motor can be done with 4 basic components and those are
- Power source
- Transistor – Mostly MOSFET’s are implemented for short vibrations and they can be of either P or N-type
- Vibration motor
- Microcontroller
The transistor functions as a switch that ON and OFF the motor. It has to be noted that in N-Type transistor when it is in ON condition and when the voltage is above the threshold voltage of the transistor applied to the gate.
The stability of the vibration rotor using Arduino can be enhanced by the addition of some other components and those are
- Schottky Diode
- Pull-Up resistor
- Pull-Dow resistor
- EMI suppression capacitor
Vibrator Motor Applications
The applications of the vibrator motor consist of:
- Implemented in cement manufacturing
- Used in petrochemical, plastic and food management industries
- Vibrations motors are used in multiple material management devices such as vibrating screens, conveyors and feeders.
- Applied in mining and power generation domains
- Extensively used in cell phones, pagers, and handsets
- Utilized in foundry shakeouts
Know more about Linear Induction Motor.
FAQs
1).What is the haptic vibrator motor?
It is the utilization of progressive vibration forms and waveforms to transmit data either to the operator of the user.
2). What develops vibration in the motor?
A huge mass substance in a spinning element will generate vibration when the unstable weight revolves across the machine’s axis thus it generates centrifugal force.
3). Can vibration be transformed into electric energy?
Electromagnetic dependent generators functioning on Faraday’s law of induction transforms vibrations to electric energy.
4). What are the basic classifications of vibrator motors?
As per the internal construction of the motor, vibration motors are classified as Linear Resonant motors, cylinder coreless motors, coin vibration motors and SMD reflow soldering motors.
5). How Arduino stability can be increased?
The permanence of the vibration rotor using Arduino can be improved by Schottky Diode, Pull-Up resistor, Pull-Dow resistor, and EMI suppression capacitor.
The above information is all about the basic working, principle, types and fundamental elements in a DC type of vibration motor. As these also hold extensive advantages and applications, this concept has to be studied in a detailed approach. Know more concepts on what are the other kinds of vibrator motors?